Abstract
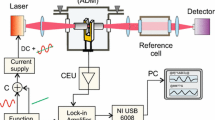
This work describes a quartz-tuning-fork enhanced photo-thermal spectroscopic (QEPTS) based gas sensors technique. A highly resonant quartz tuning fork with the capability for improved mechanical repetition has been used to boost the photo-thermal sensitivity for detecting in contrast to commonly used heat-sensitive components.The approach described in this study differs from typical QEPTS in that it uses two QTF to detect an acoustic wave generated by the first QTF as an outcome of vibrations brought on by the photo-thermoelastic action. By preventing the QTF from being exposed to laser radiation, this passive decoding by acoustic monitoring could reduce noise and improve detection capability. The development and verification of four distinct sensing combinations. The targeted gases are decided to be acetylene at a mass fraction of 1.95 percent. The numerical simulation step involves creating a simulation of the acoustic field created by the first QTF oscillating in an attempt to elucidate the modification tendency of noise and signal in the subsequnt QTF. In comparison to the conventional QEPTS, according to the limited data, the ‘Signal to Noise Ratio’ was increased by a factor of 1.37 as a result of this method. It is suggested that such technology be further enhanced.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abouelregal, A.E., Marin, M., Askar, S.: Thermo-optical mechanical waves in a rotating solid semiconductor sphere using the improved Green-Naghdi III model. Mathematics 9(22), 2902 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/math9222902
Ando, T., et al.: High-speed AFM and nano-visualization of biomolecular processes. Pflüg. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 456(1), 211–225 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-007-0406-0
Chen, Z., et al.: 3D printing technique-improved phase-sensitive OTDR for breakdown discharge detection of gas-insulated switchgear. Sensors 20(4), 1045 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/s20041045
Chen, H., Shi, R., Zhang, T.: Nanostructured photothermal materials for environmental and catalytic applications. Molecules 26(24), 7552 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26247552
Duan, W., et al.: A laser-based multipass absorption sensor for sub-PPM detection of methane, acetylene and ammonia. Sensors 22(2), 556 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/s22020556
Lang, Z., Qiao, S., He, Y., Ma, Y.: Quartz tuning fork-based demodulation of an acoustic signal induced by photo-thermo-elastic energy conversion. Photoacoustics 22, 100272 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pacs.2021.100272
Li, H., Han, W., Wang, C., Zhao, Y., Li, X., Zhang, J.: Modeling and optimization of tuning fork densitometer detector based on velocity comprehensive evaluation index. Measurement 198, 111274 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2022.111274
Liang, T., Qiao, S., Lang, Z., Ma, Y.: Highly sensitive trace gas detection based on in-plane single-quartz-enhanced dual spectroscopy. Sensors 22(3), 1035 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/s22031035
Lou, C., et al.: Graphene oxide and polydimethylsiloxane coated quartz tuning fork for improved sensitive near- and mid-infrared detection. Opt. Express 29(13), 20190 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.428003
Ma, Y., et al.: Quartz tuning forks resonance frequency matching for laser spectroscopy sensing. Photoacoustics 25, 100329 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pacs.2022.100329
Munk, D., et al.: Surface acoustic wave photonic devices in silicon on insulator. Nat. Commun. 10(1), 4214 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12157-x
Nasr, M.E., Abouelregal, A.E.: Light absorption process in a semiconductor infinite body with a cylindrical cavity via a novel photo-thermoelastic MGT model. Arch. Appl. Mech. 92(5), 1529–1549 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-022-02128-y
Peng, X., et al.: Accuracy improvement in plastics classification by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy based on a residual network. Opt. Express 29(21), 33269 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.438331
Qiao, S., Ma, Y., He, Y., Patimisco, P., Sampaolo, A., Spagnolo, V.: Ppt level carbon monoxide detection based on light-induced thermoelastic spectroscopy exploring custom quartz tuning forks and a mid-infrared QCL. Opt. Express 29(16), 25100 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.434128
Qiao, Y., et al.: Sensitivity enhanced NIR photoacoustic CO detection with SF6 promoting vibrational to translational relaxation process. Photoacoustics 25, 100334 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pacs.2022.100334
Ramesh, S., et al.: Optimization of solar hybrid power generation using conductance-fuzzy dual-mode control method. Int. J. Photoenergy 2022, 7756261 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/7756261
Ramkumar, G., et al.: A novel approach in hybrid energy storage system for maximizing solar PV energy penetration in microgrid. Int. J. Photoenergy 2022, 3559837 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/3559837
Rousseau, R., Maurin, N., Trzpil, W., Bahriz, M., Vicet, A.: Quartz tuning fork resonance tracking and application in quartz enhanced photoacoustics spectroscopy. Sensors 19(24), 5565 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/s19245565
Rust, H.-P., Heyde, M., Freund, H.-J.: Signal electronics for an atomic force microscope equipped with a double quartz tuning fork sensor. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 77(4), 043710 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2194490
Shui, C., Huang, J., Liu, H., Cai, W., Sanders, S.T.: Tomographic absorption spectroscopy based on dictionary learning. Opt. Express 29(22), 36400 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.440709
Wei, T., Wu, H., Dong, L., Tittel, F.: Acoustic detection module design of a quartz-enhanced photoacoustic sensor. Sensors 19(5), 1093 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/s19051093
Wu, Z., et al.: The model analysis of a complex tuning fork probe and its application in bimodal atomic force microscopy. Appl. Sci. 7(2), 121 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/app7020121
Yang, S., Qiao, S., Liu, X., Ma, Y.: Highly sensitive measurement of oxygen concentration based on reflector-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy. Sensors 22(14), 5087 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/s22145087
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful to the Researchers Supporting Project Number (RSPD2023R955), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MT: Investigation, methodology, writing—review and editing. TMA: Conceptualization, formal analysis, writing—review and editing. RPG: Conceptualization, formal analysis, writing—original draft writing—review and editing RN: Conceptualization, writing—review and editing. GR: Writing—review and editing. YSU: Formal analysis, writing—review and editing. MZA: Formal analysis, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tamilselvi, M., Amirthalakshmi, T.M., Guru, R.P. et al. Demodulating an acoustic signal stimulated by photo-thermal elastic energy conversion using quartz tuning forks. Opt Quant Electron 56, 69 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-05673-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-05673-0