Abstract
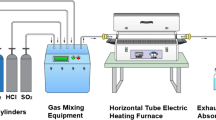
In this study, high temperature reactions of Fe–Cr alloys at 500 and 600 °C were investigated using an atmosphere of N2–O2 8 vol% with 220 vppm HCl, 360 vppm H2O and 200 vppm SO2; moreover the following aggressive salts were placed in the inlet: KCl and ZnCl2. The salts were placed in the inlet to promote corrosion and increase the chemical reaction. These salts were applied to the alloys via discontinuous exposures. The corrosion products were characterized using thermo-gravimetric analysis, scanning electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction.The species identified in the corrosion products were: Cr2O3, Cr2O (Fe0.6Cr0.4)2O3, K2CrO4, (Cr, Fe)2O3, Fe–Cr, KCl, ZnCl2, FeOOH, σ-FeCrMo and Fe2O3. The presence of Mo, Al and Si was not significant and there was no evidence of chemical reaction of these elements. The most active elements were the Fe and Cr in the metal base. The Cr presence was beneficial against corrosion; this element decelerated the corrosion process due to the formation of protective oxide scales over the surfaces exposed at 500 °C and even more notable at 600 °C; as it was observed in the thermo-gravimetric analysis increasing mass loss. The steel with the best performance was alloy Fe9Cr3AlSi3Mo, due to the effect of the protective oxides inclusive in presence of the aggressive salts.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Spiegel, Materials Science Forum 971, 369 (2001).
E. Reese and H. J. Grabke, Materials and Corrosion 43, 547 (1992).
E. Reese and H. J. Grabke, Materials and Corrosion 44, 41 (1993).
T. Jonsson, et al., Oxidation Metal 72, 213 (2009).
M. Spiegel, Materials and Corrosion 51, (5), 303 (2000).
L.-G. Johansson, et al., Critical Corrosion Phenomena on Super-heaters in Biomass and Waste-Fired Boilers. In Proceedings of Sino-Swedish Structural Materials Symposium (2007), pp. 35–39.
Y. Kawahara, H. Hagiwara, M. Nakamura, E. Shibuya, and K. Yukawa, Paper No. 564, CORROSIONl95 (NACE International, Houston, TX, 1995).
M. Sánchez-Pastén and M. Spiegel, Materials and Corrosion 57, (2), 192 (2006).
M. Danielewski, Gaseous Corrosion Mechanisms, Corrosion: Fundamentals, Testing, and Protection, ASM Handbook, vol. 13A, (ASM International, Materials Park, 2003), pp. 106–114.
J. Pettersson, et al., Oxidation of Metals 72, 159 (2009).
S. Karlsson, et al., Oxidation of Metals 78, 83 (2012).
Andreas Ruh and Michael Spiegel, Corrosion Science 48, 679 (2006).
W. M. Lu, T. J. Pan and Y. N. Zhang, Corrosion Science 50, 1900 (2008).
Y. S. Li, et al., Corrosion Science 49, 1799 (2007).
Y. S. Li, et al., Materials Chemistry and Physics 93, 217 (2005).
Acknowledgments
The present authors wish to express gratitude to their institutions: Instituto Politécnico Nacional (IPN), Instituto Tecnológico Autónomo de México (ITAM), Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACyT) for technical and assisted support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alcántara-Cárdenas, J.A., Ramirez-Lopez, A., Chávez-Alcalá, J.F. et al. Evaluation of High Temperature Corrosion in Simulated Waste Incinerator Environments. Oxid Met 85, 611–627 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-016-9615-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-016-9615-2