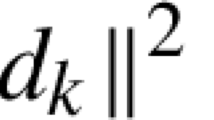Abstract
Mathematical programming has become a valuable tool in process engineering. However, optimization of hybrid dynamic systems with autonomous mode transitions still constitutes a major challenge for theoretical treatments and engineering application. Among the existing approaches for addressing this obstacle, reformulation strategies appear to be most promising. In this study, a modified smoothing strategy and an extended penalization approach to approximate the non-smooth dynamic optimization problem by a smooth one are presented. As a result, a local solution can be gained by a NLP solver after a discretization of the smoothed problem. This solution converges to that of the original non-smooth problem when the value of the introduced reformulation parameter goes to zero. Heuristic rules to select parameter values for both strategies are proposed based on their inherent features. Results from two case studies indicate the capability of the proposed approaches to efficiently obtain physically meaningful solutions.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akesson J (2010) JModelica User’s Guide. Modelon AB. http://www.jmodelica.org/page/236
Andersson M (1994) Object-oriented modeling and simulation of hybrid systems. PhD thesis, Dept. of Automatic Control, Lund Inst. of Technology, Sweden
Anitescu M, Tseng P, Wright SJ (2007) Elastic-mode algorithms for mathematical programs with equilibrium constraints: global convergence and stationarity properties. Math Program 110:337–371
Bard JF (1988) Convex two-level optimization. Math Program 40:15–27
Barton PI, Allgor RJ, Feehery WF, Galan S (1998) Dynamic optimization in a discontinuous world. Ind Eng Chem Res 37:966–981
Barton PI, Banga JR, Galan S (2000) Optimization of hybrid discrete/continuous dynamic systems. Comput Chem Eng 24:2171–2182
Barton PI, Lee CK (2002) Modeling, simulation, sensitivity analysis, and optimization of hybrid systems. ACM Trans Model Comput Simul 12(4):256–289
Barton PI, Lee CK, Yunt M (2006) Optimization of hybrid systems. Comput Chem Eng 30:1576–1589
Baumrucker BT, Biegler LT (2009) MPEC strategies for optimization of a class of hybrid dynamic systems. J Process Control 19:1248–1256
Bemporad A, Morari M (1999) Control of systems integrating logic, dynamics, and constraints. Automatica 35:402–427
Biegler L (2010) Nonlinear programming—concepts, algorithms, and applications to chemical processes, vol 10. Mos-SIAM Series on Optimization, SIAM, Philadelphia
Biegler LT (2007) An overview of simultaneous strategies for dynamic optimization. Chem Eng Process 46:1043–1053
Cassandras CG, Pepyne DL, Wardi Y (2001) Optimal control of a class of hybrid systems. IEEE Trans Autom Control 46:398–415
Cellier FE (1979a) Combined continuous/discrete system simulation by use of digital computers: Techniques and tools. PhD thesis, ETH Zuerich, Switzerland
Cellier FE (1979b) Combined continuous/discrete system simulation languages. In: Zeigler BP, Elzas MS, Klir GJ, Oeren TI (ed) Methodology in systems modelling and simulation, 201–220
Cellier FE, Elmqvist H, Otter M, Taylor JH (1993) Guidelines for modelling and simulation of hybrid systems. In Proceedings of 12th IFAC World Congress, 8: 391–397
Cervantes A, Biegler LT (1998) Large-scale DAE optimization using a simultaneous NLP formulation. AIChE J 44(5):1038–1050
Chen C, Mangasarian OL (1996) A class of smoothing functions for nonlinear and mixed complementarity problems. Comput Optim Appl 5:97–138
Chen X (2000) Smoothing methods for comlementarity problems and their applications: A survey. J Oper Res Soc Jpn 43(1):32–47
Chen X (2012) Smoothing methods for nonsmooth, nonconvex minimization. Math Program 134(1):71–99
Chen Y, Florian M (1995) The nonlinear bilevel programming problem: formulations, regularity and optimality conditions. Optimization 32(3):193–209
De la Fluente RL, Flores-Tlacuahuac A (2009) Integrated design and control using a simultaneous mixed-integer dynamic optimization approach. Ind Eng Chem Res 48:1933–1943
