Abstract
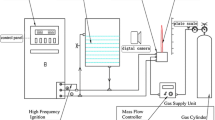
A novel direct current non-transferred arc plasma torch that can generate silent, stable and super-long laminar plasma jets in atmospheric air is investigated. The results showed that laminar plasma jets of length ranging from 100 to 720 mm in length can be generated by controlling the gas input rate ranging from 8.5 to 15 L min−1 and the output power from 8.5 to 28 kW. The length of the plasma jets generally increased with the output power and gas flow rate. Observations of temporal evolution of the plasma jet appearance and the voltage demonstrated that the jet is highly stable in the atmospheric environment. The fluid dynamic properties of the laminar plasma jet were studied using a numerical simulation incorporating a laminar flow model and an RNG turbulent flow model. Simulation results show the expansion of a high temperature region close to the torch nozzle exit, corresponding to a bright region observed in experiments.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C p :
-
Specific heat at constant pressure (J kg−1K−1)
- E :
-
Electric field (V m−1)
- T :
-
Temperature (K)
- W :
-
Power (W)
- I :
-
Current (A)
- Q :
-
Gas flow rate (kg s−1)
- k :
-
Turbulent kinetic energy (m2 s−2)
- ε :
-
Dissipation rate of turbulent kinetic energy (m2 s−3)
- ε r :
-
Net emission coefficient (W m−3sr−1)
- κ :
-
Thermal conductivity (W m−1K−1)
- μ :
-
Dynamic viscosity (kg m−1s−1)
- μ t :
-
Turbulent viscosity (kg m−1s−1)
- μ eff :
-
Effective viscosity (kg m−1s−1)
- σ :
-
Electrical conductivity (S m−1)
- ρ :
-
Density (kg m−3)
- ϕ :
-
Electric potential (V)
- LTE:
-
Local thermodynamic equilibrium
- RNG:
-
Renormalization group methods
- MHD:
-
Magnetohydrodynamic model
- NEC:
-
Net emission coefficient
References
Zhukov MF, Zasypkin IM (2006) Thermal plasma torches—design, characteristics, applications. Cambridge International Science Publishing, pp 1–15
Fauchais P (2004) Understanding plasma spraying. J Phys D Appl Phys 37(9):R86–R108. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/37/9/R02
Fauchais PL, Heberlein JVR, Boulos MI (2014) Thermal spray fundamentals. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-68991-3
Coudert JF, Rat V, Rigot D (2007) Influence of Helmholtz oscillations on arc voltage fluctuations in a dc plasma spraying torch. J Phys D Appl Phys 40(23):7357–7366. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/40/23/016
Nogues E, Vardelle M, Fauchais P, Granger P (2008) Arc voltage fluctuations: comparison between two plasma torch types. Surf Coat Technol 202(18):4387–4393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2008.04.014
An LT, Gao Y, Sun C (2011) Effects of anode arc root fluctuation on coating quality during plasma spraying. J Therm Spray Technol 20(4):775–781. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-011-9644-y
Janisson S, Vardelle A, Coudert JF, Fauchais P, Meillot E (1999) Analysis of the stability of dc plasma gun operating with Ar–He–H2, gas mixtures. Ann N Y Acad Sci 891(1):407–416
Solonenko OP (ed) (2003) Thermal plasma torches and technologies: plasma torches, basic studies and design. Cambridge international science publishing, pp 9–12
Solonenko OP, Nishiyama H, Smirnov AV, Takana H, Jang J (2014) Visualization of arc and plasma flow patterns for advanced material processing. J Vis 18:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-014-0221-6
Hideki Hamatani FW (2016) Development of laminar plasma shielded HF-ERW process—advanced welding process of HF-ERW 3. In: Proceedings of the 2012 9th international pipeline conference (pp 1–8)
Hamatani H, Ohara M, Fuji M (1999) Development of high power hybrid plasma spraying. J Japanese Inst Met 63(1):135–143. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10002548732/en/. (in Japanese)
Ma W, Pan WX, Wu CK (2005) Preliminary investigations on low-pressure laminar plasma spray processing. Surf Coat Technol 191(2–3):166–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2004.02.011
Ma W (2006) Influence of the processing conditions on the characteristics of the clad layers produced with laminar plasma technology. Appl Surf Sci 252(23):8352–8359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2005.11.043
Pan WX, Zhang W, Zhang W, Wu C (2001) Generation of long, laminar plasma jets at atmospheric pressure and effects of flow turbulence. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 21(1):23–35
Pan WX, Meng X et al (2008) Experimental observations on the stability and 3-D characteristics of laminar/turbulent plasma jets. J Eng Thermophys 29(1):2–4 (in Chinese)
Pan WX (2006) Arc voltage fluctuation in dc laminar and turbulent plasma jets generation. Plasma Sci Technol 416(4)
Meng X, Pan W, Chen X, Guo Z, Wu C (2011) Temperature measurements in a laminar plasma jet generated at reduced pressure. Vacuum 85(7):734–738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2010.11.007
Meng X, Pan WX, Wu CK (2004) Temperature and velocity measurement of laminar plasma jet. J Eng Thermophys 24(3):5–7 (in Chinese)
Meng X, Pan WX, Wu CK (2005) Transient measurement and analysis on heat flux distributions of partially-ionized high-temperature laminar flow jet. J Eng Thermophys 26(1):137–139 (in Chinese)
Cheng K, Chen X, Pan WX (2005) Efforts of shroud gas on laminar argon plasma jets impinging on a substrate in ambient air. J Eng Thermophys 26(6):1–3 (in Chinese)
Zhang WWX et al (1999) Modelling of laminar plasma jet impinging on a flat plate with approximate box relaxation method. Plasma Sci Technol 1:1
Wang HX, Xi C, Pan WX, Kai C (2007) Comparison of the characteristics of laminar and turbulent impinging plasma jets. J Eng Thermophys 28(4):7–9 (in Chinese)
