Abstract
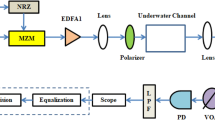
In this paper, a novel architecture of bidirectional underwater wireless optical communication (UWOC) system has been proposed to interconnect stationary and moving underwater sensor nodes for diverse applications. To achieve the bidirectional communication, wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) and remodulation approach have been used in this work. The proposed bidirectional UWOC system works at 40 Gbps data rate for both downlink (stationary node to moving node) and uplink (moving node to stationary node). Two distinct wavelengths of 532 nm and 531 nm have been used for uplink and downlink, the main attraction of the proposed architecture is that both the laser sources are placed at the stationary node. The moving node do not have any laser source and it remodulates the signal for sending data back to the stationary node. Because of this, the moving node contains lesser components which results in cost effectiveness, low power requirement and light weight. The proposed system successfully transmits the bidirectional information at a link range of 40 m under pure sea conditions in the presence of distinctive air bubble populations. The observed bit error rate (BER) values are 1.89 × 10− 13 and 1.19 × 10− 04 for the downlink and uplink respectively at a link range of 40 m, these BER values are under the acceptable forward error correction (FEC = 2 × 10− 3) limit. The proposed bidirectional UWOC system is beneficial for the development of a high-speed last-mile underwater solution.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chi, Y.-C., Hsieh, D.-H., Tsai, C.-T., Chen, H.-Y., Kuo, H.-C., Lin, G.-R.: 450-nm GaN laser diode enables high-speed visible light communication with 9-Gbps QAM-OFDM, opt. Express. 23, 13051 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1364/oe.23.013051
Cochenour, B.M., Mullen, L.J., Member, S., Laux, A.E.: Characterization of the Beam-Spread function for underwater Wireless Optical communications Links. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 33, 513–521 (2008)
Gabriel, C., Khalighi, M., Bourennane, S., Léon, P., Rigaud, V.: Monte-Carlo-Based Channel characterization for underwater Optical Communication systems. J. OPT. COMMUN. NETW. 5, 1–12 (2013)
Huang, X.-H., Lu, H.-H., Chang, P.-S., Liu, C.-X., Lin, Y.-Y., Ko, T., Chen, Y.-T.: Bidirectional White-Lighting WDM VLC–UWOC converged systems. J. Light Technol. 39, 4351–4359 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/JLT.2021.3073395
Johnson, B.D., Cooke, R.C.: Bubble populations and spectra in coastal waters: A photographic approach. J. Geophys. Res. 84, 3761 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1029/jc084ic07p03761
Kaushal, H., Kaddoum, G.: Underwater optical wireless communication. IEEE Access. 4, 1518–1547 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2552538
Li, Y., Leeson, M.S., Li, X.: Impulse response modeling for underwater optical wireless channels. Appl. Opt. 57, 4815 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1364/ao.57.004815
Li, J., Yang, B., Ye, D., Wang, L., Fu, K., Piao, J., Wang, Y., Real-Time, A.: Full-duplex system for underwater Wireless Optical Communication: Hardware structure and Optical Link Model. IEEE Access. 8, 109372–109387 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3001213
Liu, X., Yi, S., Zhou, X., Fang, Z., Qiu, Z.-J., Hu, L., Cong, C., Zheng, L., Liu, R., Tian, P.: 34.5 m underwater optical wireless communication with 2.70 gbps data rate based on a green laser diode with NRZ-OOK modulation. Opt. Express. 25, 27937–27947 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.25.027937
Medwin, H.: Situ acoustic measurements of bubble populations in Coastal Ocean Waters. J. Geophys. Res. 75, 599–611 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1029/jc075i003p00599
Oubei, H.M., Zedini, E., ElAfandy, R.T., Kammoun, A., Abdallah, M., Ng, T.K., Hamdi, M., Alouini, M.-S., Ooi, B.S.: Simple statistical channel model for weak temperature-induced turbulence in underwater wireless optical communication systems. Opt. Lett. 42, 2455 (2017a). https://doi.org/10.1364/ol.42.002455
Oubei, H.M., Zedini, E., Elafandy, R.T., Kammoun, A., Ng, T.K., Alouini, M.S., Ooi, B.S.: Efficient Weibull channel model for salinity induced turbulent underwater wireless optical communications, 2017b Opto-Electronics Commun. Conf. OECC 2017 Photonics Glob. Conf. PGC 2017 2017-Novem 1–2. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/OECC.2017.8115010
Saeed, N., Celik, A., Al-Naffouri, T.Y., Alouini, M.S.: Underwater optical wireless communications, networking, and localization: A survey. Ad Hoc Netw. 94, 1–40 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adhoc.2019.101935
Singh, M., Singh, H.G., Singh, M.L.: A study of attenuation models for underwater FSO link. J. Adv. Res. Dyn. Control Syst. 10, 2066–2073 (2018)
Singh, M., Singh, M.L., Singh, G., Gill, H.S.: Statistical channel model for underwater wireless optical communication system under a wide range of air bubble populations. Opt. Eng. 60 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1117/1.oe.60.3.036111
Tang, S., Dong, Y., Zhang, X.: Impulse response modeling for underwater wireless optical communication links. IEEE Trans. Commun. 62, 226–234 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCOMM.2013.120713.130199
Tsonev, D., Chun, H., Rajbhandari, S., McKendry, J.J.D., Videv, S., Gu, E., Haji, M., Watson, S., Kelly, A.E., Faulkner, G., Dawson, M.D., Haas, H., O’Brien, D.: A 3-Gb/s single-LED OFDM-based wireless VLC link using a gallium nitride µ LED. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 26, 637–640 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/LPT.2013.2297621
Vali, Z., Gholami, A., Ghassemlooy, Z., Michelson, D.G., Omoomi, M., Noori, H.: Modeling turbulence in underwater wireless optical communications based on Monte Carlo simulation. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A. 38, 1130 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1364/josaa.434087
Wei, Z., Mu, X., Fu, H.: Wearable Full-duplex Digital Transceiver for Underwater Optical Wireless Communications, in: CLEO Pacific Rim Conf. Optica Publishing Group, 2018: p. W3A.153. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1364/CLEOPR.2018.W3A.153
Yang, X., Tong, Z., Dai, Y., Chen, X., Zhang, H., Zou, H., Xu, J.: 100 m full-duplex underwater wireless optical communication based on blue and green lasers and high sensitivity detectors. Opt. Commun. 498, 127261 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2021.127261
Zhou, H., Zhang, M., Wang, X., Ren, X.: Design and implementation of more than 50m real-time underwater Wireless Optical Communication System. J. Light Technol. 40, 3654–3668 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/JLT.2022.3153177
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study, conception and design. Mandeep Singh, Gurpreet Kaur and Ramandeep Kaur wrote the main manuscript. Rajandeep Singh, Simranjit Singh and Mandeep Singh simulated the simulation setup. Ramandeep Kaur and Maninder Lal Singh reviewed the paper and gave technical suggestions regarding interpretation of data. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, M., Singh, M.L., Singh, R. et al. A novel bi-directional communication approach for moving underwater sensor nodes in the turbulent water channel. Opt Quant Electron 56, 943 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-024-06780-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-024-06780-2