Abstract
Biomass combustion for electric energy production is associated with corrosion. The formation of unwanted deposits on heat-exchanger surfaces with significant concentrations of alkaline species of K and Na, as well as S and Cl, are the cause. Modern biomass power plants operate at temperatures that exceed those where corrosion is not so severe. At high temperatures, molten salts deposits increase the corrosion rate. Molten sulfates are the most common cause of molten-salt corrosion, as they can dissolve the protective oxide layer, even on stainless steels alloys. Active oxidation occurs in an oxidizing environment in the presence of chlorine (KCl or NaCl) at high temperatures. Molten chlorinated compounds have great influence despite the fact that the melting temperature of KCl (s) is 774 °C, since this compound together with other substances forms eutectics at much lower temperatures that increase the corrosion rate. The high corrosiveness of biomass requires the use of more resistant steels and proposals are made for the most effective alloys. Aditionally, to reduce the effect of alkalis and chlorides, variants are analysed as co-combustion with biomass less loaded in alkalis and chlorides, the addition of sulphur compounds to convert the chlorides of low melting point into sulfates of higher melting point; the pretreatment by leaching of the biomass to reduce compounds that compromise its use or to include solutions in the design of the plants that prevent the arrival of corrosive compounds to the superheater.


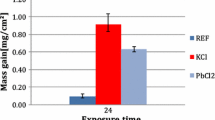
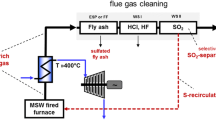
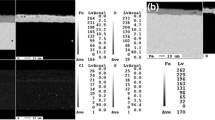
Source modified from [1]
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Berlanga-Labari, J. Fernández-Carrasquilla, Revisión sobre la corrosión de tubos sobrecalentadores en plantas de biomasa. Revista de Metalurgia, 42(4): 299–317 (2006).
Á. Rubio-González, P. Galindo, F. Pérez, et al., Estudio sobre ele empleo de los residuos agrícolas cañeros como combustibles para la generación de electricidad en la industria azucarera. Libro Editorial Feijóo. ISBN 978–959–312–384–6; ISBN 10: 959–312–384–9, (2019).
R. Muelas Gamo, Recubrimientos resistentes a los fenómenos de degradación en las nuevas turbinas generadoras de energía por vapor de agua. . Tesis Doctoral. Universidad Complutense de Madrid. Programa de Doctorado Ciencia y Tecnología de Materiales. Madrid, 2015. PDF 29 Mb. Última modificación: 13 Dic 2018. Código ID: 36549., 2015., (2018).
J. M. Johansen, J. G. Jakobsen, F. J. Frandsen, and P. Glarborg, Release of K, Cl, and S during pyrolysis and combustion of high-chlorine biomass. J Energy Fuels 25, (11), 2011 (4961–4971).
S.C. Lith, F. J. Frandsen, M. Montgomery, T. Vilhelmsen, S. A. Jensen, Lab-scale Investigation of Deposit-induced Chlorine Corrosion of Superheater Materials under Simulated Biomass-firing Conditions. Part 1: Exposure at 560 °C. . Energy & Fuels 23: 3457–3468, (2009).
R. Viswanathan, W. Bakker, International Joint Power Generation conference in Materials for boilers in ultra supercritical power plants. Miami Beach: ASME., (2000).
W. B. A. Sharp, Superheater corrosion in biomass boilers. Today’s Science and Technology. 2010, 2010 (3).
M. Spigel, H. P. Gabke, Salt melt induced corrosion of metallic materials in waste incineration plants. . J Materials corrosion, 50(7): p. 373–393. (1999).
K. H. Tostmann, Ursachen und Vermeidung, (Wiley-VCH, Korrosion, 2001).
P. Gellings and K. H. Tostmann, Korrosion und Korrosionsschutz von Metallen, (Carl Hanser Verlag, Einführung, München, Germany, 1981).
S. Retschitzegger, High-temperature corrosion in biomass-fired fixed bed boilers. Doctoral Thesis. Graz University of Technology, (2017).
A. Rubio-González, B. Martínez, M. A. Rubio Rodríguez, Programa cubano para el máximo aprovechamiento de la biomasa cañera para la generación de electricidad. Revista ATAC. 79(1): 4–11, (2018).
B. Melissari, Ash related problems with high alkalii biomass and its mitigation-Experimental evaluation. Memoria Investigaciones en Ingeniería 12, 2014 (31–44).
K. Woytiuk, Sugar cane trash processing for heat and power production. Master Thesis. Lulea University of Technology. 2006, 2006 (57).
A. M. Rubio-González, Generadores de vapor. Funcionamiento y explotación. . Editorial Feijóo. Santa Clara. Cuba. ISBN 979–959–312–128–6, (2015).
