Abstract
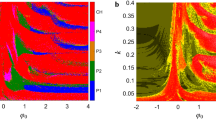
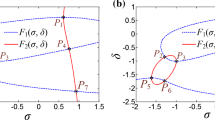
The energy interaction-induced firing and synchronization activities in existing neuronal networks have recently garnered attention. However, the initials-boosted extreme multistability and synchronization firings supplied by the field energy simulated with memristors have not been extensively documented. Therefore, it is of paramount importance to integrate Hamilton energy and dynamics in exploring these novel behaviors to unveil the physical essence of neuronal firing, enhance network flexibility and controllability, and reinforce the practical value of networks. To address these issues, using a memristor synapse to connect two Rulkov neurons that are exposed to memristive electromagnetic radiation, we construct a bionic memristor synapse-coupled bi-mRulkov neuron network model, known as the bi-mRulkov network. It possesses spatial equilibrium points, topological invariance, and synchronization convergence associated with the initial conditions of memristors. In particular, by establishing quantitative indicators based on the Hamilton energy and synchronization factor, the interesting boosting firing and its energy balance and transition processes are visualized from the two-dimensional plane and local dynamics. Theoretical analysis and numerical simulation demonstrate that the bi-mRulkov network can generate the boosting extreme multistability firing. Furthermore, the complex line-boosted complete synchronization and plane-boosted parallel offset synchronization firings are determined by the memristor-controlled energy balance and transition, respectively. Finally, both the PSpice-based analog circuit and microcontroller-based digital circuit platforms are developed to validate the abundant firing activities, which offers accurate implementation paradigms for the proposed neuronal network.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on reasonable request.
References
Zonta, M., Angulo, M.C., Gobbo, S., et al.: Neuron-to-astrocyte signaling is central to the dynamic control of brain microcirculation. Nat. Neurosci. 6(1), 43–50 (2003)
Jeyasothy, A., Sundaram, S., Sundararajan, N.: Sefron: A new spiking neuron model with time-varying synaptic efficacy function for pattern classification. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 30(4), 1231–1240 (2019)
Chua, L.O.: Memristor-the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory 18(5), 507–519 (1971)
Strukov, D.B., Snider, G.S., Stewart, D.R., et al.: The missing memristor found. Nature 453(7191), 80–83 (2008)
Chen, M., Luo, X., Zhang, Y., et al.: Initial-boosted behaviors and synchronization of memristor-coupled memristive systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 71(2), 781–793 (2024)
Jang, B., Kim, S., Yang, S., et al.: Polymer analog memristive synapse with atomic-scale conductive filament for flexible neuromorphic computing system. Nano Lett. 19(2), 839–849 (2019)
Li, Z., Zhou, H., Wang, M., et al.: Coexisting firing patterns and phase synchronization in locally active memristor coupled neurons with HR and FN models. Nonlinear Dyn. 104(2), 1455–1473 (2021)
Hajian, D.N., Ramadoss, J., Natiq, H., et al.: Dynamics of Hindmarsh–Rose neurons connected via adaptive memristive synapse. Chin. J. Phys. 87, 311–329 (2024)
Lin, H., Wang, C., Sun, Y., et al.: Generating n-scroll chaotic attractors from a memristor-based magnetized Hopfield neural network. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst II Brief Pap. 70(1), 311–315 (2023)
Zhang, S., Li, C., Zheng, J., et al.: Memristive autapse-coupled neuron model with external electromagnetic radiation effects. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 70(11), 11618–11627 (2023)
Ramakrishnan, B., Mehrabbeik, M., Parastesh, F., et al.: A new memristive neuron map model and its network’s dynamics under electrochemical coupling. Electron 11(1), 153 (2022)
