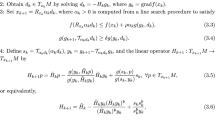Abstract
In this paper, we analyze the global convergence of a general non-monotone line search method on Riemannian manifolds. For this end, we introduce some properties for the tangent search directions that guarantee the convergence, to a stationary point, of this family of optimization methods under appropriate assumptions. A modified version of the non-monotone line search of Zhang and Hager is the chosen globalization strategy to determine the step-size at each iteration. In addition, we develop a new globally convergent Riemannian conjugate gradient method that satisfies the direction assumptions introduced in this work. Finally, some numerical experiments are performed in order to demonstrate the effectiveness of the new procedure.
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The OptSt Matlab code is available in https://github.com/wenstone/OptM
The Riemannian conjugate gradient methods Algor.1a and Algor.1b can be downloaded from http://www.optimization-online.org/DB_HTML/2016/09/5617.html
The manopt toolbox is available in http://www.manopt.org/
References
Absil, P -A, Gallivan, KA: Joint Diagonalization on the Oblique manifold for independent component analysis. In: 2006 IEEE international conference on acoustics speech and signal processing proceedings, vol. 5, pp V–V. IEEE (2006)
Absil, P-A, Mahony, R, Sepulchre, R: Optimization algorithms on matrix manifolds. Princeton University Press, Princeton (2009)
Arjovsky, M, Shah, A, Bengio, Y: Unitary evolution recurrent neural networks. In: International conference on machine learning. PMLR, pp 1120–1128 (2016)
de Andrade Bortoloti, MA, Fernandes, TA, Ferreira, OP: On the globalization of Riemannian Newton method. arXiv:2008.06557 (2020)
Boumal, N, Absil, P-A: RTRMC: A Riemannian Trust-region method for low-rank matrix completion. Adv Neural Inform Process Syst 24, 406–414 (2011)
Boumal, N, Mishra, B, Absil, P -A, Sepulchre, R: Manopt, a Matlab toolbox for optimization on manifolds. J Mach Learn Res 15(1), 1455–1459 (2014)
Dalmau, O, Oviedo, H: A projection method for optimization problems on the Stiefel manifold. In: Mexican conference on pattern recognition. Springer, pp 84–93 (2017)
Dalmau, O, Oviedo, H: Projected nonmonotone search methods for optimization with orthogonality constraints. Comput Appl Math 37(3), 3118–3144 (2018)
Edelman, A, Arias, TA, Smith, ST: The geometry of algorithms with orthogonality constraints. SIAM J Matrix Anal Appl 20(2), 303–353 (1998)
Gabay, D: Minimizing a differentiable function over a differential manifold. J Optim Theory Appl 37(2), 177–219 (1982)
Gao, B, Son, NT, Absil, P-A, Stykel, T: Riemannian optimization on the symplectic Stiefel manifold. SIAM J Optim 31(2), 1546–1575 (2021)
Grippo, L, Lampariello, F, Lucidi, S: A nonmonotone line search technique for Newton’s method. SIAM J Numer Anal 23(4), 707–716 (1986)
Grubišić, I, Pietersz, R: Efficient rank reduction of correlation matrices. Linear Algebra and Its Applications 422(2-3), 629–653 (2007)
Hager, WW, Zhang, H: A survey of nonlinear conjugate gradient methods. Pacific Journal of Optimization 2(1), 35–58 (2006)
Hu, J, Bo, J, Lin, L, Wen, Z, Yuan, Y-X: Structured quasi-Newton methods for optimization with orthogonality constraints. SIAM J Sci Comput 41(4), A2239–A2269 (2019)
Hu, J, Liu, X, Wen, Z-W, Yuan, Y-X: A brief introduction to manifold optimization. Journal of the Operations Research Society of China 8(2), 199–248 (2020)
Hu, J, Milzarek, A, Wen, Z, Yuan, Y: Adaptive quadratically regularized Newton method for Riemannian optimization. SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications 39(3), 1181–1207 (2018)
Huang, W, Gallivan, KA, Absil, P-A: A Broyden class of quasi-Newton methods for Riemannian optimization. SIAM J Optim 25(3), 1660–1685 (2015)
Iannazzo, B, Porcelli, M: The Riemannian barzilai–Borwein method with nonmonotone line search and the matrix geometric mean computation. IMA J Numer Anal 38(1), 495–517 (2018)
Journée, M, Nesterov, Y, Richtárik, P, Sepulchre, R: Generalized power method for sparse principal component analysis. J Mach Learn Res 11(2) (2010)
Kokiopoulou, E, Chen, J, Saad, Y: Trace optimization and eigenproblems in dimension reduction methods. Numer Linear Algeb Appl 18(3), 565–602 (2011)
Lai, R, Osher, S: A splitting method for orthogonality constrained problems. J Sci Comput 58(2), 431–449 (2014)
Lara, H, Oviedo, H: Solving joint diagonalization problems via a Riemannian conjugate gradient method in Stiefel manifold. Proceeding Series of the Brazilian Society of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 6(2) (2018)
Lara, H, Oviedo, H, Yuan, J: Matrix completion via a low rank factorization model and an augmented Lagrangean succesive overrelaxation algorithm. Bulletin of Computational Applied Mathematics, 2(2) (2014)
