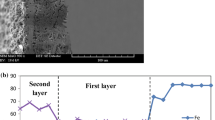
Abstract
Chromium vaporisation from chromia-forming alloys when exposed to high temperatures can deteriorate the protective property of oxide scale. This problem affects the lifetime of solid oxide fuel cells and solid oxide electrolysers using chromia-forming alloys as interconnectors. In this work, AISI 441, a commercial grade stainless steel which chromium vaporisation investigation has not been reported so far, was chosen for study. Chromium vaporisation rates of bare AISI 441 and AISI 430 and AISI 441 and AISI 430 coated with Mn–Co spinel by electroplating method were measured in an atmosphere of 5 % H2O in O2 over the temperature range of 650–900 °C with the linear velocity of the humidified oxygen stream varied in the range of 0.8–3.0 cm s−1. For uncoated samples, AISI 441 showed a lower chromium vaporisation rate in comparison with that of AISI 430. Mn–Co spinel coating could reduce the chromium vaporisation rate from AISI 430 surface. However, on the contrary, the Mn–Co spinel coating could not only fail to suppress the chromium vaporisation, but it also promoted the chromium vaporisation from AISI 441 surface by 2 times.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Caplan and M. Cohen, Journal of the Electrochemical Society 108, 438 (1961).
G. C. Fryburg, R. A. Miller, F. J. Kohl and C. A. Stearns, Journal of the Electrochemical Society 124, 1738 (1977).
B. B. Ebbinghaus, Combustion and Flame 93, 119 (1993).
E. J. Opila, D. L. Mayers, N. S. Jacobson, I. M. B. Nielsen, D. F. Johnson, J. K. Olminsky and M. D. Allendorf, Journal of Physical Chemistry A 2007, (111), 1971 (2007).
C. Gindorf, L. Singheiser and K. Hilpert, Steel Research International 72, 528 (2001).
W. J. Quadakkers, J. Piron-Abellan, V. Shemet and L. Singheiser, Materials at High Temperatures 20, 115 (2003).
Z. Yang, K. S. Weil, D. M. Paxton and J. W. Stevenson, Journal of the Electrochemical Society 150, A1188 (2003).
M. Stanislowski, E. Wessel, K. Hilpert, T. Markus and L. Singheiser, Journal of the Electrochemical Society 154, A295 (2007).
H. Kurokawa, C. P. Jacobson, L. C. DeJonghe and S. J. Visco, Solid State Ionics 178, 287 (2007).
X. Chen, P. Y. Hou, C. P. Jacobson, S. J. Visco and L. C. D. Jonghe, Solid State Ionics 176, 425 (2005).
Z. Yang, G.-G. Xia, J. W. Stevenson and X.-H. Li, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 32, 3648 (2007).
J. Wu, C. D. Johnson, R. S. Gemmen and X. Liu, Journal of Power Sources 189, 1106 (2009).
Z. H. Bi, J. H. Zhu and J. L. Batey, Journal of Power Sources 195, 3605 (2010).
S. Chandra-Ambhorn, Y. Wouters, L. Antoni, F. Toscan and A. Galerie, Journal of Power Sources 171, 688 (2007).
J. Wu, Y. Jiang, C. Johnson and X. Liu, Journal of Power Sources 177, 376 (2008).
D. J. Young and B. A. Pint, Oxidation of Metals 66, 137 (2006).
R. B. Bird, W. E. Stewart and E. N. Lightfoot, Transport Phenomena, 2nd ed, (Wiley, New York, 2007).
A. Restovic, E. Ríos, S. Barbato, J. Ortiz and J. L. Gautier, Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry 522, 141 (2002).
E. Ríos, H. Reyes, J. Ortiz and J. L. Gautier, Electrochimica Acta 50, 2705 (2005).
T. Brylewski, M. Nanko, T. Maruyama and K. Przybylski, Solid State Ionics 143, 131 (2001).
H. Kurokawa, K. Kawamura and T. Maruyama, Solid State Ionics 168, 13 (2004).
P. Jian, L. Jian, H. Bing and G. Xie, Journal of Power Sources 158, 354 (2006).
S. Chandra-Ambhorn, “Reactivity and Surface Modification of Stainless Steels Used as Electric Interconnectors in High Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cells”, Ph.D. Thesis. Institut National Polytechnique de, Grenoble, (2006).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank SIMaP Laboratory, Grenoble Institute of Technology, Grenoble, France for supplying AISI 441 specimens. This research was sponsored by Faculty of Engineering, King Mongkut’s Institute of Technology Ladkrabang, Thailand.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wongpromrat, W., Thaikan, H., Chandra-ambhorn, W. et al. Chromium Vaporisation from AISI 441 Stainless Steel Oxidised in Humidified Oxygen. Oxid Met 79, 529–540 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-013-9379-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-013-9379-x