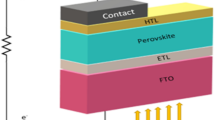
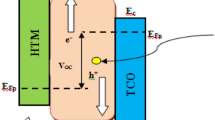
Abstract
Fill factor (FF) deficit and stability is a primary concern and challenge with the perovskite solar cell. The band alignment and resistance at the junction interface further decreases the fill factor and thus limits the performance of the device. Moreover, degradation of the intrinsic properties of the upcoming perovskite material such as methylammonium lead halide on exposure to ambience or moisture creates instability and decreases the shelf life of the device. To overcome all these challenges, we have engineered the device structure and introduces an earth-abundant material in the primitive perovskite structure by introducing an inorganic hole transport layer (HTL). It was observed from the calculation that the FF is sensitive to the band offset values. Moreover, the band alignment/band offset role and effect at the Perovskite/HTL junction were investigated. It is evident from the calculation that the inorganic material replacing Spiro-MeOTAD can enhance the stability of the device by providing insulation from ambient. The efficiency of SnS and spiro-MeOTAD were found to be comparable in the present work and thus the shelf life and moisture sensitivity challenge of the perovskite solar cell is addressed. Moreover, this work paves the way for earth-abundant p-type chalcogenides tin selenide (SnS) as a HTL layer in the perovskite solar cell.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altermatt, P.P., Kiesewetter, T., Ellmer, K., Tributsch, H.: Specifying targets of future research in photovoltaic devices containing pyrite ðFeS2 Þ by numerical modeling. Solar Energy Mater. Solar Cells 71, 181–195 (2002)
Burgelman, M., Nollet, P., Degrave, S.: Modelling polycrystalline semiconductor solar cells. Thin Solid Films 361–362, 527–532 (2000)
Burton, A., Colombara, D., Abellon, R.D., Grozema, F.C., Peter, L.M., Savenije, T.J., Dennler, G., Walsh, A.: Synthesis, characterization, and electronic structure of single crystal SnS, Sn2S3, and SnS2 L. Chem. Mater. 25, 4908–4916 (2013)
Casas, G.A., Cappelletti, M.A., Cedola, A.P., Soucase, B.M., y Blanca, E.L.P.: Analysis of the power conversion efficiency of perovskite solar cells with different materials as hole-transport layer by numerical simulations. Superlattices Microstruct. 107, 136–143 (2017)
De Angelis, A.D., Christian Kemp, K., Gaillard, N., Kim, K.S.: Antimony (III) sulfide thin films as a photoanode material in photocatalytic water splitting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 8445–8451 (2016)
Dhingra, P., Singh, P., Rana, P.J.S., Garg, A., Kar, P.: Hole-transporting materials for perovskite-sensitized solar cells. Energy Technol. 4, 891–938 (2016)
Gokmen, T., Gunawan, O., Mitzi, D.B.: Minority carrier diffusion length extraction in Cu2ZnSn(Se, S)4 solar cells. J Appl Phys 114, 114511 (2013)
Green, M.A., Emery, K., Hishikawa, Y., Warta, W., Dunlop, E.D., Levi, D.H., Ho-Baillie, A.W.Y.: Solar cell efficiency tables (version 49). Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 25, 3–13 (2017)
Hossain, M.I., Alharbi, F.H., Tabet, N.: Copper oxide as inorganic hole transport material for lead halide perovskite based solar cells. Sol. Energy 120, 370–380 (2015)
Hwang, I., Jeong, I., Lee, J., Ko, M.J., Yong, K.: Enhancing stability of perovskite solar cells to moisture by the facile hydrophobic passivation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 17330–17336 (2015)
Kumar, A.: Efficiency enhancement of CZTS solar cells using structural engineering. Superlattices Microstruct. 153, 106872 (2021a)
Kumar, A.: Numerical modelling of ion-migration caused hysteresis in perovskite solar cells. Opt. Quant. Electron. 53, 1–9 (2021b)
Kumar, A., Ranjan, P.: Impact of light soaking on absorber and buffer layer in thin film solar cells. Appl. Phys. A 126, 1–8 (2020)
Kumar, A., Ranjan, P.: Defects signature in VOC characterization of thin-film solar cells. Sol. Energy 220, 35–42 (2021)
Kumar, A.: Impact of selenium composition variation in CZTS solar cell. Optik 234, 166421 (2021)
Lim, Y., Ok, Y.W., Tark, S.J., Kang, Y., Kim, D.: Electrical contact properties of Cu2S nanowires grown vertically on Cu foil by gas–solid reaction. Curr. Appl. Physi. 9, 890–893 (2009)
