Abstract
Purpose
A novel methodology has been introduced to effectively coat intravascular stents with sirolimus-loaded polymeric microparticles.
Methods
Dry powders of the microparticulate formulation, consisting of non-erodible polymers, were produced by a supercritical, aerosol, solvent extraction system (ASES). A design of experiment (DOE) approach was conducted on the independent variables, such as organic/CO2 phase volume ratio, polymer weight and stirring-rate, while regression analysis was utilized to interpret the influence of all operational parameters on the dependent variable of particle size. The dry powders, so formed, entered an electric field created by corona charging and were sprayed on the earthed metal stent. Furthermore, the thermal stability of sirolimus was investigated to define the optimum conditions for fusion to the metal surfaces.
Results
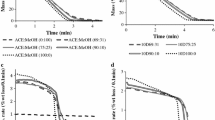
The electrostatic dry powder deposition technology (EDPDT) was used on the metal strut followed by fusion to produce uniform, reproducible and accurate coatings. The coated stents exhibited sustained release profiles over 25 days, similar to commercial products. EDPDT-coated stents displayed significant reduced platelet adhesion.
Conclusions
EDPDT appeared to be a robust accurate and reproducible technology to coat eluting stents.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sigwart U, Puel J, Mirkovitch V, Joffe F, Kappenberger L. Intravascular stents to prevent occlusion and restenosis after transluminal angioplasty. N Engl J Med. 1987;316:701–06.
Acharya G, Park K. Mechanisms of controlled drug release from drug-eluting stents. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2006;58:387–401.
Lally C, Kelly DJ, Prendergast PG. Stents. In: Akay M, editor. Encyclopedia of biomedical engineering. New Jersey: Willey; 2006. p. 1–10.
Hara H, Nakamura M, Palmaz JC, Schwartz RS. Role of stent and coatings on restenosis and thrombosis. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2006;58:37–86.
Sousa JE, Serruys PW, Costa MA. New frontier in cardiology: drug eluting stents: Part II. Circulation. 2003;107:2383–89.
Lewis AL, Cumming ZL, Goreish HH, Kirkwood LC, Tolhurst LA, Stratford PW. Crosslinkable coatings from phosphorylcholine — base polymers. Biomaterials. 2001;22:99–111.
Lewis AL, Furze JD, Small S, Robertson JD, Higgins BJ, Taylor S, et al. Long-term stability of a coronary stent coating post-implantation. J Biomed Mater Res Appl B Biomater. 2002;63:699–705.
De Scheerder I, Wang K, Wilczek K, Meuleman D, van Amsterdam R, Vogel G, et al. Experimental study of thrombogenicity and foreign body reaction induced by heparin-coated coronary stents. Circulation. 1997;95:1549–53.
Serruys PW, van Hout B, Bonnier H, Legrand V, Garcia E, Macaya C, et al. Randomised comparison of implantation of heparin-coated stents with balloon angioplasty in selected patients with coronary artery disease (Benestent II). Lancet. 1998;352:673–81.
Whelan DM, van der Giessen WJ, Krabbendam SC, van Vliet EA, Verdouw PD, Serruys PW, et al. Biocompatibility of phosphorylcholine coated stents in normal porcine coronary arteries. Heart Drug. 2000;83:338–45.
Chen MC, Liang HF, Chiu YL, Chang Y, Wei HJ, Sung HW. A novel drug-eluting stent spray-coated with multi-layers of collagen and sirolimus. J Control Rel. 2005;108:178–89.
Tarcha PJ, Verlee D, Hui HW, Setesak J, Antohe B, Radulesku D, et al. The application of Ink-Jet Technology for the coating and loading of drug-eluting stents. Ann Biomed Eng. 2007;35:1791–99.
Ozbek C, Heisel A, Gross B, Bay W, Schieffer H. Coronary implantation of silicone-carbide-coated Palmaz-Schatz stents in patients with high risk of stent thrombosis without oral anticoagulation. Cathet Cardiovasc Diagn. 1997;41:71–8.
Chen JY, Leng YX, Tian XB, Wang LP, Huang N, Chu PK, et al. Antithrombogenic investigation of surface energy and optical bandgap and hemocompatibility mechanism of Ti(Ta(+5))O2 thin films. Biomaterials. 2002;23:2545–52.