Jin, P., Wang, G., Liang, Y., et al.: Neuromorphic dynamics of Chua corsage memristor. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 68(11), 4419–4432 (2021)
Vijay, S.D., Thamilmaran, K., Ahamed, A.I.: Superextreme spiking oscillations and multistability in a memristor-based Hindmarsh–Rose neuron model. Nonlinear Dyn. 111(1), 789–799 (2023)
Yang, F., Xu, Y., Ma, J.: A memristive neuron and its adaptability to external electric field. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 33(2), 023110 (2023)
Chen, M., Sun, M., Bao, H., et al.: Flux-charge analysis of two-memristor-based Chua’s circuit: dimensionality decreasing model for detecting extreme multistability. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 67(3), 2197–2206 (2020)
Hens, C.R., Banerjee, R., Feudel, U., et al.: How to obtain extreme multistability in coupled dynamical system. Phys. Rev. E 85(3), 035202 (2012)
Chen, M., Luo, X., Suo, Y., et al.: Hidden extreme multistability and synchronicity of memristor-coupled non-autonomous memristive Fitzhugh–Nagumo models. Nonlinear Dyn. 111(8), 7773–7788 (2023)
Fossi, J.T., Deli, V., Njitacke, Z.T., et al.: Phase synchronization, extreme multistability and its control with selection of a desired pattern in hybrid coupled neurons via a memristive synapse. Nonlinear Dyn. 109(2), 925–942 (2022)
Lin, H., Wang, C., Li, C., et al.: Brain-like initial-boosted hyperchaos and application in biomedical image encryption. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 18(12), 8839–8850 (2022)
Doubla, I.S., Ramakrishnan, B., Njitacke, Z.T., et al.: Infinitely many coexisting hidden attractors in a new hyperbolic-type memristor-based HNN. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 231(11), 2371–2385 (2022)
Njitacke, Z.T., Nkapkop, J.D.D., Signing, V.F., et al.: Novel extreme multistable Tabu learning neuron: circuit implementation and application to cryptography. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 19(8), 8943–8952 (2023)
Zhang, S., Zheng, J., Wang, X., et al.: A novel no-equilibrium HR neuron model with hidden homogeneous extreme multistability. Chaos Solitons Fractals 145, 110761 (2021)
Lin, H., Wang, C., Yu, F., et al.: A triple-memristor Hopfield neural network with space multistructure attractors and space initial-offset behaviors. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 42(12), 4948–4958 (2023)
Lin, H., Wang, C., Sun, J., et al.: Memristor-coupled asymmetric neural networks: bionic modeling, chaotic dynamics analysis and encryption application. Chaos Solitons Fractals 166, 112905 (2023)
Rulkov, N.F.: Modeling of spiking-bursting neural behavior using two-dimensional map. Phys. Rev. E 65(4), 041922 (2002)
Bao, H., Li, K., Ma, J.: Memristive effects on an improved discrete Rulkov neuron model. Sci. China Tech. Sci. 66(11), 3153–3163 (2023)
Xu, Q., Liu, T., Feng, C., et al.: Continuous non-autonomous memristive Rulkov model with extreme multistability. Chin. Phys. B 30(12), 128702 (2021)
Min, F., Zhai, G., Yin, S., et al.: Switching bifurcation of a Rulkov neuron system with ReLu-type memristor. Nonlinear Dyn. (2024)
Zhang, S., Wang, C., Zhang, H., et al.: A multiplier-free Rulkov neuron under memristive electromagnetic induction: dynamics analysis, energy calculation, and circuit implementation. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 33(8), 083138 (2023)
Ma, J.: Biophysical neurons, energy, and synapse controllability: a review. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 24(2), 109–129 (2023)
Vivekanandhan, G., Mehrabbeik, M., Natiq, H., et al.: Chaotic behavior of the basal ganglia cortical thalamic model for absence seizures: a comprehensive dynamical analysis. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 33(11), 2350126 (2023)
