Abstract
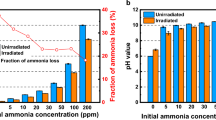
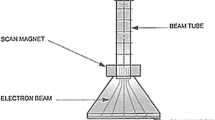
This study was carried out to determine the decomposition characteristics of ammonia using an electron beam (EB). Factors influencing these decomposition characteristics such as background gases (air, N2, O2, and He), initial ammonia concentration (50–150 ppm), relative humidity (0 or 90 %), and absorbed dose (1–15 kGy) were investigated. In the results of removal characteristics by different background gases, the decomposition efficiency of ammonia was lower (approximately 45 % at 5 kGy) when He was used as a background gas compared to the efficiencies when other background gases were selected. Ammonia removal efficiencies, when initial concentrations were 50 and 150 ppm, were 95 and 75 %, respectively, at 15 kGy. Ozone generation by EB irradiation increased from 2.5 kGy and reached a maximum of 45 ppm when 5 kGy of the absorbed dose was irradiated. However, ozone generation started to decrease when the absorbed dose exceeded 5 kGy and decreased to 0.27 ppm at 15 kGy.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yasuda T, Kuroda K, Fukumoto Y, Hanajima D, Suzuki K (2009) Evaluation of full-scale biofilter with rockwool mixture treating ammonia gas from livestock manure compositing. Bioresour Technol 100:1568–1572
Xia L, Huang L, Shu X, Zhang R, Dong W, Hou H (2008) Removal of ammonia from gas stream with dielectric barrier discharge plasma. J Hazard Mater 152:113–119
Hasegawa T, Sato M (1998) Study of ammonia removal from coal-gasified fuel. Combust Flame 114:246–258
McCulloch RB, Few GS, Murray GC, Aneja VP (1998) Analysis of ammonia, ammonium aerosols and acid gases in the atmosphere at a commercial hog farm in eastern North Carolina, USA. Environ Pollut 102:263–268
Hobbs PJ, Misselbrook TH, Pain BF (1996) Characterisation of odorous compounds and emissions from slurries produced from weaner pigs fed dry feed and liquid diets. J Sci Food Agric 73:437–445
Luo C, Zender CS, Bian H, Metzger S (2007) Role of ammonia chemistry and coarse mode aerosols in global climatological inorganic aerosol distributions. Atmos Environ 41:2510–2533
Baek BH, Aneja VP, Tong Q (2004) Chemical coupling between ammonia, acid gases, and fine particles. Environ Pollut 129:89–98
Chang MB, Tseng TD (1996) Gas-phase removal of H2S and NH3 with dielectric barrier discharges. J Environ Eng 122:41–46
Son YS, Kim KJ, Kim JC (2010) A review on VOCs control technology using electron beam. AJAE 4–2:63–71
Kim NJ, Sugano Y, Hirai M, Shoda M (2000) Removal of a high load of ammonia gas by a marine bacterium, Vibrio alginolyticus. J Biosci Bioeng 90(4):410–415
Chaichanawong J, Tanthapanichakoon W, Charinpanitkul T, Eiad-ua A, Sano N, Tamon H (2005) High-temperature simultaneous removal of acetaldehyde and ammonia gases using corona discharge. Sci Technol Adv Mater 6:319–324
Tanthapanichakoon W, Charinpanitkul T, Chaiyo S, Dhattavorn N, Chaichanawoug J, Sano N, Tamon H (2004) Effect of oxygen and water vapor on the removal of styrene and ammonia from nitrogen by non-pulse corona-discharge at elevated temperatures. Chem Eng J 97:213–223
Kim JC (2002) Factors affecting aromatic VOC removal by electron beam treatment. Radiat Phys Chem 65:429–435
Hirota K, Matzing H, Paur HR, Woletz K (1995) Analyses of products formed by electron beam treatment of VOC/air mixtures. Radiat Phys Chem 45:649–655
Son YS, Park KN, Kim JC (2010) Control factors and by-products during decomposition of butane in electron beam irradiation. Radiat Phys Chem 79:1255–1258
Sun Y, Chmielewski AG (2012) Organic pollutants treatment from air using electron beam generated nonthermal plasma—overview. In: Puzyn T, Mostrag-Szlichtyng A (eds) Organic pollutants ten years after the Stockholm convention—environmental and analytical update. InTech
Son YS, Son YS, Park JH, Kim P, Kim JC (2012) Oxidation of gaseous styrene by electron beam irradiation. Radiat Phys Chem 81:686–692
Han DH, Stuchinskaya T, Won YS, Park WS, Lim JK (2003) Oxidative decomposition of aromatic hydrocarbons by electron beam irradiation. Radiat Phys Chem 67:51–60
Son YS, Kim KJ, Kim JC (2010) Comparison of the decomposition characteristics of aromatic VOCs using an electron beam hybrid system. Radiat Phys Chem 79:1270–1274
Hakoda T, Yang M, Hirota K, Hashimoto S (1998) Decomposition of volatile organic in air by electron beam and gamma ray irradiation. J Adv Oxid Technol 3:79–86
Woods RJ, Pilaev AK (1994) Applied radiation chemistry: radiation processing. Wiley, New York
Paur RH, Matzing H, Woletz K (1991) Removal of volatile organic compounds from industrial offgas by irradiation induced aerosol formation. J Aerosol Sci 22:S509–S512
