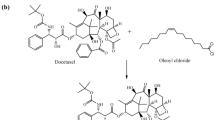
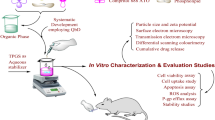
Anticancer drugs mostly produce minimal to severe side effects due to lack of selectivity. The present work envisaged selective targeting of MCF-7 breast cancer cells by synthesizing an ester conjugate using oxalyl chloride of drug raloxifene targeted for steroidal estrogen receptor alpha. The objective was to synthesize and evaluate raloxifene–oxalyl chloride conjugate as anticancer drug with side effects reduced by increasing selectivity. Synthesis of the conjugate was carried out by reflux condensation of acid chloride of oxalyl chloride with raloxifene. In vitro methods viz. lipophilicity, solubility, protein binding, drug release and permeation, hydrolysis, and cytotoxicity were employed for characterization and evaluation of the drug conjugate. The solubility and partition coefficient studies had an outcome of better solubility and lipophilicity while protein binding studies revealed a low protein binding capacity of the drug conjugate. The hemolytic study showed lesser RBC lysis with significant cytotoxicity compared to the parent drug and a selective diffusion at the pH of cancer cells rather than pH of normal cells, and hence increasing the specificity and minimizing the adverse effects. Hydrolytic study of the conjugate signified minimal hydrolysis of the conjugate at various pH, simulated gastric fluid, and simulated intestinal fluid. The synthesized conjugate thus ratifies to be a useful prodrug in reducing the systemic toxicity of raloxifene as well as selectively targeting the cancerous cells.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. H. Russo and J. Russo, J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia, 3(1), 49 – 61, (1998).
A. Huang and G. Kaley, Microcirculation, 11(1), 9 – 38, (2004).
B. L. Riggs, S. Khosla, L. and J. Melton, Endocrinol. Rev., 23(3), 279 – 302, (2002).
A. Maggi, P. Ciana, S. Belcredito, and E. Vegeto, Annu. Rev. Physiol., 66, 291 – 313, (2004).
E. J. Rossouw, G. L. Anderson, R. L Prentice, et al., JAMA, 288 (3), 321 – 333, (2002).
B. E. Henderson, R. Ross, and L. Bernstein, Cancer Res., 48(2), 246 – 253, (1988).
C. DeSantis, J. Ma, L. Bryan, and A. Jemal, CA Cancer J. Clin., 64(1), 52 – 62, (2014).
V. C. Jordan, Cancer Cell, 5(3), 207 – 213, (2004).
J. S. Lewis and V. C. Jordan, Mutat. Res., 591(1–2), 247 – 263, (2005).
M. M. Gottardis and V. C. Jordan, Cancer Res., 47(15), 4020 – 4024, (1987).
D. C. Kemp, P. W. Fan, and J. C. Stevens, Drug Metab. Dispos., 30(6), 694 – 700, (2002).
E. J. Jeong, Y. Liu, H. Lin, and M. Hu, Drug Metab. Dispos., 33(6), 785 – 794, (2005).
K. R. Snyder, N. Sparano, and J. M. Malinowski, Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm., 57(18), 1669 – 1675, (2000).
A. Furniss, A. Hannaford, and P. Smith, Vogel’s Textbook of Practical Organic Chemistry, ELBS Publications, New York, 5, 692–693, (1988).
N. Bhatia, K. Katkar, and S. Ashtekar, Asian J. Pharm. Sci., 11(3), 449 – 458, (2016).
A. Rasheed and C. K. Ashok Kumar, Int. J. Curr. Pharm. Res., 1(1), 47 – 55, (2009).
S. B. Bhise, R. J. Dias, S. G. Dhavale, and K. K. Mali, Laboratory Manual of Biopharmaceutics and Pharmakokinetics, Trinity Publishing House, India, 1, 1 – 66, (2010).
V. K. Singh and B. B. Subudhi, Med. Chem. Res., 24, 624 – 635, (2015).
K. K. Upadhyay, A. N. Bhatt, E. Castro, et al., Macromol. Biosci., 10(5), 503 – 512, (2010).
M. K. Lee, S. J. Lim, and C. K. Kim, Biomaterials, 28(12), 2137 – 2146, (2007).
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Dr. H. N. More, the Principal of Bharati Vidyapeeth College of Pharmacy, Kolhapur, for providing laboratory facilities.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bhatia, N., Shirale, P., Choudhari, P. et al. Synthesis and In-Vitro Evaluation of Raloxifene–Oxalyl Chloride Conjugate Targeting Breast Cancer. Pharm Chem J 56, 798–805 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-022-02713-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-022-02713-z