Dempe S (2002) Foundations of bilevel programming. Kluwer Academie Publishers, Dordrecht
Dempe S, Dutta J (2012) Is bilevel programming a special case of a mathematical program with complementarity constraints? Math Program 131(1–2):37–48
Diehl M, Bock HG, Schloeder JP, Findeisen R, Nagy Z, Allgoewer F (2002) Real-time optimization and nonlinear model predictive control of processes governed by differential-algebraic equations. J Process Control 12(4):577–585
Ferris MC, Pang JS (1997) Engineering and economic applications of complementarity problems. SIAM Rev 39:669–713
Filippov AF (1988) Differential equations with discontinuous righthand sides. Kluwer Academic Publisher, Dordrecht
Fischer A (1992) A special Newton-type optimization method. Optimization 24:269–284
Flegel M (2005) Constraint qualifications and stationarity concepts for mathematical programs with equilibrium constraints. PhD thesis, Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg, Germany
Fletcher R, Leyffer S (2004) Solving mathematical programs with complementarity constraints as nonlinear programs. Optim Method Softw 19:15–40
Fletcher R, Leyffer S, Ralph D, Scholtes S (2006) Local convergence of SQP methods for mathematical programs with equilibrium constraints. SIAM J Optim 17:259–286
Flores-Tlacuahuac A, Biegler LT (2007) Simultaneous mixed-integer dynamic optimization for integrated design and control. Comput Chem Eng 31:588–600
Goebel R, Sanfelice RG, Teel AR (2009) Hybrid dynamical systems. IEEE Control Syst Mag 29:28–93
Grossmann C, Kleinmichel H (1979) Verfahren der nichtlinearen Optimierung. Teubner, Leipzig
Grossmann IE (2002) Review of nonlinear mixed-integer and disjunctive programming techniques. Optim Eng 3:227
Herskovits J, Filho MT, Leontiev A (2013) An interior point technique for solving bilevel programming problems. Optim Eng 14:381–394
Hoheisel T, Kanzow C, Schwartz A (2013) Theoretical and numerical comparison of relaxation methods for mathematical programs with complementarity constraints. Math Program 137(1–2):257–288
Hu XM, Ralph D (2004) Convergence of a penalty method for mathematical programming with complementarity constraints. J Optim Theory Appl 123:365–390
Jiang H, Ralph D (1999) Smooth SQP methods for mathematical programs with nonlinear complementarity constraints. SIAM J Optim 10:779–808
Kardani A, Dussault JP, Benchakroun A (2009) A new regularization scheme for mathematical programs with complementarity constraints. J Phys Chem A 20:78–103
Kennedy J, Eberhart R (2002) Particle swarm optimization. In Neural Networks, 1995. Proceedings. IEEE 4:1942–1948
Kravanja S, Sorsak A, Kravanja Z (2003) Efficient multilevel MINLP strategies for solving large combinatorial problems in engineering. Optim Eng 4:97–151
Leyffer S (2003) Mathematical programs with complementarity constraints. SIAG/OPT Views-and-News 14:15–18
Leyffer S, Lopez-Calva G, Nocedal J (2006) Interior methods for mathematical programs with complementarity constraints. SIAM J Optim 17:52–77
Luo ZQ, Pang JS, Ralph D (1996) Mathematical programs with equilibrium constraints. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Mehrmann V, Wunderlich L (2009) Hybrid systems of differential-algebraic equations—analysis and numerical solution. J Process Control 19(8):1218–1228
Michalik C, Hannemann R, Marquardt W (2009) Incremental single shooting: a robust method for the estimation of parameters in dynamical systems. Comput Chem Eng 33:1298–1305
Morari M, Baric M (2006) Recent developments in the control of constrained hybrid systems. Comput Chem Eng 30:1619–1631
Mynttinen I, Li P (2011) A reformulation scheme for parameter estimation of hybrid systems. In: 21st European symposium on computer-aided process engineering, 778–782
Nakamura K, Fusaoka A (2005) On transfinite hybrid automata. In: Proceeding: 8th International Workshop, HSCC 2005, 495–510
Nocedal J, Wright SJ (1999) Numerical optimization. Springer-Verlag, New York
Pappala VS, Erlich I (2008) A new approach for solving the unit commitment problem by adaptive particle swarm optimization. In: Power and energy society general meeting, 2008 IEEE, 1–6