Ruan J, Li W, Shi Y, Nie Y, Wang X, Tan T (2005) Decomposition of simulated odors in municipal wastewater treatment plants by a wire-plate pulse corona reactor. Chemosphere 59:327–333
Jogan K, Mizuno A, Yamamoto T, Chang JS (1993) The effect of residence time on the CO2 reduction from combustion flue gases by an AC ferroelectric packed bed reactor. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 29:876–881
Wójtowicz MA, Miknis FP, Grimes RW, Smith WW, Serio MA (2000) Control of nitric oxide, nitrous oxide, and ammonia emissions using microwave plasmas. J Hazard Mater 74:81–89
Kogelschatz U (2003) Dielectric barrier discharge: their history, discharge physics, and industrial applications. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 23:2003
Mätzing H (1991) Chemical kinetics of flue gas cleaning by irradiation with electrons. In: Prigogine I, Rice SA (eds) Advances in chemical physics, vol LXXX. Wiley, New York, pp 315–402
Melton CE (1966) Study by mass spectrometry of the decomposition of ammonia by ionizing radiation in a wide-range radiolysis source. J Chem Phys 45:4414–4424
Prasad SS, Huntress WT Jr (1980) A model for gas phase chemistry in interstellar clouds: I. The basic model, library of chemical reactions, and chemistry among C, N, and O compounds. ApJS 43:1–35
Lesclaux R (1984) Reactivity and kinetic properties of the NH2 radical in the gas phase. Rev Chem Intermediat 5:347–392
Dransfeld P, Hack W, Kurzke H, Temps F, Wagner HG (1985) Direct studies of elementary reactions of NH2-radicals in the gas phase. Symp Int Combust 20:655–663
Miller JA, Smooke MD, Green RM, Kee RJ (1983) Kinetic modeling of the oxidation of ammonia in flames. Combust Sci Technol 34:149–176
Hack W, Horie O, Wagner HG (1981) The rate of the reaction of NH2 with O3. Ber Bunsenges Phys Chem 85:72–78
Hack W, Kurzke H (1985) The reaction of NH2-radicals with electronically excited molecular oxygen O2 (1 Δ g ). Ber Bunsenges Phys Chem 89:86–93
Hack W, Kurzke H, Wagner HG (1985) Reaction of NH (X3∑−) and O2 (1 Δ g ) in the gas phase. J Chem Soc Farad Trans 2(81):949–961
Baulch DL, Drysdale DD, Horne DG (1983) Evaluated kinetic data for high temperature reactions, vol 2. Butterworths, London
Brune WH, Schwab JJ, Anderson J (1983) Laser magnetic resonance, resonance fluorescence and resonance absorption studies of the reaction kinetics of O + OH → H + O2, O + HO2 → OH + O2, N + OH → H + NO and N + HO2 → products at 300 K between 1 and 5 torr. J Phys Chem 87:4503–4515
Cohen N (1987) The O + NH3 reaction: a review. Int J Chem Kinet 19:319–362
Dean AM, Hard JE, Lyon RK (1982) Kinetics and mechanism of NH3 oxidation. Symp Int Combust 19:97–105
Pagsberg PB, Eriksen J, Christensen HC (1979) Pulse radiolysis of gaseous ammonia–oxygen mixtures. J Phys Chem 83:582–590
Schofield K (1979) Critically evaluated rate constants for gaseous reactions of several electronically excited species. J Phys Chem Ref Data 8:723–763
Dransfeld P, Wagner HG (1987) Investigation of the gas phase reaction N + NH2 → N2 + 2H at room temperature. J Phys Chem NF 153:89–97
Ma HB, Chen P, Ruan R (2001) H2S and NH3 removal by silent discharge plasma and ozone combo-system. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 21:611–624
Ravi V, Young SM, Rakamolanth BS (2003) Temperature effect on hydrocarbon-enhanced nitric oxide conversion using a dielectric barrier discharge reactor. Fuel Process Technol 81:187–199
Li RN, Liu X (2000) Main fundamental gas reactions in denitrification and desulfurization from flue gas by non-thermal plasmas. Chem Eng Sci 55:2491–2506
Harrison JA, Whyte AR, Phillips LF (1986) Kinetics of reactions of NH with NO and NO2. Chem Phys Lett 129:346–352
Graham RA, Johnston HS (1978) The photochemistry of NO3 and the kinetics of the N2O5–O3 system. J Phys Chem 82:254–268
Howard CJ (1980) Kinetic study of the equilibrium HO2 + NO ⇌ OH + NO2 and the thermochemistry of HO2. J Am Chem Soc 102:6937–6941
Bulatov VP, Ioffe AA, Lozovsky VA, Sarkisov OM (1989) On the reaction of the NH2 radical with NO2 at 295–620 K. Chem Phys Lett 159:171–174
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2012R1A6A3A03039668). This work was also supported by the Hi-Seoul Science (Humanities) Fellowship from the Seoul Scholarship Foundation and the Korean Ministry of Environment as part of “The Eco-Technopia 21 Project”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Son, YS., Kim, KH., Kim, KJ. et al. Ammonia Decomposition Using Electron Beam. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 33, 617–629 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-013-9444-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-013-9444-x