H. P. Nielsen, F. J. Frandsen, K. Dam-Johansen, and L. L. Baxter, The implications of chlorine-associated corrosion on the operation of biomass-fired boilers. Progress in energy combustion science 26, (3), 2000 (283–298).
M. S. Bashir, P. A. Jensen, F. Frandsen, et al., Suspension-firing of biomass. Part 1: Full-scale measurements of ash deposit build-up. . J Energy, 26(4): 2317–2330. (2012).
H. P. Nielsen, L. L. Baxter, G. Sclippab et al., Deposition of potassium salts on heat transfer surfaces in straw-fired boilers: a pilot-scale study. . J Fuel. 79(2): 131–139, (2000).
P. Kofstad, High temperature corrosion. J Elsevier Applied Science Publishers, Crown House, Linton Road, Barking, Essex IG 11 8 JU, UK (1988).
R. A. Rapp, Hot corrosion of materials: a fluxing mechanism? . J Corrosion Science, 44(2):. 209–221, (2002).
J. R. Keiser, S. Sharp, M. Singh et al., Improving heat recovery in biomass-fired boilers Oak Ridge National Laboratory, U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Information Bridge., (2013).
H. P. Michelsen, F. Frandsen, K. Dam-Johansen, and O. H. Larsen, Deposition and high temperature corrosion in a 10 MW straw fired boiler. Fuel Processing Technology 54, (1998), 1998 (95–108).
K. N. Strafford, P. K. Datta, and G. Forster, High-temperature chloridation of binary Fe-Cr alloys at 1000° C. J Materials Science Engineering: A 1989, (120–121), 1989 (61–68).
J. Pettersson, N. Folkeson, L. G. Johansson, J. E. Svensson, The effects of KCl, K 2 SO 4 and K 2 CO 3 on the high temperature corrosion of a 304-type austenitic stainless steel. J Oxidation of metals, 76(1): 93–109. (2011).
I. Gogolev, T. Pikkarainen, J. Kauppinen et al., Investigation of biomass alkali release in a dual circulating fluidized bed chemical looping combustion system. J Fuel, 297: 120743, (2021).
M. K. Hossain, R. J. Saunders, Oxid. Met..12: 1–22 (1978).
R. C. John High Temperature Corrosion in Energy Systems. J AIME , EE. UU, p. 501 (1984).
H. J. Grabke, E. Reese, M. Spiegel, The effects of chlorides, hydrogen chloride, and sulfur dioxide in the oxidation of steels below deposits. . J Corrosion science, 37(7): 1023–1043. (1995).
C. C. Tsaur, J. C. Rock, C. J. Wang, Y. H. Su, The hot corrosion of 310 stainless steel with pre-coated NaCl/Na2SO4 mixtures at 750 ºC. . J Materials Chemistry Physics, 89(2–3): 445–453., (2005).
F. Wang, Y. Shu, Influence of Cr content on the corrosion of Fe–Cr alloys: the synergistic effect of NaCl and water vapor. J Oxidation of Metals, 59(3–4): 201–214, (2003).
C. J. Wang, Y. C. Chang, NaCl-induced hot corrosion of Fe–Mn–Al–C alloys.. J Materials Chemistry Physics, 76(2): 151–161, (2002).
Y. Shinata, F. Takahashi, and K. Hashiura, NaCl induced hot corrosion of stainless steels. Mater Sci. Eng. 1987, (87), 1987 (399–405).
K. Gotthjaelp, P. Bronsted, P. A. Jansen, et al., High Temperature Corrosion in Biomass Incineration Plants,. . Project nº 1323/95–0008, University Technologycal of Denmark, (1996).
A. J. B. Cutler, W.D. Halstead, J. W. Laxton, C. G. Stevens, The role of chloride in the corrosion caused by flue gases and their deposits. . J. Eng. Power. 93(3): 307–312., (1971).
M. Spiegel, H. P. Grabke, Incineration Industrial and Municipal Waste. R.W. Bryers (Eds), Nueva York, EE.UU., pp 758., (1978).
S. C. Okoro, M. Montgomery, F. J. Frandsen, and K. Pantleon, High temperature corrosion under laboratory conditions simulating biomass-firing: a comprehensive characterization of corrosion products. J Energy Fuels 26, (1), 2014 (380–390).
P. D. Miller, H. H. Kravse, D. A. Vaughan, and W. K. Boyd, The mechanism in high temperature corrosion in municipal incinerators. Corrosion 28, (7), 1972 (274–282).
D.A. Vaughan, H. H. Krause, W. D. Boyd, Proc. International Conference of Ash Deposits and Corrosion from impurities from combustion gases, Henniker, New Hampshier, EE.UU., pp. 473., (1997).
A. Mlonka-Mędrala, K. Gołombek, P. Buk, et al., The influence of potassium-rich biomass ashes on steel corrosion above 550° C. J Energy Conversion Management 2019, (187), 2019 (15–28).
