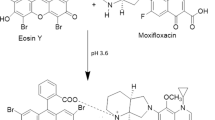
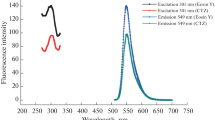
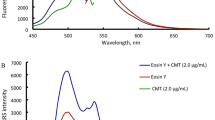
Highly sensitive and rapid method for the determination of prulifloxacin (PUFX) has been developed on the basis of ion association reaction of PUFX, Y(III) and eosin Y (EY). In pH 6.5 BR buffer medium, PUFX reacts with Y(III) to form a 2:1 cationic chelate which further reacts with EY to form 2:1 ion-association complex. As a result, not only the spectra of absorption are changed, but quenching of fluorescence and significant enhancement of resonance Rayleigh scattering (RRS) is observed. Furthermore, a new RRS spectrum would appear, and the maximum RRS wavelength was located at about 375 nm. The fluorescence quenching (FQ) and enhanced RRS intensity were directly proportional to the PUFX concentration in the ranges of 1.5 – 7.6 μg mL–1 and 0.004 – 3.0 μg mL–1 with detection limits 8.5 ng mL–1 and 1.1 ng mL–1, respectively. The optimum conditions of RRS method and the effects of coexisting substances on the reaction were investigated. In addition the composition of ion-association complexes, the reaction mechanism, the energy transfer between absorption, fluorescence and RRS and reasons for RRS enhancement were discussed. The methods were applied to the determination of PUFX in pharmaceutical samples with satisfactory results.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Yoshida and S. Mitsuhashi, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 37, 793 – 800 (1993).
Y. Okuhama, K. Momota, and A. Morino, Arzneim. Forsch., 47, 276 – 284 (1997).
M. Nakashima, T. Uematsu, K. Kosuge, et al., J. Pharmacol., 34, 930 – 937 (1994).
R. Picollo, N. Brion, V. Gualano, et al., Arzneim. Forsch., 53 (2003) 201 – 205.
J. Wen, Z. Y. Zhu, Z. Y. Hong, et al., Chromatography, 66, 37 – 41 (2007).
L. X. Guo, M. L. Qi, X. Jin, et al., J. Chromatogr. B, 832, 280 – 285 (2006).
A. T. Luo, H. F. Liu, X. K.Wang, and H. Li, Memoirs, 3, 31 – 33 (2006).
Z. Yang, X.Wang,W. Qin, and H. Zhao, Anal. Chim. Acta, 623, 231 – 237 (2008).
F. Yu, F. Chen, S. Zheng, and L. Chen, Anal. Lett., 41, 3124 – 3137 (2008).
T. Wu, B. Fang, L. Chang, et al., Luminescence, 28, 894 – 899 (2013).
Z. Yang, X.Wang,W. Qin, and H. Zhao, Anal. Chim. Acta, 623, 231 – 237 (2008).
M. Cui, F. Yu, F. Chen, and L. Chen, Anal. Lett., 41, 2001 – 2012 (2008).
X. L. Wang, A. Y. Li, H. C. Zhao, and L. P. Jin, J. Anal. Chem., 64, 75 – 81 (2009).
C. Z. Huang, K. A. Li, and S. Y. Tong, Anal. Chem., 68, 2259 – 2263 (1996).
C. Q. Ma, K. A. Li, and S. Y. Tong, Anal. Biochem., 239, 86 – 91 (1996).
S. P. Liu, H. Q. Luo, N. B. Li, and Z. F. Liu, Anal. Chem., 76, 3907 – 3914 (2001).
S. P. Liu, Z. F. Liu, and H. Q. Luo, Anal. Chim. Acta., 12, 255 – 260 (2000).
M. Oshima, N. Goto, J. P. Susanto, and S. Motomizu, Analyst, 121, 1085 – 1088 (1996).
S. P. Liu, S. Chen, Z. F. Liu, et al., Anal. Chim. Acta, 535, 169 – 175 (2005).
X. Q. Wei, Z. F. Liu, and S. P. Liu, Anal. Biochem., 346, 330 – 332 (2005).
X. L. Hu, S. P. Liu, and N. B. Li, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 376, 42 – 48 (2003).
S. H. Fu, Z. F. Liu, S. P. Liu, et al., Anal. Chim. Acta, 599, 271 – 278 (2007).
Z. Jiang, R. Cai, and H. Zhang, in: Analytical Chemistry of Rare Earths, 2nd ed., Science Publishing: Beijing (2000), pp. 21 – 30.
N. EI-Enany, Il Farmaco, 59, 63 (2004).
S. G. Stanton, R. Pecora, and B. S. Hudson, J. Chem. Phys., 75, 5615 – 5626 (1981).
S. P. Liu and L. Kong, Anal. Sci., 19, 1055 – 1060 (2003).
Chinese Macropaedia Biology (II), Chinese Macropaedia Press, Beijing (1991), p. 1374.
X. L. Tang, Z. F. Liu, S. P. Liu, and X. L. Hu, Sci. Chin. Ser. B, 50 54 – 62 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bano, S., Mohd, A., Khan, A.A.P. et al. Resonance Light-Scattering Enhancement Effect of the Y(III)–PUFX–Eosin System and its Fluorescence Study. Pharm Chem J 52, 182–190 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-018-1787-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-018-1787-4