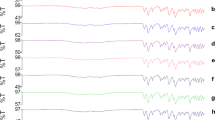
The effect of solid dispersion (SD) formation on the solubility of the antibiotic erythromycin has been studied using the parent substance of erythromycin and its SDs with polyethyleneglycol (PEG-1500), polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP-10000), and β-cyclodextrin. It is established that SD formation increases the solubility of the antibiotic by a factor of 1.3 – 1.8; the dissolution rate, 1.5 – 2.0. Results using a complex of physical and chemical methods suggest that the increase in erythromycin release from SDs takes place due to a decrease in the degree of crystallinity and the formation of intermolecular complexes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. U. Khabriev, V. G. Kukes, A. P. Arzamastsev (ed.), et al., Antibacterial Drugs. Standardization Methods of Preparations [in Russian], Meditsina, Moscow (2004), pp. 94 – 101.
I. I. Krasnyuk, Author’s Abstract of a Candidate Dissertation in Pharmaceutical Sciences, Moscow (2003).
I. I. Krasnyuk, Jr., V. A. Popkov, V. Yu. Reshetnyak, et al., Ross. Med. Zh., No. 6, 34 – 37 (2005).
Yu. V. Skovpen(, Author’s Abstract of a Candidate Dissertation in Pharmaceutical Sciences, Moscow (2002).
G. S. Babakina, G. P. Gaidukova, A. E. Gulyaev, et al., Khim.-farm. Zh., 25(4), 62 – 65 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Khimiko-Farmatsevticheskii Zhurnal, Vol. 43, No. 11, pp. 36 – 43, November, 2009.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khabriev, R.U., Popkov, V.A., Reshetnyak, V.Y. et al. Solubility of erythromycin from solid dispersions. Pharm Chem J 43, 625–631 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-010-0367-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-010-0367-z