Abstract
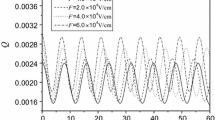
By using a variational method of Pekar type, we investigate the effects of the hydrogen-like impurity and magnetic field on the electron’s probability density (PD) and oscillating frequency (OF) of a RbCl quantum pseudodot qubit. Numerical results indicate that (1) the PD oscillates periodically; (2) the crest of the PD will decrease with increasing the cyclotron frequencies and the Coulombic impurity potential strength; (3) as the cyclotron frequency of the magnetic field and the strength of the Coulombic impurity potential increases, PD’s peaks will occur more frequently; (4) besides, Figs. 1b and 2b clearly show that in a single period the PD will decrease with increasing the cyclotron frequency and the Coulombic impurity potential strength when \( t > 1.8\;\text{fs} \); whereas the changing law is just the opposite when \( t < 1.8\;\text{fs} \); (5) the OF is an aggrandizing function of the strength of the Coulombic impurity potential, whereas it is a decaying one of the cyclotron frequencies of the magnetic field. The coherence of qubit is crucial to the investigations of quantum information and quantum computation, where the electron’s PD, the OF and the coherence time are the physical quantities representing the properties of coherence. Our research results fine that by changing the cyclotron frequency of the magnetic field and the strength of the Coulombic impurity potential one can adjust the electron’s PD and the OF.

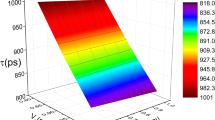
The PD \( \text{Q}\left( {r,t} \right) \) versus the time \( t \) and the cyclotron frequency of the magnetic field \( \omega_{c} \) with \( \text{V}_{0} = 10.0\,\text{meV, r}_{0} = 1.0\,\text{nm, }\beta \text{ = 1.0}\,\text{meV} \cdot \text{nm} \) and \( x = y = z = 1.0\,\text{nm} \)

The PD \( \text{Q}\left( {r,t} \right) \) versus the time \( t \) and strength of the Coulombic impurity potential \( \beta \) with \( \text{V}_{0} = 10.0\,\text{meV, r}_{0} = 1.0\,\text{nm,} \, \omega_{c} \text{ = 2.0}\, \times \text{10}^{13}\,\text{Hz} \) and \( x = y = z = 1.0\,\text{nm} \)

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asadpour, S.H.: Goos-Hanchen shifts due to spin-orbit coupling in the carbon nanotube quantum dot nanostructures. Appl. Opt. 56, 2201–2208 (2017)
Asadpour, S.H., Soleimani, H.R.: Phase control of optical bistability based biexciton coherence in a quantum dot nanostructure. Physica B 440, 124–129 (2014)
Cai, C.Y., Zhao, C.L., Xiao, J.L.: The effect of magnetic field on an asymmetric Gaussian potential quantum well qubit. Commun. Theor. Phys. 63, 159–162 (2015)
Cetin, A.: A quantum pseudodot system with a two-dimensional pseudoharmonic potential. Phys. Lett. A 372, 3852–3856 (2008)
Devreese, J.T.: Polarons in ionic crystals and polar semiconductors. North-Holland, Amsterdam (1972)
Ding, Z.H., Sun, Y., Xiao, J.L.: Optical phonon effect in an asymmetric quantum dot qubit. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 10, 1250077 (2012)
Ikhdair, S.M., Hamzavi, M.: A quantum pseudodot system with two-dimensional pseudoharmonic oscillator in external magnetic and Aharonov-Bohm fields. Physica B 407, 4198–4207 (2012)
Khordad, R.: Spin-orbit interaction in a quantum pseudodot: pressure effect. J. Comput. Electron. 13, 383–393 (2014)
Khordad, R.: Bound polaron in a quantum pseudodot under Rashba effect. Physica E 69, 249–252 (2015)
Landau, L.D., Pekar, S.I.: Effective mass of the polaron. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 18, 419–423 (1948)
Li, Z.X., Xiao, J.L.: Effects of spin on the ground-state energy of strong-coupling bound magnetopolaron in an asymmetric quantum dot. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B. 26, 1250185-1-8 (2012)
Li, W.P., Yin, J.W., Yu, Y.F., Xiao, J.L.: The effect of magnetic on the properties of a parabolic quantum dot qubit. J. Low Temp. Phys. 160, 112–118 (2010)
Ma, X.J., Qi, B., Xiao, J.L.: Coulomb impurity potential RbCl quantum pseudodot qubit. J. Low Temp. Phys. 180, 315–320 (2015)
Pekar, S.I.: Untersuchungen über die Elektronen-theorie der Kristalle. Akademie Verlag, Berlin (1954)
Pekar, S.I., Deigen, M.F.: The quantum states and the optical transitions of an electron in a polaron and in a color center in a crystal. ZH. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. (USSR) 18, 481–486 (1948)
Rezaei, G., Vaseghi, B., Taghizadeh, F., Vahdani, M.R.K., Karimi, M.J.: Intersubband optical absorption coefficient changes and refractive index changes in a two-dimensional quantum pseudodot system. Superlattices Microstruct. 48, 450–457 (2010)
Shan, S.P., Chen, S.H., Xiao, J.L.: Polaron Rashba effect in an asymmetric quantum dot. Low Temp. Phys. 40, 712–715 (2014)
Solookinejad, G., Panahi, M., Sangachin, E.A., Asadpour, S.H.: Incoherent control of Goos-Hanchen shifts in a four-level InGaN/GaN quantum dot nanostructure. Laser Phys. 26, 045202-1-6 (2016)
Sun, Y., Ding, Z.H., Xiao, J.L.: State energies and transition frequency of strong-coupling polaron in an anisotropic quantum dot. J. At. Mol. Sci. 4, 176–182 (2013)
Sun, Y., Ding, Z.H., Xiao, J.L.: The effect of phonons in RbCl quantum pseudodot qubits. J. Electron. Mater. 45, 3576–3580 (2016)
Wang, Z.W., Xiao, J.L.: Parabolic linear bound potential quantum dot qubit and its optical phonon effect. Acta. Phys. Sin. 56, 678–682 (2007)
Wang, Z.W., Li, W.P., Yin, J.W., Xiao, J.L.: Properties of parabolic linear bound potential and Coulomb bound potential quantum dot qubit. Commun. Theor. Phys. 49, 311–314 (2008)
Xiao, J.L.: Influences of temperature and coulomb bound potential on the properties of quantum rod qubit. Superlattices Microstruct. 60, 248–256 (2013)
Xiao, J.L.: The effect of magnetic field on RbCl quantum pseudodot qubit. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 29, 1550098 (2015)
Xiao, J.L.: Temperature and hydrogen-like impurity effects on the excited state of the strong coupling bound polaron in a CsI quantum pseudodot. Chin. Phys. B 26, 027104 (2017)
Xie, W.F., Chen, Y.: Optical absorption and refractive index of a donor impurity in a three-dimensional quantum pseudodot. Superlattices Microstruct. 50, 691–697 (2011)
Yu, Y.B., Wang, H.J.: Third-harmonic generation in two-dimensional pseudo-dot system with an applied magnetic field. Superlattices Microstruct. 50, 252–260 (2011)
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by the National Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 11464033 and 11464034.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, LQ., Xiao, JL. The effects of magnetic field and hydrogen-like impurity on RbCl quantum pseudodot qubit. Opt Quant Electron 49, 304 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-017-1146-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-017-1146-9