Park T, Barton PI (1996) State event location in differential-algebraic models. ACM Trans Model Comput Simul 6:137–165
Pfeiffer A, Arnold M (2010) Sensitivity analysis of discontinuous multidisciplinary models: Two examples. Non-smooth problems in vehicle systems dynamics. Springer, Berlin, pp 239–251
Prata DM, Schwaab M, Lima EL, Pinto JC (2009) Nonlinear dynamic data reconciliation and parameter estimation through particle swarm optimization: application for an industrial polypropylene reactor. Chem Eng Sci 64:3953–3967
Raghunathan A, Biegler LT (2005) An interior point method for mathematical programs with complementarity constraints. SIAM J Optim 15:720–750
Raghunathan AU, Prez-Correa JR, Agosin E, Biegler LT (2006) Parameter estimation in metabolic flux balance models for batch fermentation—formulation & solution using differential variational inequalities (DVIs). Ann Oper 148:251–270
Ralph D, Wright SJ (2004) Some properties of regularization and penalization schemes for MPECs. Optim Method Softw 19:527–556
Russell RD, Christiansen J (1978) Adaptive mesh selection strategies for solving boundary value problems. SIAM J Numer Anal 15:59–80
Sager S (2009) Reformulations and algorithms for the optimization of switching decisions in nonlinear optimal control. J Process Control 19:1238–1247
Sarabia D, Capraro F, Larsen LFS, De Prada C (2009) Hybrid NMPC of supermarket display cases. Control Eng Pract 17:428–441
Scheel H, Scholtes S (2000) Mathematical programs with complementarity constraints: stationarity, optimality and sensitivity. Math Oper Res 25:1–22
Schittkowski K (2002) Numerical data fitting in dynamical systems. Kluwer Academic Press, Dordrecht
Scholtes S (2001) Convergence properties of regularization schemes for mathematical programs with complementarity constraints. SIAM J Optim 11(4):918–936
Scholtes S, Stöhr M (2001) How stringent is the linear independence assumption for mathematical programs with complementarity constraints? Math Oper Res 26(4):851–863
Sonntag C, Stursberg O, Engell S (2006) Dynamic optimization of an industrial evaporator using graph search with embedded nonlinear programming. In: 2nd IFAC conference on analysis and design of hybrid systems, 211–216
Stein O, Oldenburg J, Marquardt W (2004) Continuous reformulations of discrete-continuous optimization problems. Comput Chem Eng 28:1951–1966
Stewart DE, Anitescu M (2010) Optimal control of systems with discontinuous differential equations. Numer Math 114:653–695
Stortelder WJH (1998) Parameter estimation in nonlinear dynamic systems, vol 124. CWI Tracts, Amsterdam
Tamimi J, Li P (2010) A combined approach to nonlinear model predictive control of fast systems. J Process Control 20(9):1092–1102
Till J, Engell S, Panek S, Stursberg O (2004) Applied hybrid system optimization: an empirical investigation of complexity. Control Eng Pract 12:1291–1303
Tiller M (2001) Introduction to physical modeling with Modelica. Springer Verlag GmbH, Berlin
Trenn S (2009) Distributional differential algebraic equations. PhD thesis, Technische Universität Ilmenau, Germany
Vassiliadis VS, Sargent RWH, Pantelides CC (1994) Solution of a class of multistage optimization problems. 2. Problems with path constraints. Ind Eng Chem Res 33:2123–2133
Waechter A, Biegler LT (2006) On the implementation of an interior-point filter line-search algorithm for large-scale nonlinear programming. Math Program 106(1):25–57
Zavala VM, Laird CD, Biegler LT (2008) Interior-point decomposition approaches for parallel solution of large-scale nonlinear parameter estimation problems. Chem Eng Sci 63:4834–4845
Acknowledgments
We thank the anonymous referees for several important clarifications, which considerably improved the readability of the present paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mynttinen, I., Hoffmann, A., Runge, E. et al. Smoothing and regularization strategies for optimization of hybrid dynamic systems. Optim Eng 16, 541–569 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11081-014-9261-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11081-014-9261-y