Jun, L, Fuxin, L, Todorovic, S: Efficient Riemannian optimization on the Stiefel manifold via the Cayley transform. arXiv:2002.01113(2020)
Li, X-B, Huang, N-J, Ansari, QH, Yao, J-C: Convergence rate of descent method with new inexact line-search on Riemannian manifolds. J Optim Theory Appl 180(3), 830–854 (2019)
Li, Z, Zhao, D, Lin, Z, Chang, EY: A new retraction for accelerating the Riemannian three-factor low-rank matrix completion algorithm. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 4530–4538 (2015)
David, G: Luenberger. The gradient projection method along geodesics. Manag Sci 18(11), 620–631 (1972)
Nocedal, J, Wright, S: Numerical optimization. Springer Science & Business Media, Berlin (2006)
Ovierdo, H: Implicit steepest descent algorithm for optimization with orthogonality constraints. Optim Lett, 1–25 (2021)
Oviedo, H, Dalmau, O: A Scaled Gradient Projection Method for Minimization over the Stiefel Manifold. In: Mexican international conference on artificial intelligence. Springer, pp 239–250 (2019)
Oviedo, H, Dalmau, O, Lara, H: Two adaptive scaled gradient projection methods for Stiefel manifold constrained optimization. Numerical Algorithms 87, 1107–1127 (2020)
Oviedo, H, Lara, H: A Riemannian Conjugate Gradient Algorithm with Implicit Vector Transport for Optimization in the Stiefel Manifold. Technical Report, Report, Report. UFSC-Blumenau, CIMAT (2018)
Oviedo, H, Lara, H, Dalmau, O: A non-monotone linear search algorithm with mixed direction on Stiefel manifold. Optim Methods Softw 34(2), 437–457 (2019)
Qi, H, Sun, D: A quadratically convergent Newton method for computing the nearest correlation matrix. SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications 28(2), 360–385 (2006)
Ring, W, Wirth, B: Optimization methods on Riemannian manifolds and their application to shape space. SIAM J Optim 22(2), 596–627 (2012)
Sakai, H, Iiduka, H: Hybrid Riemannian conjugate gradient methods with global convergence properties. Comput Optim Appl 77(3), 811–830 (2020)
Sato, H: A dai–Yuan-type Riemannian conjugate gradient method with the weak Wolfe conditions. Comput Optim Appl 64(1), 101–118 (2016)
Sato, H, Iwai, T: A new, globally convergent Riemannian conjugate gradient method. Optimization 64(4), 1011–1031 (2015)
Seibert, M, Kleinsteuber, M, Hüper, K: Properties of the BFGS method on Riemannian manifolds. In: Mathematical System Theory C Festschrift in Honor of Uwe Helmke on the Occasion of his Sixtieth Birthday, 395–412 (2013)
Smith, ST: Optimization techniques on Riemannian manifolds. Fields Institute Communications 3(3), 113–135 (1994)
Udriste, C: Convex functions and optimization methods on Riemannian manifolds, vol. 297. Springer Science & Business Media, Berlin (2013)
Wen, Z, Yin, W: A feasible method for optimization with orthogonality constraints. Math Program 142(1), 397–434 (2013)
Yang, C, Meza, JC, Lee, B, Wang, L-W: KSSOLV—A Matlab toolbox for solving the kohn-Sham equations. ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software (TOMS) 36(2), 1–35 (2009)
Yang, Y: Globally convergent optimization algorithms on Riemannian manifolds: Uniform framework for unconstrained and constrained optimization. J Optim Theory Appl 132(2), 245–265 (2007)
Yao, T-T, Bai, Z-J, Zhao, Z: A Riemannian variant of the fletcher–Reeves conjugate gradient method for stochastic inverse eigenvalue problems with partial eigendata. Numerical Linear Algebra with Applications 26(2), e2221 (2019)
Zhang, H, Hager, WW: A nonmonotone line search technique and its application to unconstrained optimization. SIAM Journal on Optimization 14(4), 1043–1056 (2004)
Li, Z, Zhou, W, Li, D: Global convergence of a modified fletcher–Reeves conjugate gradient method with Armijo-type line search. Numerische Mathematik 104(4), 561–572 (2006)
Zhu, X: A Riemannian conjugate gradient method for optimization on the Stiefel manifold. Computational optimization and Applications 67(1), 73–110 (2017)
Acknowledgements
The author was financially supported by FGV (Fundação Getulio Vargas) through the excellence post-doctoral fellowship program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Data availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were analyzed during the current study. In particular, the data studied were generated randomly and we explained how they were explicitly generated.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oviedo, H. Global convergence of Riemannian line search methods with a Zhang-Hager-type condition. Numer Algor 91, 1183–1203 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11075-022-01298-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11075-022-01298-8