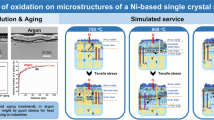
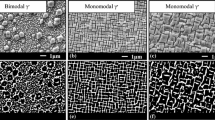
Abstract
In situ environmental transmission electron microscopy has previously been applied to traditional alloys and has been verified as a powerful tool for studying oxidation mechanisms. Single-crystal Ni-based superalloys are often used for commercial turbine blades, especially 1st- to 3rd-generation superalloys. The reactivity to oxidation of the single-crystal Ni-based superalloys was the main factor in deciding their bulk oxidation resistance. An overall study on different generations of various Re-containing Ni-based superalloys was conducted in this study to compare their difference in oxidation properties using an in situ technique. Nanoscale structural and elemental distributions across the γ/γ′ interface were assessed on three typical 1st- to 3rd-generation superalloys via modern electron microscopy. Oxidation at the γ/γ′ interface was systematically analysed by an in situ oxidation process in an environmental transmission electron microscope to reveal the nanoscale oxidation mechanisms and the roles of key elements. Preferential oxidation of the γ/γ′ interface is revealed in oxidation mechanisms. Aggregation of Cr and Re in the γ/γ′ interfaces of the 0Re and 7Re alloys induced a larger lattice misfit and a corresponding stress, which prompted priority oxidation at the interface. Key factors, including alloy elements and microstructures, are extracted, and this technique is expected to be applicable to more materials.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. S. Nalwa, Handbook of Surfaces and Interfaces of Materials. in Handbook of Surfaces and Interfaces of Materials, ed. H. S. Nalwa (Academic Press, Burlington, 2001), pp. xxv–xxviii.
Y. Yu, Principles of Metallurgy, (Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, 2000).
R. E. Smallman and A. H. W. Ngan, Chapter 4 - Introduction to Dislocations. in Modern Physical Metallurgy, 8th ed, eds. R. E. Smallman and A. H. W. Ngan (Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2014), pp. 121–158.
Q. Pan, J. Tong, and M. Tian, Fundamentals of Material Science, (Tsinghua University Press, Beijing, 2011).
H. Over and A. P. Seitsonen, Science 297, 2002 (2003).
L. Li, L. Luo, J. Ciston, W. A. Saidi, E. A. Stach, J. C. Yang, and G. Zhou, Physical Review Letters 113, 2014 136104.
R. C. Reed, The Superalloy Fundamentals and Applications, (Cambridge University Press & Mechanical Industry Press, London, 2016).
K. Kumar, R. Sankarasubramanian, and U. V. Waghmare, Computational Materials Science 97, 2015 (26).
F. Forghani, J. Moon, J. C. Han, R. Rahimi, R. Abbaschian, C. G. Park, H. S. Kim, and M. Nili-Ahmadabadi, Materials Characterization 153, 2019 (284).
A. B. Parsa, P. Wollgramm, H. Buck, A. Kostka, C. Somsen, A. Dlouhy, and G. Eggeler, Acta Materialia 90, 2015 (105).
H. S. Kitaguchi, M. P. Moody, H. Y. Li, H. E. Evans, M. C. Hardy, and S. Lozano-Perez, Scripta Materialia 97, 2015 (41).
S. Sanyal, U. V. Waghmare, P. R. Subramanian, and M. F. X. Gigliotti, Scripta Materialia 63, 2010 (391).
Y. X. Wu, X. Y. Li, and Y. M. Wang, Acta Materialia 55, 2007 (4845).
F. S. Pettit, G. H. Meier, and N. Birks, Introduction to the High Temperature Oxidation of Metals, 2nd ed (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2006),.
A. Akhtar, S. Hegde, and R. C. Reed, JOM 58, 2006 (37).
J. D. Ramsay, H. E. Evans, D. J. Child, M. P. Taylor, and M. C. Hardy, Corrosion Science 154, 2019 (277).
X. Sun, L. Zhang, Y. Pan, X. Wang, Z. Huang, and L. Jiang, Corrosion Science 154, 2019 108216.
S. Cruchley, H. Evans, and M. Taylor, Materials at High Temperatures 33, 2016 (465).
S. R. Hegde, High temperature oxidation behaviour of the single crystal superalloy CMSX-10. in Materials Engineering, (The University of British Columnbia, Columnbia, 2005), p. 58.
