Abstract
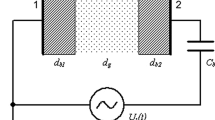
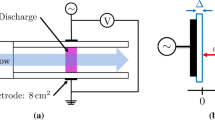
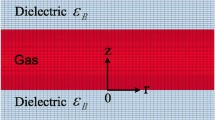
The asymmetric pulse-periodic dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) in a mixture of argon with sulfur vapor exhibits the emission spectrum of the discharge with intense bands of S2 molecules (B3Σ − > X3Σ transition) in the visible region. The modeling of the discharge characteristics in Ar–S2 mixture within the 1D fluid model is presented showing that during a voltage pulse (150 ns), an electropositive plasma is formed in the entire discharge gap with the electron number density reaching values above 1.5*1018 m−3 at the maximum under the mean electron energy of about 3 eV. The high electron number density during the current pulse leads to efficient excitation of sulfur dimers, as a result, their radiative efficiency during the voltage pulse reaches approximately 4%. The discharge is considered as promising one for creating radiation source in visible region of spectrum.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pollak J, Moisan M, Kéroack D, Boudam MK (2008) Low-temperature low-damage sterilization based on UV radiation through plasma immersion. J Phys D Appl Phys 41:135212
Lerouge S, Wertheimer MR, Yahia LH (2001) Plasma sterilization: a review of parameters, mechanisms, and limitations. Plasmas Polym 6(3):175–188
Erickstad M, Gutierrez E, Groisman A (2015) A low-cost low-maintenance ultraviolet lithography light source based on light-emitting diodes. Lab Chip 15:57
Flesch P (2006) Light and light sources: high-intensity discharge lamps. Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg
Gross U, Ubelis A, Spietz P, Burrows J (2000) Iodine and mercury resonance lamps for kinetics experiments and their spectra in the far ultraviolet. J Phys D Appl Phys 33:1588–1591
Lister GG, Lawler JE, Lapatovich WP, Godyak VA (2004) The physics of discharge lamps. Rev Mod Phys 76(2):541–598
Giuliani JL, Petrov GM, Apruzese JP, Davis J (2005) Non-local radiation transport via coupling constants for the radially inhomogeneous Hg–Ar positive column. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 14:236
Baeva M, Reiter D (2003) Monte carlo simulation of radiation trapping in Hg–Ar fluorescent discharge lamps. PCPP 23:371
Zalach J, Araoud Z, Charrada K, Franke S, Schoepp H, Zissis G (2011) Experimental and theoretical investigations on the warm-up of a high-pressure mercury discharge lamp. Phys Plasmas 18:033511
Dolan JT, Ury MG and Wood CH (1992) Novel high efficacy microwave powered light source. In: VIth international symposium on the science and technology of light sources, Budapest, Hungary
Childs AH, Schrenk WG (1976) Some characteristics of low pressure, sulfur, microwave-excited, electrodeless discharge lamps. Appl Spectroscopy 30(5):507–509
Turner BP, Ury MG, Leng Y, Love WG (1997) Sulfur lamps—progress in their development. J Illum Eng Soc 26(1):10–16
Aleksandrova OYu, Bondarenko SM, Guttsayt EM, Zhidkov RA (2013) Plasma lighting devices based on microwave discharge. T Comm Telecommun Transp 9:9–11
Van der Heijden H, Van der Mullen J, Baier J, Körber A (2002) Radiative transfer of a molecular S2 B-X spectrum using semiclassical and quantum-mechanical radiation coefficients. J Phys B At Mol Opt Phys 35(17):3633–3654
Johnston CW, Van der Heijden HWP, Janssen GM, Van Dijk J, Van der Mullen JJAM (2002) A self-consistent LTE model of a microwave-driven, high-pressure sulfur lamp. J Phys D Appl Phys 35:342–351
Gibson ND, Lawler JE (1996) A radiometric and electrical characterization of low pressure dc positive column sulfur discharges. J Appl Phys 79:86
Gibson ND, Kortshagen U, Lawler JE (1996) A radiometric investigation of low-pressure rf sulfur discharges. J Appl Phys 79:7523
Baële P, Bès A, Lacoste A, Pelletier J (2019) Sulfur: an alternative to mercury for UV emission in low-pressure low-power fluorescent discharges. J Phys D Appl Phys 52:32LT02
General AA, Kelman VA, Zhmenyak YuV, Zvenigorodsky VV (2016) Optical radiation of a gas discharge in an argon-sulfur mixture. J Appl Spectrosc 83:598–602
Avtaeva SV, Heneral AA (2020) The pulsed periodic discharge in mixtures of Ar with sulfur vapour. PCPP 40:839–855
Avtaeva S (2021) 1D model of the dielectric barrier discharge in Ar–S2 mixtures. PCPP 41:1059–1079
Avtaeva S, Heneral A (2022) Emission of chalcogens in the dielectric barrier discharge. In: Belarus M. (ed) Proceeding of the X Intern conference “plasma physics and plasma technology” (PPPT-10), Tarasenko NV, Nevar AA, Tarasenka NN, Usachonak MS. Minsk, Kovcheg, 251–254, Sept 12–16, 2022
Avtaeva S, Heneral A (2021) The pulse DBD in mixtures of argon with sulfur and selenium vapours. In: The 48th international conference on plasma science (Virtual ICOPS 2021), Nevada, Sept 12–16 2021
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Avtaeva, S. Modeling of the Sulfur Emission in the Asymmetric Pulse Dielectric Barrier Discharge. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 43, 867–877 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-023-10326-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-023-10326-x