Abstract
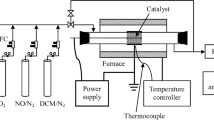
The emission of greenhouse gases, such as N2O and fluorinated gases, has been increasingly regulated in the semiconductor industry. Pressure effects on the abatement of N2O and CF4 were investigated in a low-pressure plasma reactor by using Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. The destruction and removal efficiency (DRE) of N2O and CF4 was significantly lowered below 0.2 Torr. When the pressure was increased, the DRE of CF4 with H2O as the reactant gas increased continuously, but that with O2 or without any reactant gas first increased and then decreased. A larger electrode length yielded a higher DRE of N2O and CF4, especially at lower pressures. To understand this phenomenon, the electrical waveforms for the discharge in N2O were analyzed in conjunction with its optical emission profiles, and the rotational temperatures for different electrode lengths were compared using the N2 + ion band (λ = 391.4 nm). They provided insights into the mechanism involved in terms of plasma property and gas residence time.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang MB, Chang JS (2006) Ind Eng Chem Res 45:4101
Liao MY, Wong K, McVittie JP, Saraswat KC (1999) J Vac Sci Technol B 17:2638
Xu XP, Rauf S, Kushner MJ (2000) J Vac Sci Technol A 18:213
Kiehbauch MW, Graves DB (2001) J Appl Phys 89:2047
Kuroki T, Mine J, Okubo M, Yamamoto T, Saeki N (2005) IEEE Trans Ind Appl 41:215
Kuroki T, Mine J, Odahara S, Okubo M, Yamamoto T, Saeki N (2005) IEEE Trans Ind Appl 41:221
Suzuki K, Ishihara Y, Sakoda K, Shirai Y, Teramoto A, Hirayama M, Ohmi T, Watanabe T, Ito T (2009) J Vac Sci Technol A 27:465
Hur M, Lee JO, Song YH (2011) J Korean Phys Soc 59:2742
Hur M, Lee JO, Song YH, Yoo HA (2012) J Vac Sci Technol A 30:021305
Hur M, Lee JO, Kang WS, Song YH (2015) Plasma Process Polym 12:583
Hartz CL, Beban JW, Jackson MW, Wofford BA (1998) Environ Sci Technol 32:682
Vitale SA, Sawin HH (2000) J Vac Sci Technol A 18:2217
Hur M, Lee JO, Kang WS, Song YH (2014) Plasma Chem Plasma Process 34:1187
Hur M, Lee JO, Lee JY, Kang WS, Song Y-H (2016) Plasma Sources Sci Technol 25:015008
Tonnis EJ, Graves DB (2002) J Vac Sci Technol A 20:1787
Cleland TA, Hess DW (1987) Plasma Chem Plasma Process 7:379
Austin JM, Smith ALS (1973) J Phys D Appl Phys 6:2236
Date L, Radouane K, Caquineau H, Despax B, Couderc JP, Yousfi M (1999) Surf Coat Technol 116–119:1042
Mi L, Xu P, Wang P-N (2005) J Phys D Appl Phys 38:3885
Huang X-J, Xin Y, Yang L, Yuan Q-H, Ning Z-Y (2008) Phys Plasmas 15:113504
Laux CO, Spence TG, Kruger CH, Zare RN (2003) Plasma Sources Sci Technol 12:125
Laux CO (2002) Radiation and nonequilibrium collisional-radiative models. In: Fletcher D, Charbonnier J-M, Sarma GSR, Magin T (eds) von Karman Institute Lecture Series 2002–07, Physico-chemical modeling of high enthalpy and plasma flows. Rhode-Saint-Genése, Belgium (www.specair-radication.net)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the World Class 300 Project funded by Korea Small and Medium Business Administration and by the Development program of Manufacturing Technology for Flexible Electronics with High Performance funded by Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (KIMM). The World Class 300 project has been performed in cooperation with Lotvacuum Co., Ltd.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hur, M., Lee, J.O., Lee, J.Y. et al. Effects of Pressure and Electrode Length on the Abatement of N2O and CF4 in a Low-Pressure Plasma Reactor. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 36, 1589–1601 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-016-9744-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-016-9744-z