Abstract
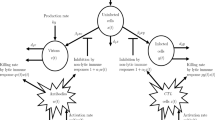
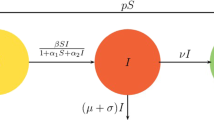
Based on the Caputo fractional-order derivative, this work investigates the dynamics of a newly developed co-infection model of Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and Hepatitis C virus (HCV). Due to their ability to take into account memory history and heritability, Caputo fractional-order derivatives are a natural candidate to study the HIV/HCV co-infection where these two properties are critical to study how infections spread. Furthermore, applying the Caputo fractional-derivative to the co-infection model helps forecast disease progression and offers optimal treatment strategies for understanding complex HIV/HCV interactions and co-evolutionary dynamics. Mathematical analysis of the co-infection model reveals two equilibria, one without sickness and the other with sickness. The next-generation matrix approach is employed to calculate the basic reproduction number for the cases of HIV and HCV only respectively, and the co-infection model of HIV and HCV, jointly that demonstrates the mutual influence of the two diseases. Using the reproduction numbers, the Lyapunov functional method, and the Routh-Hurwitz criterion, we establish the global dynamics of the model. To validate theoretical predictions, the fractional Adams Method (FAM), a popular numerical technique with a predictor-corrector structure, is utilized to compute the model’s numerical solutions. Finally, numerical simulations confirm the theoretical findings, elucidating the high degree of agreement between the theoretical analysis and the numerical results. Different from the existing literature using the L1 scheme, we incorporated a memory trace (MT) procedure in our paper that captures and amalgamates the historical dynamics of the system to evoke the memory effect in detail. One of the novel results obtained from this study is that the memory trace starts to come into existence once fractional power \(\zeta \) starts to increase from 0 to 1 and completely disappears when \(\zeta \) becomes 1. Upon increasing the fractional-order \(\zeta \) from 0, the memory effect exploits a nonlinear proliferation starting from zero. This observed memory effect emphasizes the difference between the integer and non-integer order derivatives and thus claims the existence of memory effects of fractional-order derivatives. The findings of the paper will contribute to a better understanding of the disease outbreak, as well as aid in the development of future predictions and control strategies.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that supports the findings of this work are available within the article.
References
Lavanchy, D.: Hepatitis B virus epidemiology, disease burden, treatment, and current and emerging prevention and control measures. J. Viral Hepat. 11(2), 97–107 (2004)
Hsu, Y.C., Huang, D.Q., Nguyen, M.H.: Global burden of hepatitis B virus: current status, missed opportunities and a call for action. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 20, 524–537 (2023)
Ott, J.J., Stevens, G.A., Groeger, J., Wiersma, S.T.: Global epidemiology of hepatitis B virus infection: new estimates of age-specific HBsAg seroprevalence and endemicity. Vaccine 30(12), 2212–2219 (2012)
Wang, F.S., Fan, J.G., Zhang, Z., Gao, B., Wang, H.Y.: The global burden of liver disease: the major impact of China. Hepatology 60(6), 2099–2108 (2014)
WHO, Global progress report on HIV, viral hepatitis and sexually transmitted infections, 2021. Accountability for the global health sector strategies 2016-2021: actions for impact. World Health Organization, Geneva2021, (2021)