C. M. Younes, G. C. Allen, and J. A. Nicholson, Science and Technology 42, 2007 (80).
L. Wang, Y. Zhang, Z. Zeng, H. Zhou, J. He, P. Liu, M. Chen, J. Han, D. J. Srolovitz, J. Teng, Y. Guo, G. Yang, D. Kong, E. Ma, Y. Hu, B. Yin, X. Huang, Z. Zhang, T. Zhu, and X. Han, Science 375, 2022 (1261–1265).
S. Sun, D. Li, C. Yang, L. Fu, D. Kong, Y. Lu, Y. Guo, D. Liu, P. Guan, Z. Zhang, J. Chen, W. Ming, L. Wang, and X. Han, Phys. Rev. Lett. 128, 2022 015701.
T. W. Hansen, Controlled Atmosphere Transmission Electron Microscopy Principles and Practice, (Springer, Berlin, 2016).
R. Sharma, Journal of Materials Research 20, 2005 (1695).
H. Yoshida, Y. Kuwauchi, J. R. Jinschek, K. Sun, S. Tanaka, M. Kohyama, S. Shimada, M. Haruta, and S. Takeda, Science 20, 2012 (317).
L. Luo, L. Zou, D. K. Schreiber, D. R. Baer, S. M. Bruemmer, G. Zhou, and C.-M. Wang, Scripta Materialia 114, 2016 (129).
X. Fang, J. Zhang, Y. Zhao, Z. Yang, J. Xu, Q. Wu, H. Jiang, and Y. Luo, Materials for Mechanical Engineering 42, 2018 (33).
J. Zhang, Y. Li, X. Li, Y. Zhai, Q. Zhang, D. Ma, S. Mao, Q. Deng, Z. Li, X. Li, X. Wang, Y. Liu, Z. Zhang, and X. Han, Nature Communications 12, 2021 (2218).
K. Sohlberg, T. J. Pennycook, W. Zhou, and S. J. Pennycook, Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 17, 2015 (3982).
D. B. Williams and C. B. Carter, Transmission Electron Microscopy—A Textbook for Materials Science, 2nd ed (Springer, Berlin, 2009),.
R. F. Egerton, Electron Energy-Loss Spectroscopy in the Electron Microscope, 3 Edition (Springer, Boston, MA, 2011),.
Z. Chen, T. Dong, W. Qu, Y. Ru, H. Zhang, Y. Pei, S. Gong, and S. Li, Corrosion Science 156, 2019 (161).
J. X. Chang, D. Wang, G. Zhang, L. H. Lou, and J. Zhang, Corrosion Science 117, 2017 (35).
M. Solecka, A. Radziszewska, and B. Rutkowski, Corrosion Science 149, 2019 (244).
C. M. F. Rae and R. C. Reed, Acta Materialia 49, 2001 (4113).
B. Seiser, R. Drautz, and D. G. Pettifor, Acta Materialia 59, 2011 (749).
Y. Zhai, Y. Chen, Y. Zhao, H. Long, X. Li, Q. Deng, H. Lu, X. Yang, G. Yang, W. Li, L. Yang, S. Mao, Z. Zhang, A. Li, and X. Han, Acta Materialia 215, 2021 (116991).
N. B. Pilling and R. E. Bedworth, J. Inst. Metals 29, 1923 (529).
Y. Chen, W. Zhang, Y. Zhao, Y. Zhai, B. Zhang, H. Lu, G. Yang, L. Yang, and A. Li, Scripta Materialia 203, 2021 114106.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 91860202, 51988101, 51872008), the “111” Project under the DB18015 grant and Beijing Outstanding Young Scientists Projects (BJJWZYJH01201910005018). The authors thank Dr. Dongchang Wu from Thermofisher Scientific Shanghai Nanoport for useful discussion and assistance with the Titan-ETEM and Titan-Themis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Qiao, S., Zhao, Y. et al. In Situ Oxidation in Ni-Based Single-Crystal Superalloys with Varying Re Contents Observed by Environmental Transmission Electron Microscopy. Oxid Met 98, 399–414 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-022-10128-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-022-10128-0