Wang H-X, Chen X, Cheng K, Pan W (2007) Modeling study on the characteristics of laminar and turbulent argon plasma jets impinging normally upon a flat plate in ambient air. Int J Heat Mass Transf 50(3–4):734–745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2006.07.002
Cheng K, Chen X, Wang H-X, Pan W (2006) Modeling study of shrouding gas effects on a laminar argon plasma jet impinging upon a flat substrate in air surroundings. Thin Solid Films 506–507:724–728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2005.08.148
Pan WMX (2007) Comparative observation of Ar, Ar–H2 and Ar–N2 DC arc plasma jets and their arc root behaviour at reduced pressure. Plasma Sci Technol 9:2
Peng Y (2012) Numerical simulation study on flow fields in a non-transferred direct current plasma generator operating at reduced pressure. M. D. thesis, Institute of Mechanics, China Academy of Science
Xu DY (2003) Studies of long laminar plasma jet generation and characteristics. Ph.D. thesis, Tsinghua University
Wang Hai-Xing, Chen Xi, Pan Wenxia (2007) Modeling study on the entrainment of ambient air into subsonic laminar and turbulent argon plasma jets. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 27(2):141–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-006-9047-x
Wang H-X, Chen X, Pan W (2007) Effects of the length of a cylindrical solid shield on the entrainment of ambient air into turbulent and laminar impinging argon plasma jets. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 28(1):85–105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-007-9109-8
Xu D-Y, Chen X, Pan W (2005) Effects of natural convection on the characteristics of a long laminar argon plasma jet issuing horizontally into ambient air. Int J Heat Mass Transf 48(15):3253–3255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2005.02.039
Xu D-Y, Chen X, Cheng K (2003) Three-dimensional modelling of the characteristics of long laminar plasma jets with lateral injection of carrier gas and particulate matter. J Phys D Appl Phys 36(13):1583–1594
Huang H, Pan W, Guo Z, Wu C (2008) Laminar/turbulent plasma jets generated at reduced pressure. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 36(4):1052–1053
Duan Z, Heberlein J (2002) Arc instabilities in a plasma spray torch. J Therm Spray Technol 44–51
Liu SH, Li CX, Zhang SH et al (2018) A novel structure of YSZ coatings by atmospheric laminar plasma spraying technology. Scr Mater 153:73–76
Liu SH, Li CX et al (2018) Development of long laminar plasma jet on thermal spraying process: microstructures of zirconia coatings. Surf Coat Technol 337:241–249
Liu S-H, Li C-X, Murphy AB, Li CJ (2018) Numerical simulation of the flow characteristics inside a novel plasma spray torch. Plasma Chem Plasma Process (under review)
Mohanty P, Stanisic J, Stanisic J, George A, Wang Y (2010) A study on arc instability phenomena of an axial injection cathode plasma Torch. J Therm Spray Technol 19(1–2):465–475. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-009-9444-9
Osaki K, Fukumasa O, Kobayashi A (2000) High thermal efficiency-type laminar plasma jet generator for plasma processing. Vacuum 59:47–54
Solonenko OP, Zhukov MF (eds) (1994) Thermal plasma and new materials technology vol 1 investigation and design of thermal plasma generators. Cambridge Interscience Publishing, pp 5–43
Vilotijevic M, Dacic B, Bozic D (2009) Velocity and texture of a plasma jet created in a plasma torch with fixed minimal arc length. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 18(1):15016. https://doi.org/10.1088/0963-0252/18/1/015016
Wang JL (2015) Investments of mental rapid manufacturing by laminar plasma torch. University of Science and Technology of China, M.D. dissertation. (In Chinese)
ANSYS Inc. (2016) ANSYS fluent theory guide. USA
Cram LE (1985) Statistical evaluation of radiative power losses from thermal plasmas due to spectral lines. J Phys D Appl Phys 18(3):401–411. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/18/3/009
Murphy AB, Arundelli CJ (1994) Transport coefficients of argon, nitrogen, oxygen, argon-nitrogen, and argon-oxygen plasmas. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 14(4):451–490. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01570207
Boulos M, Fauchais P, Pfender E (1994) Thermal plasmas: fundamentals and applications. Springer
Pfender E, Fincke J, Spores R (1991) Entrainment of cold gas into thermal plasma jets. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 11(4):529–543
Murphy AB, Kovitya P (1993) Mathematical model and laser-scattering temperature measurements of a direct-current plasma torch discharging into air. J Appl Phys 73(10):4759–4769. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.353840
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Prof. Ren-zhong Huang from the Department of New Materials of Guangzhou Non-Ferrous Metal Research Institute for his selfless help with the computer programming. This work was supported by the Natural Key R&D Program of China (Basic Research Project, Grant No. 2017YFB0306104), the Ph.D. Short-term Academic Visiting Program of Graduate School of Xi’an Jiaotong University and National Ph.D. Degree Program of the China Scholarship Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, SH., Zhang, SL., Li, CX. et al. Generation of Long Laminar Plasma Jets: Experimental and Numerical Analyses. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 39, 377–394 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-018-9949-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-018-9949-4