Ekqvist S, Svedman C, Lundh T, Möller H, Björk J, Bruze M. A correlation found between gold concentration in blood and patch test reactions in patients with coronary stents. Contact Dermatitis. 2008;59:137–42.
Kuraishi K, Iwata H, Nakano S, Kubota S, Tonami H, Toda M, et al. Development of nanofiber-covered stents using electrospinning: in vitro and acute phase in vivo experiments. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2009;88:230–9.
Kim TG, Lee H, Jang Y, Park TG. Controlled release of paclitaxel from heparinized metal stent fabricated by layer-by-layer assembly of polylysine and hyaluronic acid-g-poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) micelles encapsulating paclitaxel. Biomacromolecules; 2009. (in press).
De Scheerder I, Verbeken E, Van Humbeeck J. Metallic surface modification. Semin Interv Cardiol. 1998;3:139–44.
FDA patient safety news. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/psn/printer.cfm?id=356 Importance of antiplatelet therapy with drug eluting stents. (assessed 09/03)
Virmani R, Guagliumi G, Farb A, Musumeci G, Grieco N, Motta T, et al. Localized hypersensitivity and late coronary thrombosis secondary to a sirolimus-eluting stent: should we be cautious? Circulation. 2004;109:701–5.
Bleich J, Mueller BW, Wassmus W. Aerosol solvent extraction system. A new microparticle production technique. Int J Pharm. 1993;97:111–21.
Zochowska D, Bartłomiejczyk I, Kaminska A, Senatorski G, Paczek L. High-performance liquid chromatography versus immunoassay for the measurement of sirolimus: comparison of two methods. Transplant Proc. 2006;38:78–80.
Steckel H, Thies J, Müller BW. Micronizing of steroids for pulmonary delivery by supercritical carbon dioxide. Int J Pharma. 1997;152:99–110.
Bustami RT, Chan HK, Dehghani F, Foster NR. Generation of micro - particles of proreins for aerosol delivery using high pressure modified carbon dioxide. Pharm Res. 2000;17:1360–66.
Kim YH, Sioutas C, Fine P, Shing KS. Effect of albumin on physical characteristics of drug particles produced by supercritical fluid technology. Powder Technol. 2008;182:354–63.
Ghaderi R, Artursson P, Carlfors J. A new method for preparing biodegradable microparticles and entrapment of hydrocortisone in DL-PLG microparticles using supercritical fluids. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2000;10:1–9.
Nelson FC, Stachel SJ, Eng CP, Sehgal SN. Manipulation of the C(22)–C(27) region of rapamycin: stability issues and biological implications. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 1999;9:295–300.
Ricciutelli M, Di Martino P, Barboni L, Martelli S. Evaluation of rapamycin chemical stability in volatile-organic solvents by HPLC. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2006;41:1070–74.
Zhou CC, Stewart KD, Dhaon MK. An intramolecular ionic hydrogen bond stabilizes a cis amide bond rotamer of a ring-opened rapamycin-degradation product. Magn Reson Chem. 2005;43:41–6.
Lee YK, Park JH, Moon HT, Lee D, Yun JH, Byun Y. The short-term effects on restenosis and thrombosis of echinomycin-eluting stents topcoated with a hydrophobic heparin-containing polymer. Biomaterials. 2007;28:1523–30.
Wang X, Venkatraman SS, Boey FY, Loo JS, Tan LP. Controlled release of sirolimus from a multilayered PLGA stent matrix. Biomaterials. 2006;27:5588–95.
Barletta M, Gisario A, Tagliaferri V. Electrostatic spray deposition (ESD) of polymeric powders on thermoplastic (PA66) substrate. Surf Coat Techn. 2006;201:296–308.
Thierry B, Merhi Y, Silver J, Tabrizian M. Biodegradable membrane-covered stent from chitosanbased polymers
Lewis A. Phosphorylcholine-based polymers and their use in the prevention of biofouling. Colloids Surf, B Biointerfaces. 2000;18:261–75.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nukala, R.K., Boyapally, H., Slipper, I.J. et al. The Application of Electrostatic Dry Powder Deposition Technology to Coat Drug-Eluting Stents. Pharm Res 27, 72–81 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-009-0008-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-009-0008-y