Abstract
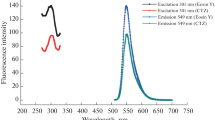
An easy, verified spectrofluorimetric approach was established for the investigation of moxifloxacin in pure forms, pharmaceutical preparations, and biological fluids. The approach involves forming a binary complex of moxifloxacin and eosin Y in an acetate buffer with a pH of 3.6. The highest quenching of eosin Y with moxifloxacin occurs at 545 nm. Several factors, such as pH, buffer type and concentration, and eosin Y concentration, were carefully studied. The calibration graph showed a linear relationship between fluorescence intensity and moxifloxacin concentrations between 0.2 and 10 µg mL−1 with a correlation coefficient of 0.998. It was determined that the detection and quantification limits were 0.0322 µg mL−1 and 0.0976 µg mL−1, respectively. The impact of common excipients was investigated, but no interferences were discovered. Standard forms of moxifloxacin, pharmaceuticals, and biological samples have all been studied using the established methodology. The method, which successfully complied with ICH requirements, was used for the analysis of moxifloxacin in its pure form, pharmaceutical dosage forms, and biological samples. The percentage recoveries obtained were ranged from 99.50 to 102.50% for pharmaceutical preparations and from 100.50 to 102.50% for human blood plasma and urine.
Graphical abstract
Proposed mechanisms for the reaction between moxifloxacin and eosin Y










Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.R. Johnson, Fluoroquinolones in urinary tract infection, in Fluoroquinolones antibiotics (milestones in drug therapy). ed. by A.R. Ronald, D.E. Low (Birkhauser Verlag, Berlin, 2003), p.107
H. Stass, A. Dalhoff, D. Kubitza, U. Schühly, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 42, 2060 (1998)
A. Dalhoff, H. Stass, Drugs 58, 239 (1999)
J. Sousa, G. Alves, A. Fortuna, A. Falcao, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 403, 93 (2012)
D. Predrag, C. Andrija, D. Aleksandra, J.S. Milena, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 50, 117 (2007)
H.A. Nguyena, J. Grelleta, B.B. Ba, C. Quentin, M.C. Saux, J. Chromatogr. B 810, 77 (2004)
F.U. Khan, F. Nasir, Z. Iqbal, I. Khan, N. Shahbaz, M. Hassan, F. Ullah, J. Chromatogr. B 1017–1018, 120 (2016)
J.D. Smet, K. Boussery, K. Colpaert, P.D. Suttera, P.D. Paepe, J. Decruyenaere, J.V. Bocxlaer, J. Chromatogr. B 877, 961 (2009)
A.P. Dewani, B.B. Barik, S.K. Kanungo, B.R. Wattyani, Am. Eurasian J. Sci. Res. 6, 192 (2011)
R. Kant, R. Bodla, R. Bhuthani, G. Kapoor, Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 7, 316 (2015)
S.K. Motwani, S. Chopra, F.J. Ahmad, R.K. Khar, Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 68, 250 (2007)
P. Patel, B. Suhagia, M. Patel, Indian Drugs 2, 155 (2005)
J.G. Möller, H. Stass, R. Heinig, G. Blaschke, J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 716, 325 (1998)
R. Inam, H. Mercan, E. Yilmaz, B. Uslu, Anal. Lett. 40, 529 (2007)
N. Erk, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 378, 1351 (2004)
J.A. Ocana, F.J. Barragan, M. Callejon, Analyst 125, 2322 (2000)
M.N. Khan, W. Ali, Z. Shah, M. Idrees, H. Gulab, Adnan, Anal. Sci. 36, 361 (2020)
R.W. Sabnis, Handbook of biological dyes and stains: synthesis and industrial applications (Wiley, New York, 2010), p.173
M.I. Walash, M.S. Rizk, M.I. Eid, M.E. Fathy, J. AOAC Int. 90, 1579 (2007)
M.E.K. Wahba, N. El-Enany, F. Belal, Anal. Methods 7, 10445 (2015)
F. Belal, A. El-Brashy, N. El-Enany, N. El-Bahay, J. AOAC Int. 91, 1309 (2008)
M.N. Khan, M. Mursaleen, Luminescence 36, 515 (2021)
S.M.S. Derayea, Anal. Methods 6, 2270 (2014)
H. Rahman, Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 9, 1 (2017)
D. Harvey, Modern analytical chemistry (McGraw-Hill, New York, 2000)
M. Walash, F. Belal, N. El-Enany, H. Elmansi, Int. J. Biomed. Sci. 6, 327 (2010)
M.I. Walash, F.F. Belal, M.I. Eid, S.A.E. Mohamed, Chem. Cent. J. 5, 60 (2011)
R.M.W. Kazan, H. Seddik, M. Aboudane, Int. J. Acad. Sci. Res. 5, 67 (2017)
P. Djurdjevic, A. Ciric, A. Djurdjevic, M.J. Stankov, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 50, 117 (2009)
Acknowledgements
The authors express their gratitude to Allama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad, Pakistan, for allowing them to perform this study. The authors also extend their appreciation to Bacha Khan University, Charsadda, Pakistan for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, M.N., Zaman, N., Mursaleen, M. et al. Eco-friendly approach for determination of moxifloxacin in pharmaceutical preparations and biological fluids through fluorescence quenching of eosin Y. ANAL. SCI. 38, 1541–1547 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44211-022-00192-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s44211-022-00192-6