Lv, M., Zhu, J., Huang, Y., Li, Y., Shao, Z., Xu, Y., Dai, S.: Colloidal CuInS2 quantum dots as inorganic hole-transporting material in perovskite solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 17482–17488 (2015)
Mattheis, J., Werner, J.H., Rau, U.: Finite mobility effects on the radiative efficiency limit of pn-junction solar cells. Phys Rev B 77, 085203 (2008)
Minemoto, T., Murata, M.: Impact of work function of back contact of perovskite solar cells without hole transport material analyzed by device simulation. Curr. Appl. Phys. 14, 1428–1433 (2014)
Minemoto, T., Murata, M.: Theoretical analysis on effect of band offsets in perovskite solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 133, 8–14 (2015)
Mitzi, D.B., Gunawan, O., Todorov, T.K., Barkhouse, D.A.R.: Prospects and performance limitations for Cu–Zn–Sn–S–Se photovoltaic technology. Philos. Trans. r. Soc. A 371, 20110432 (2013)
Popov, P.A., Fedorov, P.P., Kuznetsov, S.V.: Thermal conductivity of FeS2 pyrite crystals in the temperature range 50–300 K. Crystallogr. Rep. 58, 319–321 (2013)
Qin, P., Tanaka, S., Ito, S., Tetreault, N., Manabe, K., Nishino, H., Nazeeruddin, M.K., Gratzel, M.: Inorganic hole conductor-based lead halide perovskite solar cells with 12.4% conversion efficiency. Nat. Commun. 5, 1–6 (2014)
Rached, D., Mostefaoui, R.: Influence of the front contact barrier height on the Indium Tin Oxide/hydrogenated p-doped amorphous silicon heterojunction solar cells. Thin Solid Films 516, 5087–5092 (2008)
Rau, U., Schock, H.W.: Electronic properties of Cu(In, Ga)Se2 heterojunction solar cells–recent achievements, current understanding, and future challenges. Appl. Phys. A 69, 131–147 (1999)
Shin, B., Gunawan, O., Zhu, Y., Bojarczuk, N.A., Chey, S.J., Guha, S.: Thin film solar cell with 8.4% power conversion efficiency using an earth-abundant Cu2ZnSnS4 absorber. Prog. Photovolt: Res. Appl. 21, 72–76 (2013)
Skelton, J.M., Jackson, A.J., Dimitrievska, M., Wallace, S.K., Walsh, A.: Vibrational spectra and lattice thermal conductivity of kesterite-structured Cu2ZnSnS4 and Cu2ZnSnSe4. APL Mater. 3(4), 041102 (2015)
Tang, Y.Q., Ge, Z.G., Feng, J.: Synthesis and thermoelectric properties of copper sulfides via solution phase methods and spark plasma sintering. Crystals. 7(5), 141 (2017)
Wang, D., Wright, M., Elumalai, N.K., Uddin, A.: Stability of perovskite solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 147, 255–275 (2016)
Wei, L., Chen, J., He, Q., Teng, W.: Study of lattice thermal conductivity of PbS. J. Alloys Compd. 584, 381–384 (2014)
Wu, Q., Xue, C., Li, Y., Zhou, P., Liu, W., Zhu, J., Dai, S., Zhu, C., Yang, S.: Kesterite Cu2ZnSnS4 as a low-cost inorganic hole-transporting material for high-efficiency perovskite solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 28466–28473 (2015)
Xu, L., Deng, L., Cao, J., Wang, X., Chen, W., Jiang, Z.: Solution-processed Cu(In, Ga)(S, Se)2, nanocrystal as inorganic hole-transporting material for efficient and stable perovskite solar cells. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 12, 1–8 (2017)
Yang, W.S., Noh, J.H., Jeon, N.J., Kim, Y.C., Ryu, S., Seo, J., Seok, S.I.I.: High performance photovoltaic perovskite layers fabricated through intramolecular exchange. Science 348, 1234–1237 (2015)
Yeon, D.H., Mohanty, B.C., Lee, S.M., Cho, Y.S.: Effect of band-aligned double absorber layers on photovoltaic characteristics of chemical bath deposited PbS/CdS thin film solar cells. Sci. Rep. 5, 1–7 (2015)
You, J., Meng, L., Song, T., Guo, T., Yang, Y.M., Chang, W., Hong, Z., Chen, H., Zhou, H., Chen, Q., Liu, Y., Marco, N.D., Yang, Y.: Improved air stability of perovskite solar cells via solution-processed metal oxide transport layers. Nat. Nanotechnol. 11, 75–51 (2016)
Yu, W., Li, F., Wang, H., Alarousu, E., Chen, Y., Lin, B., Wang, L., Hedhili, M.N., Li, Y., Wu, K., Wang, X., Mohammed, O.F., Wu, T.: Ultrathin Cu2O as an efficient inorganic hole transporting material for perovskite solar cells. Nanoscale 8, 6173–6179 (2016)
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledgment Dr Marc Burgelman, Honorary Professor, University of Gent for providing SCAPS-1D software.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, A., Ranjan, P. Computational analysis of chalcogenides as an inorganic hole transport layer in perovskite solar cells. Opt Quant Electron 53, 511 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-021-03186-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-021-03186-2