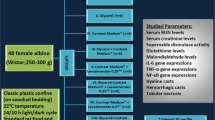
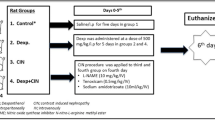
A controlled, randomized study using an experimental model of contrast (iopromide)-induced nephropathy (CIN) in normal mongrel rats showed that the combination of treatment by hydration with the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD)-containing formulation Nadcin®, with cytoprotective and antiischemic actions, decreased the plasma creatinine and urea nitrogen levels 72 h after induction of CIN. Aclose correlational relationship (r = 0.78, p < 0.001) was found between the blood endothelin-1 (ET-1) level and O2 – generation, while there was no relationship between hydrogen peroxide production and the ET-1 level (r = 0.13, p > 0.05) or between the ET-1 level and catalase activity (r = 0.41, p > 0.05). In contrast to monotherapy with hydration, inclusion of Nadcin normalized blood ET-1 and the blood ET-1/creatinine ratio, the blood and renal NAD/NADH and NADP/NADPH redox potentials, and had more marked actions on reversing the overproduction of free radicals and on the antioxidant defense system in the blood and renal tissue. It is suggested that ET-1, the ET-1/creatinine ratio, and the plasma redox potential can be used as early markers for increases in the risk of developing stable impairment of renal function on use of x-ray contract agents.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. G. Karmazanovskii, Yu. A. Polyaev, A. L. Yudin, and N. L. Shimanovskii, Med. Viz., 1, 135 – 144 (2007).
N. L. Shimanovskii, Contrast Media [in Russian], GEOTAR-Media, Moscow (2009); Series: Specialist Medical Library: Radiodiagnosis.
T. H. Au, A. Bruckner, S. M. Mohiuddin, and D. E. Hilleman, Am. Pharmacother., 48, 1332 – 1342 (2014).
A. Bienholtz, B. Wilde, and A. Kribben, Clin. Kidney J., 8(4), 405 – 414 (2015).
N. Gassanov, A. M. Nia, E. Caglayan, and F. Er, J. Am. Soc. Nephrol., 25, 216 – 224 (2014).
N. Katsiki, V. G. Athyros, A. Karagiannis, and D. P. Mikhailidis, Angiology, 66(6), 508 – 513 (2015).
R. Anand, D. Harry, S. Holt, et al., Gut, 50, 111 – 117 (2002).
S. N. Heyman, S. Rosen, and C. Rosenberg, Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol., 3, 288 – 296 (2008).
S. M. Sancho-Martinez, J. M. Lopez-Nov, and V. Golovach, Atherosclerosis, 235(2), e162 (2014).
F. Heunish, G. Von Einem, M. Alter, et al., Life Sci., 118, 440 – 445 (2014).
V. C. Ikamaise, T. B. Ekanem, K. E. Obeten, and G. Udo-Affah, Global. J. Sci. Front. Res. Biol. Sci., 2, 5 – 10 (2015).
W. Muetzel and U. Speck, Am. J. Neuroradiol., 4, 350 – 352 (1983).
M. D. Adams, M. S. Robbins, R. M. Hopkins, and G. B. Hoey, Investigative Radiol., 19(4), S124 (1984).
C. F. Pinto, M. Watanabe, and M. F. Vattimo, J. Nephrol., 21, 783 – 788 (2008).
N. A. Andriadze, G. V. Sukoyan, N. O. Otarishvili, et al., Ros. Med. Vestn., No. 2, 31 – 42 (2001).
N. V. Karsanov, G. V. Sukoyan, A. V. Antelava, and N. A. Varazanashvili, Éksperim. Klin. Farmakol., 66(5), 17 – 21 (2003).
G. V. Sukoyan, N. A. Andriadze, E. I. Guchua, and N. V. Karsanov, Byul. Éksperim. Biol. Med., 139(1), 53 – 56 (2005).
S. K. Morcos, H. S. Thomsen, and J. A. Webb, Eur. Radiol., 9, 1602 – 1613 (1999).
A. Papadimitriou, K. C. Silva, E. Peixoto, et al., Am. J. Renal. Physiol., 308, F209-F225 (2015).
S. Quadri and H. M. Siragy, Am. J. Renal. Physiol., 307, F593-F600 (2014).
R. K. Gupta and T. J. Bang, Seminars Int. Radiol., 27(4), 348 – 359 (2010).
M. Maeder, M. Klein, T. Fehr, and H. Rickli, J. Am. Coll. Cardiol., 44, 1763 – 1771 (2004).
M. Heinrich and M. Uder, Rofo, 178(4), 378 – 384 (2006).
G-S. Oh, H-J. Kim, A. Shen, et al., Biomed. Res. Intern., Article ID 4048390; http: //dx.doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/4048390 (2016).
O. H. Lowry, J. V. Passoneau, and M. K. Rock, J. Biol. Chem., 236(10), 2756 – 2759 (1961).
O. H. Lowry and J. V. Passoneau, A Flexible System of Enzymatic Analysis, Academic Press, New York, London (1972).
M. R. Buhl, E. Kemp, and G. Kemp, Transplant Proc., 9(3), 1603 – 1606 (1977).
O. H. Lowry, J. V. Passoneau, and M. K. Rock, J. Biol. Chem., 236(10), 2756 – 2759. (1961).
O. H. Lowry and J. V. Passoneau, A Flexible System of Enzymatic Analysis, Academic Press, New York, London (1972).
D. Rothwell and M. James, Urological Res., 9(2), 75 – 78 (1981).
G. V. Sukoyan and I. K. Kavadze, Byul. Éksperim. Biol. Med., 141(9), 297 – 300 (2008).
W. Ying, Scientifica (Cairo); doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/691251 (2013).
L. A. Bokeriya, V. E. Malikov, M. A. Arzumanyan, et al., Klin. Fiziol. Krovoobrashch., 1, 39 – 44 (2008).
M. Rogava, T. Bochorishvili, K. Kapanadze, and E. Berberashvili, Cardiol. Int. Med., 3 – 4, 33 – 37 (2010).
M. Rogava, T. Bochorishvili, V. E. Malikov, et al., Cardiol. Int. Med., 3 – 4, 18 – 23 (2007).
G. V. Sukoyan, A. V. Antelava, I. K. Kavadze, et al., Éksperim. Klin. Farmakol., 67(2), 19 – 23 (2003).
N. V. Gongadze, T. D. Kezeli, G. V. Sukoyan, et al., Pharmacol. Pharmacy, 7, 81 – 88 (2016).
N. Braidy, G. J. Guillemin, H. Mansour, et al., PLoS One, 6(e19194), 1 – 17 (2011).
Y. Ido, Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, 9, No. 7, 931 – 942 (2007).
H-C. Lee, J-G. Chang, H-W. Yen, et al., J. Nephrol., 24(3), 376 – 380 (2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Khimiko-Farmatsevticheskii Zhurnal, Vol. 51, No. 9, pp. 49 – 54, September, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sukoyan, G.V., Kezeli, T.D., Dolidze, N.M. et al. Sites of Action of Subtoxic Doses of the Iodine-Containing X-Ray Contrast Medium Iopromide on the Kidney and the Search for Means of Preventing the Development of Nephropathy. Pharm Chem J 51, 818–823 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-017-1699-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-017-1699-8