Abstract
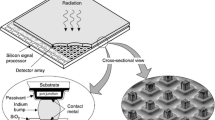
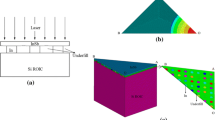
InSb infrared focal plane arrays (IRFPAs) detector, active in 3–5 μm range, has been widely used in military fields. In the fabrication of InSb IRFPAs, the InSb chip is usually thinned down to 10 μm by means of both the chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) process and the wet chemical etching process. In order to confirm the operation limitation of the CMP process, in light of the proposed equivalent method, we create the deformation analysis modeling of InSb IRFPAs. In order to learn the evolving tendency of the deformation distribution characteristic appearing on the top surface of InSb IRFPAs during the thinning process of InSb chip, we reduce the thickness of InSb chip from 300 μm down to 6 μm in a suitable step. And the simulated Z-components of strain distribution are identical with the measured deformation distribution, appearing on the top surface of InSb IRFPAs with different InSb chip thickness values. According to the dependence of the deformation distribution characteristic of InSb IRFPAs on the thickness of InSb chip, we conclude that the thickness of InSb chip should not be thinner than 30 μm after the CMP process is executed completely. A series of thickness values of GaSb substrate, which is thinned down to 60, 50 or 30–40 μm by CMP process in the fabrication of type-IIsuperlattice IRPFAs, support our conclusion. All these cases prove that the operation limitation of the CMP process proposed in this paper is accurate and acceptable in the fabrication of IRFPAs.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang, R.W., Patrick, M.F.: Constitutive relations of indium in extreme temperature electronic packaging based on Anand model. J. Electron. Mater. 38, 1855–1859 (2009)
Cheng, X., Liu, C., Silberschmidt, V.V.: Numerical analysis of thermo-mechanical behavior of indium micro joint at cryogenic temperatures. Comput. Mater. Sci. 52, 274–281 (2012)
Delaunay, P.Y., Nguyen, B.M., Hoffman, D., Razeghi, M.: Substrate removal for high quantum efficiency back side illuminated type-II InAs/GaSb photodetectors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 231106–1–231106–3 (2007)
Gong, H.M., Liu, D.F.: Developments and trends in spaceborne infrared detectors. Infrared Laser Eng. 37, 18–24 (2008)
He, Y., Moreira, B.E., Overson, A., Nakamura, S.H., Bider, C., Briscoe, J.F.: Thermal characterization of an epoxy-based underfill material for flip chip packaging. Thermochim. Acta 357–358, 1–8 (2000)
Hu, W.D., Liang, J., Yue, F.Y., Chen, X.S., Lu, W.: Recent progress of subwavelength photon trapping HgCdTe infrared detector. J. Infrared Millim. Waves 35, 25–36 (2016)
Huang, E.K., Hoang, M., Chen, G.X., Shaban, R.D., Haddadi, A., Razeghi, M.: Highly selective two-color mid-wave and long-wave infrared detector hybrid based on Type-II superlattices. Opt. Lett. 37, 4744–4746 (2012)
Jia, X.H., Liang, X.G., Tang, S., Zhou, X.F.: Research on dynamic simulation technique for infrared imaging air-to-air missile guidance system. Acta Aeronaut. Astronaut. Sin. 26, 397–401 (2005)
Jiang, J.T., Tsao, S., O’Sullivan, T., Razeghi, M., Brown, G.J.: Fabrication of indium bumps for hybrid infrared focal plane array applications. Infrared Phys. Technol. 45, 143–151 (2004)
Jiun, H.H., Ahmad, I., Jalar, A., Omar, G.: Effect of wafer thinning methods towards fracture strength and topography of silicon die. Microelectron. Reliab. 46, 836–845 (2006)
Meng, Q.D., Yu, Q., Zhang, L.W., Lü, Y.Q.: Mechanical parameters selection in InSb focal plane array detector normal direction. Acta Phys. Sin. Ch Ed. 61, 226103–1–226103–5 (2012a)
Meng, Q.D., Zhang, X.L., Zhang, L.W., Lü, Y.Q.: Structural modeling of 128 × 128 InSb focal plane array detector. Acta Phys. Sin. Ch Ed. 61, 190701–1–190701–6 (2012b)
Nathan, V., Razeghi, M.: Type II superlattice infrared detectors and focal plane arrays. Proc. SPIE 6542, 654209–1–654209–11 (2007)
Qiu, W.C., Hu, W.D.: Laser beam induced current microscopy and photocurrent mapping for junction characterization of infrared photodetectors. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 58, 027001–1–027001–13 (2015)
Sadeghinia, M., Jansen, K.M.B., Ernst, L.J.: Characterization and modeling the thermo-mechanical cure-dependent properties of epoxy molding compound. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 32, 82–88 (2012)
Tidrow, M.Z., Dyer, W.R.: Infrared sensors for ballistic missile defense. Infrared Phys. Technol. 42, 333–336 (2001)
Wasmer, K., Ballif, C., Pouvreau, C., Schulz, D., Michler, J.: Dicing of gallium-arsenide high performance laser diodes for industrial applications part I. scratching operation. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 198, 114–121 (2008)
White, G.K., Collins, J.G.: Thermal expansion of copper, silver, and gold at low temperatures. J. Low Temp. Phys. 7, 43–75 (1972)
Yamaguchi, H., Enomoto, T., Sato, T.: Stress variation analysis during curing process of epoxy underfill. Proc. ICEP 23–25, 507–510 (2014)
Zhang, X.L., Meng, C., Zhang, W., Lü, Y.Q., Si, J.J., Meng, Q.D.: Design rule of indium bump in infrared focal plane array for longer cycling life. Infrared Phys. Technol. 76, 631–635 (2016)
Zhang, X.L., Meng, Q.D., Zhang, L.W., Lü, Y.Q.: Modeling and deformation analyzing of InSb focal plane arrays detector under thermal shock. Infrared Phys. Technol. 63, 28–34 (2014)
Zhang, X.L., Si, L.F., Meng, Q.D., Lü, Y.Q., Si, J.J.: Structural model of InSb IRFPAs including underfill curing process. Acta Phys. Sin. Ch Ed. 66, 016102–1–016102–9 (2017)
Acknowledgements
The research was supported by the Young Scientists Fund of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61505048) and by the Aero Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 20152442001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, Q., Zhang, X., Lü, Y. et al. Operation limitation of CMP in back-thinning process of InSb IRFPAs. Opt Quant Electron 49, 211 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-017-1056-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-017-1056-x