Purpose
Substance P (SP; NH3 +-Arg+-Pro-Lys+-Pro-Gln-Gln-Phe-Phe-Gly-Leu-Met-NH2) belongs to a group of neurokinins that are widely distributed in the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. The biological effects mediated by SP in the central nervous system include regulation of affective behavior, emesis, and nociception. Many of these actions are believed to be the result of the binding of SP to the neurokinin-1 (NK-1) receptor and subsequent transport across the blood–brain barrier (BBB). The objective of the study was to investigate the involvement of the NK-1 receptor in the permeation of SP across the BBB.
Methods
Transport of 3H SP (1–13 nM) was investigated using BBMEC monolayers grown on polycarbonate membranes mounted on a Side-bi-Side™ diffusion apparatus. 3H SP samples were analyzed by scintillation spectrometry. Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry was used to monitor the transport at higher concentrations (micromolar).
Results
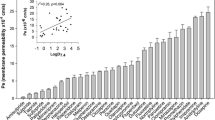
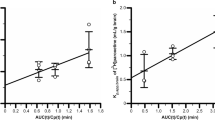
SP transport across BBMEC monolayers was found to be saturable (K m = 8.57 ± 1.59 nM, V max = 0.017 ± 0.005 pmol min−1 mg−1 protein) in the concentration range of 0–13 nM. Significant (p < 0.05) decline in 3H SP permeation was observed in the presence of unlabeled SP and at 4°C, indicating that the transport process is carrier-mediated. High-performance liquid chromatography analysis showed no significant metabolism of 3H SP in either the donor or receiver chambers. 3H SP transport was inhibited by 2–11 SP (p < 0.05) but not by any other fragments, indicating that both the C- and N-terminal regions are essential for molecular recognition by the receptor. Endocytic inhibitors (chloroquine, phenylarsine oxide, monensin, and brefeldin) did not inhibit SP transport, suggesting the involvement of a nonendocytic mechanism in SP permeation. Pro9 SP, a high-affinity substrate for the NK-1 major subtype receptor, significantly (p < 0.05) inhibited the transport of SP. However, Sar9Met(O2)11 SP, a high-affinity substrate for the NK-1 minor subtype receptor, septide, and neurokinin A, inhibitors of NK-1 and neurokinin-2 (NK-2) receptors, respectively, did not produce any inhibition of SP transport. Western blot analysis confirmed the presence of the NK-1 receptor in BBMEC monolayers.
Conclusions
The above results provide functional and molecular evidence for the existence of a carrier-mediated mechanism in the transport of SP across the BBB. The effects of specific inhibitors and the results of Western blot analyses demonstrate the involvement of the NK-1 receptor in the transport of SP across the BBB.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Severini G. Improta G. Falconieri-Erspamer S. Salvadori V. Erspamer (2002) ArticleTitleThe tachykinin peptide family Pharmacol. Rev. 54 285–322 Occurrence Handle12037144 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XltVOhsr0%3D Occurrence Handle10.1124/pr.54.2.285
Y. Q. Cao P. W. Mantyh E. J. Carlson A. M. Gillespie C. J. Epstein A. I. Basbaum (1998) ArticleTitlePrimary afferent tachykinins are required to experience moderate to intense pain Nature 392 339–390 Occurrence Handle10.1038/32789
M. S. Kramer (2000) ArticleTitleUpdate on substance P (NK-1 receptor) antagonists in clinical trials for depression Neuropeptides 34 255 Occurrence Handle11049729 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXnvVGitL8%3D Occurrence Handle10.1054/npep.2000.0830
C. Bouras P. G. Vallet P. R. Hof Y. Charnay J. Golaz J. Constantinidis (1990) ArticleTitleSubstance P immunoreactivity in Alzheimer disease: a study in cases presenting symmetric or asymmetric cortical atrophy Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 4 24–34 Occurrence Handle1690554 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By%2BC1MfhtVY%3D
P. J. Gresch P. D. Walker (1999) ArticleTitleSerotonin-2 receptor stimulation normalizes striatal preprotachykinin messenger RNA in an animal model of Parkinson’s disease Neuroscience 93 831–841 Occurrence Handle10473249 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXltlKmsbo%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0306-4522(99)00238-9
S. H. Buck T. F. Burks M. R Brown H. I. Yamamura (1981) ArticleTitleReduction in basal ganglia and substantia nigra substance P levels in Huntington’s disease Brain Res. 209 464–469 Occurrence Handle6164436 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:Bi6C1crkt1w%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/0006-8993(81)90171-2
G. W. Roberts I. N. Ferrier Y. Lee T. J. Crow E. C. Johnstone D. G. Owens A. J. Bacarese-Hamilton G. McGregor D. O’Shaughnessey J. M. Polak (1983) ArticleTitlePeptides, the limbic lobe and schizophrenia Brain Res. 288 199–211 Occurrence Handle6198024 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2cXms1Wgsw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/0006-8993(83)90095-1