Shepard, C.W., Simard, E.P., Finelli, L., Fiore, A.E., Bell, B.P.: Hepatitis B virus infection: epidemiology and vaccination. Epidemiol. Rev. 28, 112–25 (2006)
Schweitzer, A., Horn, J., Mikolajczyk, R.T., Krause, G., Ott, J.J.: Estimations of worldwide prevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus infection: a systematic review of data published between 1965 and 2013. Lancet Lond. Engl. 386(10003), 1546–1555 (2015)
Qureshi, S., Akanbi, M., Shaikh, A., et al.: A new adaptive nonlinear numerical method for singular and stiff differential problems. Alex. Eng. J. 74, 585–597 (2023)
Rahman, M.U., Arfan, M., Shah, Z., Kumam, P., Shutaywi, M.: Nonlinear fractional mathematical model of tuberculosis (TB) disease with incomplete treatment under Atangana-Baleanu derivative. Alex. Eng. J. 60(3), 2845–2856 (2021)
Tang, T.Q., Jan, R., Bonyah, E., Shah, Z., Alzahrani, E.: Qualitative analysis of the transmission dynamics of dengue with the effect of memory, reinfection, and vaccination. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2022, 7893570 (2022)
Gu, Y., Khan, M., Zarin, R., Khan, A., Yusuf, A., Humphries, U.W.: Mathematical analysis of a new nonlinear dengue epidemic model via deterministic and fractional approach. Alex. Eng. J. 67, 1–21 (2023)
Shah, Z., Jan, R., Kumam, P., Deebani, W., Shutaywi, M.: Fractional dynamics of HIV with source term for the supply of new CD4+ T-cells depending on the viral load via Caputo-Fabrizio derivative. Molecules 26(6), 1806 (2021)
Naik, P.A., Farman, M., Zehra, A., Nisar, K.S., Hınçal, E.: Analysis and modeling with fractal-fractional operator for an epidemic model with reference to COVID-19 modeling. Partial Differ. Equ. Appl. Math. 10, 100663 (2024)
Zarin, R., Khan, A., Aurangzeb, Akgül, A., Akgül, E.K., Humphries, U.W.: Fractional modeling of COVID-19 pandemic model with real data from Pakistan under the ABC operator. AIMS Math. 7(9), 15939–15964 (2022)
Khan, A., Zarin, R., Hussain, G., Usman, A.H., Humphries, U.W., Aguilar, J.F.G.: Modeling and sensitivity analysis of HBV epidemic model with convex incidence rate. Results Phys. 22, 103836 (2021)
Joshi, H., Jha, B.K., Yavuz, M.: Modelling and analysis of fractional-order vaccination model for control of COVID-19 outbreak using real data. Math. Biosci. Eng. 20(1), 213–240 (2022)
Naik, P.A., Ghoreishi, M., Zu, J.: Approximate solution of a nonlinear fractional-order HIV model using homotopy analysis method. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Model. 19(1), 52–84 (2022)
Kaymakamzade, B.H.: A fractional-order two-strain epidemic model with two vaccinations. AIP Conf. Proc. 2325(1), 020048 (2021)
Özköse, F., Yavuz, M., Şenel, M.T., Habbireeh, R.: Fractional order modelling of omicron SARS-CoV-2 variant containing heart attack effect using real data from the United Kingdom. Chaos Soliton Fract. 157, 111954 (2022)
Nisar, K.S., Farman, M., Abdel-Aty, M., Cao, J.: A review on epidemic models in sight of fractional calculus. Alex. Eng. J. 75, 81–113 (2023)
Zafar, Z.U.A., Khan, M.A., Akgül, A., Asiri, M., Riaz, M.B.: The analysis of a new fractional model to the Zika virus infection with mutant. Heliyon 10(1), e23390 (2024)
Ahmad, A., Farman, M., Naik, P.A., et al.: Modeling and numerical investigation of fractional-order bovine babesiosis disease. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 37(3), 1946–1964 (2021)
Tang, T.Q., Shah, Z., Jan, R., Alzahrani, E.: Modeling the dynamics of tumor-immune cells interactions via fractional calculus. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 137, 367 (2022)
Zarin, R., Khaliq, H., Khan, A., Khan, D., Akgül, A., Humphries, U.W.: Deterministic and fractional modeling of a computer virus propagation. Results Phys. 33, 105130 (2022)