A. Karlsson, P. J. Møller, V. Johansen, Iron and steel corrosion in a system of O2, SO2 and alkali chloride. The formation of low melting point salt mixtures. Corrosion science, 30(2–3): 153–158, (1990).
A. J. B. Cuttler, E. Raask, External corrosion in coal-fired boiler: assessment fron laboratory data. . Corros., 21 (11): 789–800, (1981).
J. Zhang, Z. Rahman, X. Wang et al., , Hot corrosion behaviors of TP347H and HR3C stainless steel with KCl deposit in oxy-biomass combustion. . J Journal of environmental management, 263: 110411, (2020).
C. Berlanga-Labari, J. Fernández Carrasquilla, Estudio de la oxidación a elevada temperatura de ocho aleaciones en atmósferas de combustión de biomasa. . J. Revista de Metalurgia 44(4): 343–354. (2008).
P. A. Jensen, F. J. Frandsen, J. Hansen, et al., SEM investigation of superheater deposits from biomassfired boilers. J Energy Fuels, 18(2):378–384., (2004).
Y. Laxminarayan, A. B. Nair, P. A. Jensen, et al., Tensile adhesion strength of biomass ash deposits: effect of the temperature gradient and ash chemistry. . J Energy Fuels, 32(4): 4432–4441. (2018).
Y. Laxminarayan, P. A. Jensen, H. Wu, F. Jappe Frandsen, B. Sander, and P. Glarborg, Deposit Shedding in Biomass-Fired Boilers: Shear Adhesion Strength Measurements. Energy and Fuels 31, (8), 2017 (8733–8741).
A. Zbogar, F. Frandsen, P. A. Jensen, P. Glarborg, Shedding of ash deposits. . J Progress in energy combustion science, 35(1): 31–56 (2009).
H. Zhou, P. A. Jensen, F. J. Frandsen, Dynamic mechanistic model of superheater deposit growth and shedding in a biomass fired grate boiler. . J Fuel, 86(10–11): 1519–1533, (2007).
A. Zahs, M. Spiegel, H. J. Grabke, Chloridation and oxidation of iron, chromium, nickel and their alloys in chloridizing and oxidizing atmospheres at 400–700°C. . Corrosion Science. 42(6): 1093–1122 (2000).
A. Zahs, M. Spiegel, and H. J. Grabke, The influence of alloying elements on the chlorine-induced high temperature corrosion of Fe-Cr alloys in oxidizing atmospheres. Materials and Corrosion 1999, (50), 1999 (561–578).
J. Eklund, A. Persdotter, I. Hanif, S. Bigdeli, T. Jonsson, Secondary corrosion protection of FeCr(Al) model alloys at 600ºC – The influence of Cr and Al after breakaway corrosion. Corrosion Science 189: 109584, (2021).
H. Asteman, K. Segerdahl, J. E. Svensson et al., Oxidation of stainless steel in H2O/O2 environments–Role of chromium evaporation. in Materials Science Forum. Swizerland: Trans Tech Publ Ltd., (2004).
H. Asteman, J. E. Svensson, L. G. Johansson, M. Norell, Indication of chromium oxide hydroxide evaporation during oxidation of 304L at 873 K in the presence of 10% water vapor. J Oxidation of Metals, 52(1): 95–111, (1999).
J. Pettersson, H. Asteman, J. E. Svensson, L. G. Johansson, KCl induced corrosion of a 304-type austenitic stainless steel at 600ºC; the role of potassium. . J Oxidation of Metals, 64(1): 23–41 (2005).
M. Oksa, P. Auerkari, J. Salonen, and T. Varis, Nickel-based HVOF coatings promoting high temperature corrosion resistance of biomass-fired power plant boilers. J Fuel processing technology 2014, (125), 2014 (236–245).
A. Agüero, I. Baráibara, M. Gutiérrez, et al., Biomass corrosion behavior of steels and coatings in contact with KCl/K2SO4 at 550 °C under an oxy-fuel combustion atmosphere: A screening laboratory test. Surface & Coatings Technology 2018, (350), 2018 (188–200).
H. Gada, D. Mudgal, S. Parvez, B. Ahmad, Investigation of High Temperature Corrosion Resistance of Ni25Cr Coated and Bare 347H SS in Actual Husk Fired Boiler Atmosphere. Engineering Failure Analysis., (2019).
D. Fantozzi, V. Matikainen, M. Uusitalo, H. Koivuluoto, and P. Vuoristo, Chlorine-induced high temperature corrosion of Inconel 625 sprayed coatings deposited with different thermal spray techniques. J Surface Coatings Technology 2017, (318), 2017 (233–243).