C. Tomaz P. J. Nogueira (1997) ArticleTitleFacilitation of memory by peripheral administration of substance P Behav. Brain Res. 83 143–145 Occurrence Handle9062673 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXhs1yrsLY%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0166-4328(97)86058-5
R. Mattioli E. M. Santangelo A. C. Costa L. Vasconcelos (1997) ArticleTitleSubstance P facilitates memory in goldfish in an appetitively motivated learning task Behav. Brain Res. 85 117–120 Occurrence Handle9095345 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXivFGhsr0%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0166-4328(96)00166-0
B. Kerdelhue K. Gordon R. Williams V. Lenoir V. Fardin P. Chevalier C. Garret P. Duval P. Kolm G. Hodgen H. Jones G. S. Jones (1997) ArticleTitleStimulatory effect of a specific substance P antagonist (RPR 100893) of the human NK1 receptor on the estradiol-induced LH and FSH surges in the ovariectomized cynomolgus monkey J. Neurosci. Res. 50 94–103 Occurrence Handle9379497 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXmvFSntrc%3D Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1097-4547(19971001)50:1<94::AID-JNR10>3.0.CO;2-A
T. Battmann S. Melik Parsadaniantz B. Jeanjean B. Kerdelhue (1991) ArticleTitle In-vivo inhibition of the preovulatory LH surge by substance P and in-vitro modulation of gonadotrophin-releasing hormone-induced LH release by substance P, oestradiol and progesterone in the female rat J. Endocrinol. 130 169–175 Occurrence Handle1717625 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXkvVKjsL8%3D Occurrence Handle10.1677/joe.0.1300169
D. I. Diz B. Westwood S. M. Bosch D. Ganten C. Ferrario (1998) ArticleTitleNK1 receptor antagonist blocks angiotensin II responses in renin transgenic rat medulla oblongata Hypertension 31 473–479 Occurrence Handle9453348 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXptF2ltA%3D%3D
N. M. Rupniak M. S. Kramer (1999) ArticleTitleDiscovery of the antidepressant and anti-emetic efficacy of substance P receptor (NK1) antagonists Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 20 485–490 Occurrence Handle10671176 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXhs1On Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0165-6147(99)01396-6
K. L. Audus R. T. Borchardt (1991) Transport of macromolecules across the capillary endothelium R. L. Juliano (Eds) Targeted Drug Delivery Springer Berlin Heidelberg New York 43–70
W. A. Banks A. J. Kastin (1996) ArticleTitlePassage of peptides across the blood–brain barrier: pathophysiological perspectives Life Sci. 59 1923–1943 Occurrence Handle8950292 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XntVags7s%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0024-3205(96)00380-3
F. L. Strand (1999) Neuropeptides: Regulators of Physiological Processes Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 90–94
G. Griebel (1999) ArticleTitleIs there a future for neuropeptide receptor ligands in the treatment of anxiety disorders? Pharmacol. Ther. 82 1–61 Occurrence Handle10341356 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXitF2jt7k%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0163-7258(98)00041-2
A. Holmes M. Heilig N. M. Rupniak T. Steckler G. Griebel (2003) ArticleTitleNeuropeptide systems as novel therapeutic targets for depression and anxiety disorders Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 24 580–588 Occurrence Handle14607081 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXos12ks7o%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.tips.2003.09.011
R. Benoliel E. Eliav A. J. Mannes R. M. Caudle S. Leeman M. J. Iadarola (1999) ArticleTitleActions of intrathecal diphtheria toxin–substance P fusion protein on models of persistent pain Pain 79 243–253 Occurrence Handle10068170 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXotVKhsLg%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0304-3959(98)00170-5
C. E. Fisher J. A. Sutherland J. E. Krause J. R. Murphy S. E. Leeman J. C. vanderSpek (1996) ArticleTitleGenetic construction and properties of a diphtheria toxin-related substance P fusion protein: in-vitro destruction of cells bearing substance P receptors Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 93 7341–7351 Occurrence Handle8692995 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28Xkt1Wgtbw%3D Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.93.14.7341
R. G. Wiley D. A. Lappi (1997) ArticleTitleDestruction of neurokinin-1 receptor expressing cells in vitro and in vivo using substance P–saporin in rats Neurosci. Lett. 230 97–100 Occurrence Handle9259473 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXltFGmtbw%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0304-3940(97)00490-4
