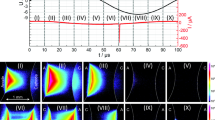
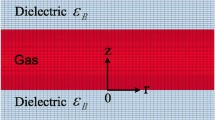
Abstract
Dielectric barrier discharges (DBDs) bring a long history of application and leave many interesting scientific questions. A positive streamer concept describes a temporal development of a microdischarge well, and memory charge effect explains spatially distributed microdischarges over the entire area of DBD. To properly model plasma chemistry occurring in a DBD, knowledge of microdischarges, distributed spatially and temporally, is essential. Here we present experimental result of multiple microdischarges, occurring successively and rooted at the same location. By employing a triangular waveform to a pointed electrode and a high conductivity layer at a surface of a dielectric barrier, a physical mechanism of the successive microdischarges was revealed: a slew rate of an external alternating current compensated a voltage drop caused by memory charges from a former microdischarge. A time interval between two neighboring microdischarges was inversely proportional to the slew rate, and the number of microdischarges depended primarily on an applied voltage. The number of microdischarges with an uncoated barrier was higher than that with an Ag-coated barrier; however, the charges delivered by each microdischarge were smaller in cases with an uncoated barrier. To investigate interactions between spatially separated microdischarges, this study will be extended to a configuration having multiple pointed electrodes. The effect of the successive microdischarges on plasma chemistry will also be a future study.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data presented in this study will be available upon request to the corresponding author (M.S.C.).
References
Kogelschatz U (2003) Dielectric-barrier discharges: their history, discharge physics, and industrial applications. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 23(1):1–46
Borcia G, Anderson CA, Brown NMD (2003) Dielectric barrier discharge for surface treatment: application to selected polymers in film and fibre form. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 12:335
Borcia G, Anderson CA, Brown NMD (2006) Surface treatment of natural and synthetic textiles using a dielectric barrier discharge. Surf Coat Technol 201(6):3074–3081
Massines F, Gouda G, Gherardi N, Duran M, Croquesel E (2001) The role of dielectric barrier discharge atmosphere and physics on polypropylene surface treatment. Plasma Process Polym 6:35–49
Tu X, Whitehead JC (2012) Plasma-catalytic dry reforming of methane in an atmospheric dielectric barrier discharge: understanding the synergistic effect at low temperature. Appl Catal B Environ 125(21):439–448
Zhang X, Cha MS (2013) Electron-induced dry reforming of methane in a temperature-controlled dielectric barrier discharge reactor. J Phys D Appl Phys 46:415205
Zhang X, Lee BJ, Im HG, Cha MS (2016) Ozone production with dielectric barrier discharge: effects of power source and humidity. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 44(10):2288–2296
Zhang X, Cha MS (2015) Partial oxidation of methane in a temperature-controlled dielectric barrier discharge reactor. Proc Combust Inst 35(3):3447–3454
Mouele ESM, Tijani JO, Badmus KO, Pereao O, Badajide O, Fatoba OO, Zhang C, Shao T, Sosnin E, Tarasenko V, Laatikainen K, Petrik LF (2021) A critical review on ozone and co-species, generation and reaction mechanisms in plasma induced by dielectric barrier discharge technologies for wastewater remediation. J Environ Chem Eng 9(5):105758
Li S, Dang X, Yu X, Abbas G, Zhang Q, Cao L (2020) The application of dielectric barrier discharge non-thermal plasma in VOCs abatement: a review. Chem Eng J 388:124275
Corke TC, Enloe CL, Wilkinson SP (2010) Dielectric barrier discharge plasma actuators for flow control. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 42:505–529
Boeuf JP, Pitchford LC (2005) Electrohydrodynamic force and aerodynamic flow acceleration in surface dielectric barrier discharge. J Appl Phys 97:103307
Thomas FO, Corke TC, Iqbal M, Kozlov A, Schatzman D (2009) Optimization of dielectric barrier discharge plasma actuators for active aerodynamic flow control. AIAA J 47(9):2169–2178
Corke TC, Post ML, Orlov DM (2009) Single dielectric barrier discharge plasma enhanced aerodynamics: physics, modeling and applications. Exp Fluids 46:1–26