Khan, A., Zarin, R., Ahmed, I., Yusuf, A., Humphries, U.W.: Numerical and theoretical analysis of Rabies model under the harmonic mean type incidence rate. Results Phys. 29, 104652 (2021)
Tang, T.Q., Jan, R., Rehman, A.U., Shah, Z., Vrinceanu, N., Racheriu, M.: Modeling the dynamics of chronic myelogenous leukemia through fractional-calculus. Fractals 30(10), 2240262 (2022)
Naik, P.A., Eskandari, Z., Madzvamuse, A., Avazzadeh, Z., Zu, J.: Complex dynamics of a discrete-time seasonally forced SIR epidemic model. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 46(6), 7045–7059 (2023)
Farman, M., Tabassum, M.F., Naik, P.A., Akram, S.: Numerical treatment of a nonlinear dynamical hepatitis B model: an evolutionary approach. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 135(12), 941 (2020)
Naik, P.A., Eskandari, Z.: Nonlinear dynamics of a three-dimensional discrete-time delay neural network. Int. J. Biomath. 17(6), 2350057 (2024)
Naik, P.A., Pardasani, K.R.: Finite element model to study calcium signalling in oocyte cell. Int. J. Modern Math. Sci. 15(1), 58–71 (2017)
Joshi, H., Jha, B.K.: Chaos of calcium diffusion in Parkinson’s infectious disease model and treatment mechanism via Hilferfractional derivative. Math. Model. Numer. Simul. Appl. 1(2), 84–94 (2021)
Naik, P.A., Zehra, A., Farman, M., et al.: Forecasting and dynamical modeling of reversible enzymatic reactions with a hybrid proportional fractional derivative. Front. Phys. 11, 1307307 (2024)
Joshi, H., Yavuz, M.: Analysis of the disturbance effect in intracellular calcium dynamic on fibroblast cells with an exponential kernel law. Bull. Biomath. 1(1), 24–39 (2023)
Gholami, M., Khoshsiar, R., Eskandari, Z.: Three-dimensional fractional system with the stability condition and chaos control. Math. Model. Numer. Simul. Appl. 2(1), 41–47 (2023)
Farman, M., Akgül, A., Abdeljawad, A., et al.: Modeling and analysis of fractional order Ebola virus model with Mittag-Leffler kernel. Alex. Eng. J. 61(3), 2062–2073 (2022)
Naik, P.A., Owalabi, K.M., Yavuz, M., Zu, J.: Chaotic dynamics of a fractional order HIV-1 model involving AIDS-related cancer cells. Chaos Soliton Fract. 140, 110272 (2020)
Qureshi, S., Jan, R.: Modeling of measles epidemic with optimized fractional order under Caputo differential operator. Chaos Soliton Fract. 145, 110766 (2021)
Joshi, H., Yavuz, M.: Transition dynamics between a novel co-infection model of fractional-order for COVID-19 and tuberculosis via a treatment mechanism. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 138, 468 (2023)
Lacombe, K., Rockstroh, J.: HIV and viral hepatitis coinfections: advances and challenges. Gut 61, i47–i58 (2012)
Wiktor, S., Ford, N., Ball, A., Hirnschall, G.: HIV and HCV: distinct infections with important overlapping challenges. J. Int. AIDS Soc. 17(1), 19323 (2014)
Kraef, C., Bentzon, A., Skrahina, A., Mocroft, A., et al.: Improving healthcare for patients with HIV, tuberculosis and hepatitis C in eastern Europe: a review of current challenges and important next steps. HIV Med. 23, 48–59 (2022)
Carvalho, A.R.M., Pinto, C.A.M.: A coinfection model for HIV and HCV. Biosys. 124, 46–60 (2014)
Chen, J.Y., Feeney, E.R., Chung, R.T.: HCV, and HIV co-infection: mechanisms and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 11(6), 362–371 (2014)
Dayan, F., Ahmed, N., Bariq, A., et al.: Computational study of a co-infection model of HIV/AIDS and hepatitis C virus models. Sci. Rep. 13, 21938 (2023)
Moualeu, D.P., Mbang, J., Ndoundam, R., Bowong, S.: Modeling, and analysis of HIV and hepatitis c co-infections. J. Biol. Sys. 19(4), 683–723 (2011)
Podlubny, I.: Fractional differential equations. Academic Press, San Diego, CA, USA (1999)
Owolabi, K.M., Atangana, A.: Numerical methods for fractional differentiation. Springer, Singapore 54, (2019)
