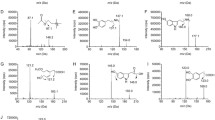
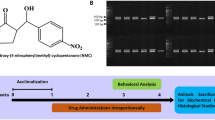
The present study was designed to investigate anti-Alzheimer’s activity and to quantify brain neurotransmitter of newly developed isoindoline-1,3-dione derivatives (IDDs). The anti-Alzheimer’s activity was evaluated using the elevated plus maze (EPM) and Morris water maze (MWZ) tests. Rats were divided into five groups, each containing six animals, which were treated with vehicle, scopolamine, donepezil and newly developed phthalimide derivatives (IDDs). Each model was studied for 5 days and the in-vivo anti-oxidant activity indices of brain including catalase, lipid peroxidase (LPO), glutathione (GSH) and acetylcholinesterase (AChE) levels were estimated spectrophotometrically. The levels of neurotransmitters serotonin and dopamine were estimated in rat brain homogenate using HPLC method. Treatment with high dose (30 mg/kg) of IDD showed significant anti-Alzheimer’s activity in EPM and MWM tests in a dose-dependent manner in comparison with standard drug donepezil (4 mg/kg). In estimating the biochemical parameters, the level of catalase in the test group increased significantly, whereas LPO and GSH levels in treated groups decreased as compared to the untreated disease control group. The HPLC method confirmed that the concentrations of biogenic amines like dopamine and serotonin were significantly increased in phthalilmide group as compared to the control group. Thus, the present study reveals that the newly developed IDDs exhibit anti-Alzheimer’s activity in various experimental animal models.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Kumar, A. Singh, and Ekavali, Pharmacol. Rep., 67(2), 195 – 203 (2015).
M. S. Parihar and Taruna Hemnani, J. Clin. Neurosci., 11(5), 456 – 467 (2004).
P. T. Francis, A. M. Palmer, M. Snape, and G. K. Wilcock, J. Neuron. Neurosurg. Psychiatry, 66, 137 – 147 (1999).
A. Gella, N. Durany, Cell Adhesion Migration, 3(1), 88 – 93 (2009).
L. F. Nunes Lemes, G. de Andrade Ramos, A. S. de Oliveira, et al., Eur. J. Med. Chem., 108, 687 – 700 (2016).
A. Burns, M. Rossor, et al., Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord., 10, 237 – 244 (1999).
N. Guzior, M. Bajda, M. Skrok, et al., Eur. J. Med. Chem., 92, 21 – 47 (2015).
www.webmd.com [Alzheimer’s disease guide].
alz.org®|alzheimer’s association
I. Melnikova, Nature Rev. Drug Discov., 6, 341 – 342 (2015).
M. N. Sabbagh, S. Richardson, and N. Relkin, Alzheimers Dementia, 4(Supply 1), S109–S118 (2008).
P. Rocca, E. Cocuzza, L. Marchiaro, and F. Bogetto, Progr. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. & Biol. Psychiatry, 26, 369– 373 (2002).
N. Guzior and M. Bajda, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 92, 738 – 743 (2015).
W. Si, T. Zhang, L. Zhang, et al., Bioorg. Med. Chem., 26(9), 2380 (2016).
M. Ignasik, M. Bajda, N. Guzior, et al., Arch. Pharm. Chem. Life Sci., 345, 509 – 516 (2012).
D. Panek, A.Wiêckowska, T.Wichur, et al., Eur. J. Med. Chem., 125, 676 – 695 (2017).
M. Bajda, A.Wiêckowska, M. Hebda, et al., Int. J. Mol. Sci., 14, 5608 – 5632 (2013).
M. Hebda, M. Bajda, A. Wiêckowska, et al., Molecules, 21(4), 410 (2016).
D. Alonso, I. Dorronsoro, L. Rubio, et al., Bioorg. Med. Chem., 13, 6588 – 6597 (2005).
A. Aliabadi and F. Alireza, Iran J. Basic Med. Sci., 16, 10 (2013).
S. Azimi, A. Zonouzi, O. Firuzi, et al., Eur. J. Med. Chem., 138, 729 – 737 (2017).
O. Grundmann, J. I. Nkajima, S. Seo, and V. Butterweck, J. Ethnopharmacol., 110, 406 – 411 (2007).
J. Itoh, T. Nabeshima, and T. Kameyama, Psychopharmacol., 101, 27 – 33 (1990).
Z. Hlinak and I. Krejc, Behav. Brain Res., 91, 83 – 89 (1998).
D. Dhingra and V. Kumar, Adv. Pharmacol. Sci., 2012, 357 – 368 (2012).
R. K. McNamara and R. W. Skelton, Brain Res. Rev., 18, 33 – 49 (1993).
R. D. Hooge and P. P. De Deyn, Brain Res. Rev., 36, 60 – 90 (2001).
M. C. Carrillo, C. Minami, K. Kitani, et al., Life Sci., 67, 577 – 585 (2000).
A. Bhattacharya, S. Ghosal, and S. K. Bhattacharya, J. Ethnopharmacol., 74, 1 – 6 (2001).
F. Liu and T. B. Ng, Biochem. Cell Biol., 78, 447 – 453 (2000).
T. Matsunami, Y. Sato, T. Sato, and M. Yukawa, Physiol. Res., 59, 97 – 104 (2010).
A. Nurrochmad, A. R. Hakim, S. A. Marogono, et al., Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci., 2(3), 45 – 48 (2010).
M. Schlumpf, W. Lichtensteiger, H. Langemann, et al., Biochem. Pharmacol., 23, 2337 – 2446 (1974).
A. Mohammadi-Farani, N. Abdi, A. Moradi, and A. Aliabadi, Iran J. Basic Med. Sci., 20, 59 – 66 (2017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Patel, V.C., Samresh, P.R., Dipayan, T. et al. Investigation into Anti-Alzheimer Activity of Newly Developed Phthalimide Derivatives in Experimental Animals. Pharm Chem J 57, 60–69 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-023-02851-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-023-02851-y