Abstract
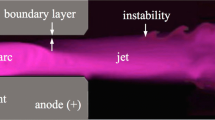
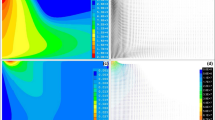
In most of the numerical approaches proposed for modeling high-intensity plasma-arcs, the effects of turbulence on the arc structure are often excluded because of the intricate physics originating from the interaction of turbulent scales, high-temperature gas dynamics, magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) and chemical kinetics. The goal of this study is threefold: to develop a generic turbulent MHD model to simulate free-burning arc discharges, to validate the code with available experimental data, and to investigate the effect of an external field and turbulent cross flow on the free-burning arc configuration. The governing equations are solved in conservative form using a hybrid scheme that combines a high-order monotonic upwind scheme with a second-order central scheme. The fluid and MHD turbulence are resolved using a large eddy simulation (LES) approach with a recently developed sub-grid closure model. An implicit scheme is used to compute the magnetic diffusion term appearing in the magnetic induction equation to alleviate the severe time-step constraint. The comparison of the model prediction with experimental data for Argon arcs at different current intensities shows generally good agreement. When an external field is applied, the overall shape of the free-burning arc drastically changes. The straightening of the arc indicates the potential for stabilization of a free-burning arc by magnetic forces. Even though the turbulence is significantly attenuated as a result of the thermal expansion near the cathode, it adds an unsteady characteristic to the arc and, in general, has a negative impact on the stabilization of the electrical discharge.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sanders N, Etmadi K, Hsu KC, Pfender E (1982) Studies of the anode region of a high-intensity argon arc. J Appl Phys 53(6):4136–4145
Girard R, Belhaouari JJ, Gonzalez JB, Gleizes A (1999) A two-temperature kinetic model of sf6 plasma. J Phys D Appl Phys 32(22):2890–2901
Hsu KC, Etemadi K, Pfender E (1983) Study of the free-burning high-intensity argon arc. J Appl Phys 54(3):1293–1301
Wu CS, Ushio M, Tanaka M (1996) Analysis of the tig welding arc behavior. Comput Mater Sci 7(3):308–314
Freton P, Gonzalez JJ, Gleizes A (2000) Comparison between a two- and a three-dimensional arc plasma configuration. J Phys D Appl Phys 33(19):2442–2452
Kelkar M, Heberlein J (2000) Physics of an arc in cross flow. J Phys D Appl Phys 33(17):2172–2182
Westhoff R, Szekely J (1991) A model of fluid, heat flow, and electromagnetic phenomena in a nontransferred arc plasma torch. J Appl Phys 70(7):3455–3466
Lago F, Gonzalez JJ, Freton P, Gleizes A (2004) A numerical modelling of an electric arc and its interaction with the anode: part i. The two-dimensional model. J Phys D Appl Phys 37(6):883–897
Gonzalez JJ, Lago F, Freton P, Masquere M, Franceries X (2005) Numerical modelling of an electric arc and its interaction with the anode: part ii. The three-dimensional model-influence of external forces on the arc column. J Phys D Appl Phys 38(2):306–318
Lago F, Gonzalez JJ, Freton P, Uhlig F, Lucius N, Piau GP (2006) A numerical modelling of an electric arc and its interaction with the anode: part iii. Application to the interaction of a lightning strike and an aircraft in flight. J Phys D Appl Phys 39(10):2294–2310
Bauchire JM, Gonzalez JJ, Gleizes A (1997) Modeling of a dc plasma torch in laminar and turbulent flow. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 17(4):409–432
Schlitz LZ, Garimella SV, Chan SH (1999) Gas dynamics and electromagnetic processes in high-current arc plasma: part ii. Effects of external magnetic fields and gassing materials. J Appl Phys 85(5):2546–2547