K. L Audus L. Ng W. Wang R. T. Borchardt (1996) Brain microvessel endothelial cell culture systems R. T. Borchardt P. L. Smith G. Wilson (Eds) Models for Assessing Drug Absorption and Metabolism Plenum Press New York
P. M. Reardon K. L. Audus (1993) ArticleTitleApplications of primary cultures of brain microvessel endothelial cell monolayers in the study of vasoactive peptide interaction with the blood–brain barrier STP Pharm. Sci. 3 63–68 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXisVyjsr8%3D
I. Fristad V. Vandevska-Radunovic K. Fjeld S. J. Wimalawansa I. Hals Kvinnsland (2003) ArticleTitleNK1, NK2, NK3 and CGRP1 receptors identified in rat oral soft tissues, and in bone and dental hard tissue cells Cell Tissue Res. 311 383–391 Occurrence Handle12658446 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXitlOqsL4%3D
J. Reubi H. Macke E. Krenning (2005) ArticleTitleCandidates for peptide receptor radiotherapy today and in the future J. Nucl. Med. 46 IssueID1 67S–75S Occurrence Handle15653654 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXhsVeksLg%3D
A. Delgado A. McManus J. Chambers (2005) ArticleTitleExogenous administration of substance P enhances wound healing in a novel skin-injury model Exp. Biol. Med. 230 271–280 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXjtFequrY%3D
A. Rosen Y. Zhang I. Lund T. Lundeberg L. Yu (2004) ArticleTitleSubstance P microinjected into the periaqueductal gray matter induces antinociception and is released following morphine administration Brain Res. 1001 87–94 Occurrence Handle14972657 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXht1yrsrg%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.brainres.2003.11.060
R. Millet L. Goossens K. Bertrand-Caumont J. Goossens R. Houssin J. Henichart (2001) ArticleTitleA flexible approach to the design of new potent substance P receptor ligands J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 53 929–934 Occurrence Handle11480541 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXlsV2nt7o%3D Occurrence Handle10.1211/0022357011776324
C. Pean A. Wijkhuisen F. Djedaini-Pilard J. Fischer S. Doly M. Conrath J. Couraud J. Grassi B. Perly C. Creminon (2001) ArticleTitlePharmacological in vitro evaluation of new substance P–cyclodextrin derivatives designed to drug targeting towards NK1-receptor bearing cells Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1541 150–160 Occurrence Handle11755209 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XitFSh Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0167-4889(01)00139-2
W. A. Breeman M. P. VanHagen H. A. Visser-Wisselaar M. E. Pluijm Particlevan der J. W. Koper B. Setyono-Han W. H. Bakker D. J. Kwekkeboom M. P. Hazenberg S. W. Lamberts T. J. Visser E. P. Krenning (1996) ArticleTitle In-vitro and in-vivo studies of substance P receptor expression in rats with the new analog [indium-111-DTPA-Arg1]substance P J Nucl Med. 37 IssueID1 108–117 Occurrence Handle8543978 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28Xht1agtLw%3D
P. W. Mantyh S. D. Rogers P. Honore B. J. Allen J. R. Ghilardi J. Li R. S. Daughters D. A. Lappi R. G. Wiley D. A. Simone (1997) ArticleTitleInhibition of hyperalgesia by ablation of lamina I spinal neurons expressing the substance P receptor Science 278 275–279 Occurrence Handle9323204 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXms1Cqur0%3D Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.278.5336.275
A. Freed K. Audus S. Lunte (2002) ArticleTitleInvestigation of substance P transport across the blood–brain barrier Peptides 23 157–165 Occurrence Handle11814631 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XovFCktQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0196-9781(01)00592-7
C. G. Charlton C. J. Helke (1985) ArticleTitleCharacterization and segmental distribution of 125I-Bolton‐Hunter-labeled substance P binding sites in rat spinal cord J. Neurosci. 5 1293–1299 Occurrence Handle2582102 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2MXksVylsLc%3D
S. R. Vigna J. J. Bowden D. M. McDonald J. Fisher A. Okamoto D. C. McVey D. G. Payan N. W. Bunnett (1994) ArticleTitleCharacterization of antibodies to the rat substance P (NK-1) receptor and to a chimeric substance P receptor expressed in mammalian cells J. Neurosci. 14 834–845 Occurrence Handle7507985 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXhvVeisbs%3D
A. T. Michael-Titus D. Blackburn Y. Connolly J. V. Priestley R. Whelpton (1999) ArticleTitleN- and C-terminal substance P fragments: differential effects on striatal [3H] substance P binding and NK1 receptor internalization NeuroReport 10 2209–2213 Occurrence Handle10424700 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXkvFClu7c%3D
