Abstract
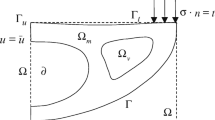
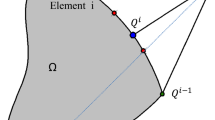
The present paper addresses the robustness and convergence behavior of the direct limit analysis (LA) based methodology developed for the topology design of continuum structures subject to prescribed statically and plastically admissible loads. The design methodology, based on a direct method formulation of the static LA problem, has recently been proposed for continuous topology optimization and its merits were highlighted. One of its remarkable features is the outstanding similarity of the topology design mathematical problem with its underlying direct static form of the LA problem. Subsequently, it has been extended to solve two dimensional discrete, i.e. black-and-white, topology design problems by modifying the objective function into a square root form in a way to penalize the intermediate densities and solving a sequence of conic quadratic programming problems of identical scale and algebraic structure as the continuous design problem, leaving a number of issues to be investigated, pertaining to convergence. In the present work different families of penalization function forms are proposed and assessed as alternatives to the original square root function. The performance is evaluated in terms of robustness, accuracy in the sense of closeness of the final design to a 0–1 topology and efficiency or number of approximate problems required for convergence. Convergence of the discrete topology design is shown to be improved using higher order power functions as well as trigonometric and exponential type penalty functions. The performance of the design method in solving example problems using the various penalization schemes is compared and the factors that affect it are analyzed.























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allaire G (2007) Conception optimale de structures. Part of the Mathématiques & applications book series (MATHAPPLIC, vol 58). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-36856-4
Barros GCG (2017) Topology optimization considering limit analysis. Master’s thesis, PUC-Rio
Bendsøe MP (1989) Optimal shape design as a material distribution problem. Struct Optim 1(4):193–202
Bendsøe MP, Kikuchi N (1988) Generating optimal topologies in structural design using a homogenization method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 71(2):197–224
Bendsøe MP, Sigmund O (1999) Material interpolation schemes in topology optimization. Arch Appl Mech 69(9–10):635–654
Bleyer J, De Buhan P (2014) Lower bound static approach for the yield design of thick plates. Int J Numer Methods Eng 100(11):814–833
Browne PA (2013) Topology optimization of linear elastic structures. Ph.D. thesis, Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Bath
Cao L, Dolovich A, Zhang WJ (2013) On understanding of design problem formulation for compliant mechanisms through topology optimization. Mech Sci 4(2):357–369
Cao L, Dolovich AT, Schwab AL, Herder JL, Zhang WC (2015) Toward a unified design approach for both compliant mechanisms and rigid-body mechanisms: module optimization. J Mech Des 137(12):122301
Colson B, Bruyneel M, Grihon S, Raick C, Remouchamps A (2010) Optimization methods for advanced design of aircraft panels: a comparison. Optim Eng 11(4):583–596
Das R, Jones R, Xie Y-M (2011) Optimal topology design of industrial structures using an evolutionary algorithm. Optim Eng 12(4):681–717
Duysinx P (1996) Optimisation topologique: du milieu continu à la structure élastique. PhD thesis, Université de Liège
Eschenauer HA, Olhoff N (2001) Topology optimization of continuum structures: a review. Appl Mech Rev 54(4):331–390
Fin J, Borges LA, Fancello EA (2019) Structural topology optimization under limit analysis. Struct Multidiscip Optim 59(4):1355–1370
Herfelt MA, Poulsen PN, Hoang LC (2018) Strength-based topology optimisation of plastic isotropic von Mises materials. Struct Multidiscip Optim 59:893–906. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-018-2108-y
Kammoun Z (2016) A formulation for multiple loading cases in plastic topology design of continua. C R Méc 344(10):725–735
Kammoun Z, Smaoui H (2014) A direct approach for continuous topology optimization subject to admissible loading. C R Méc 342(9):520–531
Kammoun Z, Smaoui H (2015) A direct method formulation for topology plastic design of continua. In: Fuschi P, Pisano AA, Weichert D (eds) Direct methods for limit and shakedown analysis of structures. Springer, Berlin, pp 47–63
Kammoun Z, Pastor F, Smaoui H, Pastor J (2010) Large static problem in numerical limit analysis: a decomposition approach. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 34:1960–1980
Lagaros ND, Vasileiou N, Kazakis G (2019) Ac# code for solving 3d topology optimization problems using SAP2000. Optim Eng 20(1):1–35
Lyamin AV, Sloan SW (2002) Lower bound limit analysis using non-linear programming. Int J Numer Methods Eng 55(5):573–611
Maute K, Schwarz S, Ramm E (1998) Adaptive topology optimization of elastoplastic structures. Struct Optim 15(2):81–91
MOSEK ApS (2002) C/O Symbion Science Park, Fruebjergvej 3, Box 16, 2100 Copenhagen \(\phi\), Denmark. www.mosek.com
Pastor J (1978) Analyse limite: détermination numérique de solutions statiques complètes. Application au talus vertical. J Méc Appl (Eur J Mech A Solids) 2:167–196
Pastor F, Kammoun Z, Loute E, Pastor J, Smaoui H (2009) Large problems in numerical limit analysis: a decomposition approach. In: Weichert D, Ponter A (eds) Limit states of materials and structures. Springer, Berlin, pp 23–43
Rahmatalla S, Swan CC (2003) Form finding of sparse structures with continuum topology optimization. J Struct Eng 129(12):1707–1716
Rozvany GIN (2009) A critical review of established methods of structural topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 37(3):217–237
Rozvany GIN, Zhou M, Birker T (1992) Generalized shape optimization without homogenization. Struct Optim 4(3–4):250–252
Salençon J (1967) Théorie des charges limites: poinçonnement d’une plaque par deux poinçons symétriques en déformation plane. Comptes Rendus Mécanique. Acad Sc Paris 265:869–872
Salençon J (1974) Théorie de la plasticité pour les applications à la mécanique des sols. Eyrolles, Paris
Salençon J (2013) Yield design. Wiley, Hoboken
Senne TA, Gomes FAM, Santos SA (2019) On the approximate reanalysis technique in topology optimization. Optim Eng 20(1):251–275
Yuge K, Kikuchi N (1995) Optimization of a frame structure subjected to a plastic deformation. Struct Optim 10(3–4):197–208
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR), King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, under Grant No. (305-219-D1440). The authors, therefore, acknowledge with thanks DSR technical and financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smaoui, H., Kammoun, Z. Convergence of the direct limit analysis design method for discrete topology optimization. Optim Eng 23, 1–24 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11081-020-09543-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11081-020-09543-6