E. Sadeghimereshta, L. Reddy, T. Hussain, N. Markocsana, and Sh. Joshia, Chlorine-induced high temperature corrosion of HVAF-sprayed Ni-based alumina and chromia forming coatings. Corrosion Science 2018, (132), 2018 (170–184).
S. Karlsson, L. E. Åmand, and J. Liske, Reducing high-temperature corrosion on high-alloyed stainless steel superheaters by co-combustion of municipal sewage sludge in a fluidised bed boiler. J Fuel 2015, (139), 2015 (482–493).
D. Paz, J. Phother, S. Andersson, and T. Jonsson, High temperature corrosion memory in a waste fired boiler. Influence of sulfur. Waste Management. 130, (30–37), 2021 (2021).
R. Antunes and M. Olivera, Corrosion in biomass combustion: A materials selection analysis and its interaction with corrosion mechanisms and mitigation strategies. J Corrosion Science 2013, (76), 2013 (6–26).
M. Broström, H. Kassman, A. Helgesson, et al., Sulfation of corrosive alkali chlorides by ammonium sulfate in a biomass fired CFB boiler. Fuel Processing Technology 2007, (88), 2007 (1171–1177).
D. Mudgal, S. Singh, S. Prakash, Corrosion problems in incinerators and biomass-fuel-fired boilers. Internat. Journal of Corr., p. 14 pages, Article ID505306., (2014).
P. Viklund, Superheater corrosion in biomass and waste fired boilers Characterisation, causes and prevention of chlorine-induced corrosion Doctoral Thesis Copyright © Peter Viklund, 2013, TRITA-CHE Report 2013:7 KTH Royal Institute of Technology. Division of Surface and Corrosion Science. Stockholm Sweden., (2013).
B. Coda, M. Aho, R. Berger, K.R.G. Hein, Behavior of chlorine and enrichment of risky elements in bubbling fluidized bed combustion of biomass and waste assisted by additives. Energy Fuels, 15(3): 680–690. (2001).
N. Henriksen, R. Blum, and O. H. Larsen, Investigations of the possibilities of influencing the corrosive environment in an external ash cooler. International Flame Research Foundation, Livorno. 2003, 2003 (271–294).
K. O. Davidsson, B. M. Steenari, D. Eskilsson, Kaolin addition during biomass combustion in a 35MW circulating fluidized bed boiler. Energy Fuels, 21 (4), 1959–1966, (2007).
N. Israelsson, K. Hellström, J. E. Svensson, L. G. Johansson, KCl induced corrosion of the FeCrAl alloy Kanthal AF at 600° C and the effect of H2O. . J of Metals, 2015. 83(1): p. 1–27., (2015).
S. Kiamehr, K.V. Dahl, M. Montgomery, M. A.J. K. Somers, Cl‐ induced high temperature corrosion of selected commercial alloys: Part I: chromia‐ formers. . J Materials Corrosion, 2015. 66(12): p. 1414–1429., (2015).
S. C. Okoro, M. Montgomery, F. J. Frandsen, and K. Pantleon, Influence of preoxidation on high temperature corrosion of a Ni-based alloy under conditions relevant to biomass firing. J Surface Coatings Technology 2017, (319), 2017 (76–87).
P. Viklund, A. Hjörnhede, P. Henderson, A. Stålenheim, and R. Pettersson, Corrosion of superheater materials in a waste-to-energy plant. J Fuel Processing Technology 2013, (105), 2013 (106–112).
Q. Liu, Pretreatment and Posttreatment Approaches for Reducing Biomass Inorganic Impurities during Gasification. . Master Thesis in the University of Tennessee. (2017).
A. Mlonka-Mędrala, K.. Gołombek, P. Buk, E. Cieślik, W. Nowak, The influence of KCl on biomass ash melting behaviour and high-temperature corrosion of low-alloy steel. J. Energy, 2019. 188: p. 116062., (2019).
A. A. Bhuiyan and J. Naser, Numerical modeling of biomass Co–combustion with pulverized coal in a small scale furnace. J Procedia Engineering 2015, (105), 2015 (504–511).
A.A. Bhuiyan, J. Naser, Computational Modelling of Biomass Co-firing and Slag Formation under Air/Oxy-fuel Combustion in Furnaces. Thesis. 2016, Swinburne University of Technology Australia., (2016).
Funding
This research was supported by the “National Program of Development of the Agroindustry of Sugar Cane” In the proyect “Evaluation of alternatives for the increment of sugar cane agriculture residues in cogeneration with bagaze as fuel in biomass boilers”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are not conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lariot-Sánchez, C., Rivas-Gutierrez, A., Rodríguez-Machín, L. et al. Impact of Alkalis and Chlorides from Sugarcane Agriculture Residues on High Temperature Corrosion: A Review. Oxid Met 97, 451–475 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-022-10102-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-022-10102-w