D. Regoli Q. T. Nguyen D. Jukic (1994) ArticleTitleNeurokinin receptor subtypes characterized by biological assays Life Sci. 54 2035–2047 Occurrence Handle8208061 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXktVWisbw%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/0024-3205(94)00712-8
U. Bickel T. Yoshikawa W. M. Pardridge (2001) ArticleTitleDelivery of peptides and proteins through the blood–brain barrier Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 46 247–279 Occurrence Handle11259843 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXitVOhsLk%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0169-409X(00)00139-3
W. Pan A. J. Kastin (2004) ArticleTitleWhy study transport of peptides and proteins at the neurovascular interface Brain Res. Rev. 46 32–43 Occurrence Handle15297153 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXmsVGit7g%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.brainresrev.2004.04.006
C. Hertel S. J. Coulter J. P. Perkins (1985) ArticleTitleA comparison of catecholamine-induced internalization of beta-adrenergic receptors and receptor-mediated endocytosis of epidermal growth factor in human astrocytoma cells. Inhibition by phenylarsine oxide J. Biol. Chem. 260 12547–12553 Occurrence Handle2995380 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2MXlslarurs%3D
S. Pippig S. Andexinger M. J. Lohse (1995) ArticleTitleSequestration and recycling of beta 2-adrenergic receptors permit receptor resensitization Mol. Pharmacol. 47 666–676 Occurrence Handle7723728 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXltFSltL4%3D
J. Lippincott-Schwartz L. Yuan C. Tipper M. Amherdt L. Orci R. D. Klausner (1991) ArticleTitleBrefeldin A’s effects on endosomes, lysosomes, and the TGN suggest a general mechanism for regulating organelle structure and membrane traffic Cell 67 601–616 Occurrence Handle1682055 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XitVCi Occurrence Handle10.1016/0092-8674(91)90534-6
Y. Takayama P. May R. G. Anderson J. Herz (2005) ArticleTitleLow density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP1) controls endocytosis and c-CBL-mediated ubiquitination of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta (PDGFRbeta) J. Biol. Chem. 280 18504–18510 Occurrence Handle15753096 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXjsl2htbg%3D Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.M410265200
C. Maggi T. Schwartz (1997) ArticleTitleThe dual nature of the tachykinin NK1 receptor TIPS 18 351–353 Occurrence Handle9357319 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXmvFehtbs%3D
S. Sagan S. Lavielle (2001) ArticleTitleInternalization of [3H]substance P analogues in NK-1 receptor transfected CHO cells Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 282 958–964 Occurrence Handle11352645 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXisVyrsb0%3D Occurrence Handle10.1006/bbrc.2001.4687
H. R. Kim S. Lavielle S. Sagan (2003) ArticleTitleThe two NK-1 binding sites are distinguished by one radiolabelled substance P analogue Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 306 725–729 Occurrence Handle12810079 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXks1aksb0%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0006-291X(03)01063-5
A. Wijkhuisen M. A. Sagot Y. Frobert C. Creminon J. Grassi D. Boquet J. Y. Couraud (1999) ArticleTitleIdentification in the NK1 tachykinin receptor of a domain involved in recognition of neurokinin A and septide but not of substance P FEBS Lett. 447 155–159 Occurrence Handle10214937 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXis1aku7Y%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0014-5793(99)00298-7
H. Hastrup T. W. Schwartz (1996) ArticleTitleSeptide and neurokinin A are high-affinity ligands on the NK-1 receptor: evidence from homologous versus heterologous binding analysis FEBS Lett. 399 264–266 Occurrence Handle8985159 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXkt1yrsg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0014-5793(96)01337-3
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully thank Dr. Ronald T. Borchardt for his valuable suggestions, Nancy Harmony for her help with the preparation of this manuscript, and Dr. Josh Cooper and Kathy Heppert for their help with the mass spectrometer. Financial support from the NIH (R01 NS042929) and NSF (CHE-0111618) is greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chappa, A.K., Audus, K.L. & Lunte, S.M. Characteristics of Substance P Transport Across the Blood–Brain Barrier. Pharm Res 23, 1201–1208 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-006-0068-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-006-0068-1