ABSTRACT
Purpose
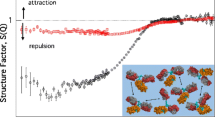
Concentrated protein formulations are strongly influenced by protein-protein interactions. These can be probed at low protein concentration by e.g. virial coefficients. It was recently suggested that interactions are attractive at short distances and repulsive at longer distances. Measurements at low concentrations mainly sample longer distances, hence may not predict high concentration behavior. Here we demonstrate that small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) measurements simultaneously collect information on interactions at short and long distances.
Methods
IgG2 antibody samples at concentrations up to 122 mg/ml are analyzed using SAXS and compared to Circular Dichroism (CD), Fluorescence, Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) and Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) analysis.
Results
DLS and SEC analyses reveal attraction between antibodies at high concentrations. SAXS data analysis provides an elaborate understanding and shows both attractive and repulsive forces. The protein-protein interactions are strongly affected by excipients. No change in the solution state of IgG2 is observed at pH 4–8, while samples at pH 3 exhibit heavy oligomerization. The solution conformation of the examined IgG2 derived from SAXS data is a T-shape.
Conclusion
SAXS analysis resolves simultaneous attractive and repulsive interactions, and details the effect of excipients on the interactions, while providing three-dimensional structural information from low-concentration samples.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- +NaCl:
-
154 mM sodium chloride
- +Sucrose:
-
270 mM sucrose
- A2 :
-
second virial coefficient
- BSA:
-
bovine serum albumine
- Buffer only:
-
no further excipients
- CD:
-
circular dichroism
- DLS:
-
dynamic light scattering
- Dmax :
-
maximal dimension
- FF:
-
form factor
- KD :
-
diffusion virial coefficient
- MM:
-
molecular mass MM
- P(r):
-
pair distance distribution function
- Rg :
-
radius of gyration
- Rh :
-
hydrodynamic radius
- SAXS:
-
small angle x-ray scattering
- SEC:
-
size exclusion chromatography
- SF:
-
the structure factor
- SFeff :
-
effective structure factor
- SLS:
-
static light scattering
REFERENCES
Wang W, Singh S, Zeng DL, King K, Nema S. Antibody structure, instability, and formulation. J Pharm Sci. 2007;96(1):1–26.
Shire SJ, Shahrokh Z, Liu J. Challenges in the development of high protein concentration formulations. J Pharm Sci. 2004;93(6):1390–402.
Chari R, Jerath K, Badkar AV, Kalonia DS. Long- and shortrange electrostatic interactions affect the rheology of highly concentrated antibody solutions. Pharm Res. 2009;26(12):2607–18.
Yadav S, Liu J, Shire SJ, Kalonia DS. Specific interactions in high concentration antibody solutions resulting in high viscosity. J Pharm Sci. 2010;99:1152–68.
Saluja A, Badkar AV, Zeng DL, Nema S, Kalonia DS. Application of high-frequency rheology measurements for analyzing protein-protein interactions in high protein concentration solutions using a model monoclonal antibody (igg2). J Pharm Sci. 2006;95(9):1967–83.
Svergun DI, Koch MHJ. Small-angle scattering studies of biological macromolecules in solution. Rep Prog Phys. 2003;66:1735–82.
Hansen S. Simultaneous estimation of the form factor and structure factor for globular particles in small-angle scattering. J Appl Cryst. 2008;41:436–45.
Petoukhov MV, Konarev PV, Kikhney AG, Svergun DI. ATSAS 2.1 - towards automated and web-supported small-angle scattering data analysis. J Appl Cryst. 2007;40:223–8.
Toft KN, Vestergaard B, Nielsen SS, Snakenborg D, Jeppesen MG, Jacobsen JK, Arleth L, Kutter JP. High-throughput small angle x-ray scattering from proteins in solution using a microfluidic front-end. Anal Chem. 2008;80:3648–54.
Konarev PV, Volkov VV, Sokolova AV, Koch MHJ, Svergun DI. PRIMUS: a windows PC-based system for small-angle scattering data analysis. J Appl Cryst. 2003;36:1277–82.
Konarev PV, Petoukhov MV, Volkov VV, Svergun DI. ATSAS 2.1, a program package for small-angle scattering data analysis. J Appl Cryst. 2006;39:277–86.
Svergun DI, Semenyuk AV, Feigin LA. Small-angle-scattering-data treatment by the regularization method. Acta Crystallogr A Found Crystallogr. 1988;A44:244–50.
Svergun DI. Determination of the regularization parameter in indirect-transform methods using perceptual criteria. J Appl Cryst. 1992;25:495–503.
Svergun DI, Barberato C, Koch MHJ. Crysol-a program to evaluate X-ray solution scattering of biological macromolecules from atomic coordinates. J Appl Cryst. 1995;28:768–73.
Franke D, Svergun DI. DAMMIF, a program for rapid ab-initio shape determination in small-angle scattering. J Appl Cryst. 2009;42:342–6.
Volkov VV, Svergun DI. Uniqueness of ab initio shape determination in small angle scattering. J Appl Cryst. 2003;36:860–4.
Teraoka I. Polymer solutions: An introduction to physical properties, John Wilet & sons, Inc., 2002.
Cao A. Light Scattering. Recent Applications. Anal Lett. 2003;36:3185–225.
Yadav S, Shire SJ, Kalonia DS. Viscosity behavior of high-concentration monoclonal antibody solutions: correlation with interaction parameter and electroviscous effects. J Pharm Sci. 2012;101:998–1011.
DeLano WL. The PyMOL molecular graphics system. Palo Alto: DeLano Scientific LLC; 2008.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS & DISCLOSURES
This work was financially supported by Novo Nordisk A/S, the Drug Research Academy, The Danish Council for Independent Research | Medical Sciences and DANSCATT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mosbæk, C.R., Konarev, P.V., Svergun, D.I. et al. High Concentration Formulation Studies of an IgG2 Antibody Using Small Angle X-ray Scattering. Pharm Res 29, 2225–2235 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-012-0751-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-012-0751-3