Speckhofer G, Schmidt HP (1996) Experimental and theoretical investigation of high-pressure arcs—part ii: the magnetically deflected arc (three-dimensional modeling). IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 24(4):1239–1248
Boulos MI, Fauchais P, Pfender E (1994) Thermal Plasma Fundamentals and Applications. Plenum, New York
Miki K, Schulz J, Menon S (2008) Large eddy simulation of equilibrium plasma-assisted combustion in supersonic flow. Proc Combust Inst 32(2):2413–2420
Miki K, Menon S (2008) Localized dynamic subgrid closure for simulation of MHD turbulence. Phys Plasmas 15(7):072306
Trelles JP, Chazelas C, Vardelle A, Heberlein JVR (2009) Arc plasma tourch modeling. J Them Spray Technol 18(5):728–752
Morel P, Banon Navarro A, Albercht-Marc M, Carati D, Merz F, Gorler T, Jenko F (2011) Gyrokinetic large eddy simulations. Phys Plasmas 18:072301
Kaziz S, Ben Ahmed H, Helali H, Gazzah H, Charrada K (2011) Contribution to the numerical study of turbulence in high intensity discharge lamps. Phys Plasmas 18:073502
Evans DL, Tankin RS (1967) Measurement of emission and absorption of radiation by an argon plasma. Phys Fluids 10:1137–1144
Miki K, Schulz J, Menon S (2007) Large eddy simulation of a supersonic plasma flow over a backward facing step. In: Proceedings of the 5th international symposium on turbulence and, shear flow phenomena, pp 985–990
Kim W–W, Menon S, Mongia HC (1999) Large-eddy simulation of a gas turbine combustor flow. Combust Sci Technol 143(1):25–62
Yoshizawa A, Hamba F (1988) A turbulent dynamo model for the reversed field pinches of plasma. Phys Plasmas 31(8):2276–2284
Brandt A (1977) Multi-level adaptive solutions to boundary value problems. Math Comput 31(138):333–390
Peaceman DC, Rachford HH (1955) The numerical solution of parabolic and elliptic differential equations. J Soc Ind Appl Math 3(1):28–41
Gabor T (2000) The ∇·b = 0 constraint in shock-capturing magnetohydrodynamic code. J Comput Phys 161(2):605–652
Brackbill JU, Barnes DC (1980) The effect of nonzero ∇·b = 0 on the numerical solution of the magnetohydrodynamic equations. J Comput Phys 35:426–430
Evans CR, Hawley JF (1988) Simulation of magnetohydrodynamic flows: a constrained transport method. Astrophys J 332:659–677
Miyoshi T, Kusano K (2005) A multi-state HLL approximate Riemann solver for ideal magnetohydrodynamics. J Comput Phys 208(1):315–344
Einfeldt B, Munz CD, Roe PL, Sjgreen B (1991) On godunov-type methods near low densities. J Comput Phys 92(2):273–295
Genin F, Menon S (2010) Studies of shock/turbulent shear later interaction using large-eddy simulation. Comput Fluid. doi:10.1016/j.compfluid.2009.12.008
Benenson DM, Baker AJ, Cenkner AA (1969) Diagnostics on steady-state cross-flow arcs. IEEE Trans Power Apparatus Syst 88(5):513–521
Bini R, Monno M, Boulos MI (2006) Numerical and experimental study of transferred arcs in argon. J Phys D Appl Phys 39(15):3253–3266
Menart J, Lin L (1999) Numerical study of a free-burning argon arc with copper contamination from the anode. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 19(2):153–170
Rogallo RS (1981) Numerical experiments in homogenous turbulence. Technical Memorandum, NASA-TM-81315
Blais A, Proulx P, Boulos MI (2001) Modeling of a dc transferred arc in presence of an external magnetic field. In: 15th ISPC, Orleans, vol 3, pp 1009–1014
Acknowledgments
This research is supported in part by DTRA grant and the second author was supported by the National Science Foundation under a Graduate Research Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miki, K., Schulz, J. & Menon, S. Large Eddy Simulation of a Free-Burning Arc Discharge in Argon with a Turbulent Cross Flow and External Field. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 33, 959–978 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-013-9468-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-013-9468-2