Andersen JA, Veer K, Christensen JM, Østberg M, Bogaerts A, Jensen AD (2023) Ammonia decomposition in a dielectric barrier discharge plasma: insights from experiments and kinetic modeling. Chem Eng Sci 271:118550
Bang S, Snoeckx R, Cha MS (2023) Kinetic study for plasma assisted cracking of NH3: approaches and challenges. J Phys Chem A 172(5):1271–1282
Wang J, Zhang K, Meynen V, Bogaerts A (2023) Dry reforming in a dielectric barrier discharge reactor with non-uniform discharge gap: effects of metal rings on the discharge behavior and performance. Chem Eng J 465:142953
Snoeckx R, Jun D, Lee BJ, Cha MS (2022) Kinetic study of plasma assisted oxidation of H2 for an undiluted lean mixture. Combust Flame 242:112205
Manley T (1943) The electric characteristics of the ozonator discharge. Trans Electrochem Soc 84(1):83
Fridman A (2008) Plasma chemistry. Cambridge University Press
Eliasson B, Kogelschatz U (1991) Nonequilibrium volume plasma chemical processing. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 19(6):1063–1077
Kogelschatz U, Eliasson B, Egli W (1997) Dielectric-barrier discharges. principle and applications. J Phys IV France 7:C4-47-C4-66
Akishev Y, Aponin G, Balakirev A (2011) ‘Memory’ and sustention of microdischarges in a steady-state DBD: volume plasma or surface charge? Plasma Sources Sci Technol 20:024005
Akishev Y, Aponin G, Balakirev A (2011) Role of the volume and surface breakdown in a formation of microdischarges in a steady-state DBD. Eur Phys J D 61:421–429
Yurgelenas YV, Wagner HE (2006) A computational model of a barrier discharge in air at atmospheric pressure: the role of residual surface charges in microdischarge formation. J Phys D Appl Phys 39:4031
Chirokov A, Gutsol A, Fridman A, Sieber KD, Grace JM, Robinson KS (2004) Analysis of two-dimensional microdischarge distribution in dielectric-barrier discharges. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 13:623–635
Lukas C, Spaan M, Schulz-Von Der Gathen V (2001) Dielectric barrier discharges with steep voltage rise: mapping of atomic nitrogen in single filaments measured by laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 10:445
Grosch H, Hoder T, Weltmann KD, Brandenburg R (2010) Spatio-temporal development of microdischarges in a surface barrier discharge arrangement in air at atmospheric pressure. Eur Phys J D 60:547–553
Kozlov KV, Wagner HE, Brandenburg R, Michel P (2001) Spatio-temporally resolved spectroscopic diagnostics of the barrier discharge in air at atmospheric pressure. J Phys D Appl Phys 34:3164
Jahanbakhsh S, Brüser V, Brandenburg R (2018) Single microdischarges in a barrier corona arrangement with an anodic metal pin: discharge characteristics in subsequent breakdowns. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 27:115011
Jahanbakhsh S, Brüser V, Brandenburg R (2020) Experimental investigation of single microdischarges in a barrier corona arrangement with a cathodic metal pin. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 29:015001
Peeters FJJ, Rumphorst RF, Sanden MCM (2016) Dielectric barrier discharges revisited: the case for mobile surface charge. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 25:03LT03
Brandenburg R (2017) Dielectric barrier discharges: progress on plasma sources and on the understanding of regimes and single filaments. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 26:053001
Peeters F, Butterworth T (2019) In: atmospheric pressure plasma—from diagnostics to applications. IntechOpen, London
Acknowledgements
The research reported in this publication was funded by King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST), under Award Number BAS/1/1384-01-01.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JP conducted the experiment and analysed the data. MSC designed the experiment. JP and MSC wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.



Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Park, J., Cha, M.S. Successive Multi-microdischarges Occurring in Pin-to-Line Geometry of Dielectric Barrier Discharge. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 43, 1435–1452 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-023-10357-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-023-10357-4