Patel, D.C., Tewar, B.P., Chaunsali, L., et al.: Neuron-glia interactions in the pathophysiology of epileps. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 20(5), 282–297 (2019)
Xu, Q., Liu, T., Ding, S., et al.: Extreme multistability and phase synchronization in a heterogeneous bi-neuron Rulkov network with memristive electromagnetic induction. Cognit. Neurodyn. 17(3), 755–766 (2023)
Ma, M., Lu, Y., Li, Z., et al.: Multistability and phase synchronization of Rulkov neurons coupled with a locally active discrete memristor. Fractal Fract. 7(1), 82 (2023)
Li, K., Bao, B., Ma, J., et al.: Synchronization transitions in a discrete memristor-coupled bi-neuron model. Chaos Solitons Fractals 165, 112861 (2022)
Bao, B., Hu, J., Bao, H., et al.: Memristor-coupled dual-neuron mapping model: initials-induced coexisting firing patterns and synchronization activities. Cognit. Neurodyn. (2023)
Torrealdea, F.J., d’Anjou, A., Graña, M., et al.: Energy aspects of the synchronization of model neurons. Phys. Rev. E 74(1), 011905 (2006)
Ma, J.: Energy function for some maps and nonlinear oscillators. Appl. Math. Comput. 463, 128379 (2024)
Lv, M., Wang, C., Ren, G., et al.: Model of electrical activity in a neuron under magnetic flow effect. Nonlinear Dyn. 85(3), 1479–1490 (2016)
Wang, C., Sun, G., Yang, F., et al.: Capacitive coupling memristive systems for energy balance. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 153, 154280 (2022)
Xie, Y., Zhou, P., Ma, J.: Energy balance and synchronization via inductive-coupling in functional neural circuits. Appl. Math Comput. 113, 175–187 (2023)
Rajagopal, K., Jafari, S., Li, C., et al.: Suppressing spiral waves in a lattice array of coupled neurons using delayed asymmetric synapse coupling. Chaos Solitons Fractals 146, 110855 (2021)
Fossi, J.T., Deli, V., Edima, H.C., et al.: Phase synchronization between two thermo-photoelectric neurons coupled through a Josephson Junction. Eur. Phys. J. B 95(4), 66 (2022)
Sun, J., Li, C., Wang, Z., et al.: Dynamic analysis of HR-FN-HR neural network coupled by locally active hyperbolic memristors and encryption application based on Knuth–Durstenfeld algorithm. Appl. Math. Model. 121, 463–483 (2023)
Yu, X., Bao, H., Chen, M., et al.: Energy balance via memristor synapse in Morris–Lecar two-neuron network with FPGA implementation. Chaos Solitons Fractals 171, 113442 (2023)
Bao, H., Yu, X., Zhang, Y., et al.: Initial condition-offset regulating synchronous dynamics and energy diversity in a memristor-coupled network of memristive HR neurons. Chaos Solitons Fractals 177, 114167 (2023)
Li, C., Sprott, J., Mei, Y.: An infinite 2-D lattice of strange attractors. Nonlinear Dyn. 89(4), 2629–2639 (2017)
Li, Y., Li, C., Lei, T., et al.: Offset boosting-entangled complex dynamics in the memristive Rulkov neuron. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. (2024)
Dhamala, M., Jirsa, V.K., Ding, M., et al.: Transitions to synchrony in coupled bursting neurons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92(2), 028101 (2004)
Etémé, A.S., Tabi, C.B., Beyala Ateba, J.F., et al.: Chaos break and synchrony enrichment within Hindmarsh–Rose-type memristive neural models. Nonlinear Dyn. 105(1), 785–795 (2021)
Funding
The work was sponsored by Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (Grant Nos. 2022D01E33 and 2022D01C367), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 52065064 and 52267010), and Innovation Project for Excellent Doctoral Candidates of Xinjiang University (Grant No. XJU2022BS096).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no Conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Zhang, H., Lin, H. et al. Energy-based initials-boosted firings in memristor synapse-coupled bi-mRulkov neuron network. Nonlinear Dyn (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-024-09661-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-024-09661-1