Garrappa, R.: On the linear stability of predictor-corrector algorithms for fractional differential equations. Int. J. Comput. Math. 87(10), 2281–2290 (2010)
Pinto, C.M., Carvalho, A.: Effects of treatment, awareness and condom use in a coinfection model for HIV and HCV in MSM. J. Biol. Sys. 23(2), 165–193 (2015)
Renzaho, A.M., Kamara, J.K., Georgeou, N., Kamanga, G.: Sexual, reproductive health needs, and rights of young people in slum areas of Kampala, Uganda: a cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE 12(1), e0169721 (2017)
Pinkerton, S.D.: Probability of HIV transmission during acute infection in Rakai. Uganda. AIDS Behav. 12, 677–684 (2008)
Bhunu, C.P., Mushayabasa, S.: Modelling the transmission dynamics of HIV/AIDS and hepatitis C virus co-infection. HIV and AIDS Rev. 12(2), 37–42 (2013)
Sanchez, A.Y.C., Aerts, M., Shkedy, Z., Vickerman, P., et al.: A mathematical model for HIV and hepatitis C co-infection and its assessment from a statistical perspective. Epidemics 5(1), 56–66 (2013)
Shen, M., Xiao, Y., Zhou, W., Li, Z.: Global dynamics and applications of an epidemiological model for hepatitis C virus transmission in China. Discrete Dyn. Nat. Soc. 6, 543029 (2015)
Shah, N.H., Patel, Z.A., Yeolekar, B.M.: Vertical transmission of HIV-HBV co-infection with liquor habit and vaccination. Malays. J. Math. Sci. 16(1), 119–142 (2022)
Özköse, F., Yavuz, M.: An investigation of interactions between COVID-19 and diabetes with hereditary traits using real data: a case study in Turkey. Comput. Biol. Med. 141, 105044 (2022)
Naik, P.A.: Global dynamics of a fractional-order SIR epidemic model with memory. Int. J. Biomath. 13(8), 2050071 (2020)
Xu, C., Liu, Z., Pang, Y., et al.: Dynamics of HIV-TB coinfection model using classical and Caputo piecewise operator: a dynamic approach with real data from South-East Asia, European and American regions. Chaos Soliton Fract. 165, 112879 (2022)
Cheneke, K.R.: Caputo fractional derivative for analysis of COVID-19 and HIV/AIDS transmission. Abstr. Appl. Anal. 2023, 6371148 (2023)
Al-Shomrani, M.M., Musa, S.S., Yusuf, A.: Unfolding the transmission dynamics of monkeypox virus: an epidemiological modelling analysis. Mathematics 11(5), 1121 (2023)
Ahmad, H., Khan, M.N., Ahmad, I., Omri, M., Alotaibi, M.F.: A meshless method for numerical solutions of linear and nonlinear time-fractional Black-Scholes models. AIMS Math. 8(8), 19677–19698 (2023)
Qayyum, M., Ahmad, E., Saeed, T., Ahmad, H., Askar, S.: Homotopy perturbation method-based soliton solutions of the time-fractional (2+1)-dimensional Wu-Zhang system describing long dispersive gravity water waves in the ocean. Front. Phys. 11, 1178154 (2023)
Hashemi, M.S., Mirzazadeh, M., Ahmad, H.: A reduction technique to solve the (2+ 1)-dimensional KdV equations with time local fractional derivatives. Opt. Quantum Electron. 55(8), 721 (2023)
Zarin, R., Khan, M., Khan, A., Yusuf, A.: Deterministic and fractional analysis of a newly developed dengue epidemic model. Waves in Random and Complex Media (2023). https://doi.org/10.1080/17455030.2023.2226765
Partohaghighi, M., Yusuf, A., Alshomrani, A.S., Sulaiman, T.A., Baleanu, D.: Fractional hyper-chaotic system with complex dynamics and high sensitivity: applications in engineering. Int. J. Modern Phys. B. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0217979224500127
Al-deiakeh, R., Al-Smadi, M., Yusuf, A., Al-Omari, S., Momani, S.: Explicit solutions for fractional Chaffee-Infante reaction-diffusion coupled hierarchy system with conservation laws. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 46(12), 12777–12793 (2023)
Diethelm, K.: An algorithm for the numerical solution of differential equations of fractional order. Electron T. Numer. Ana. 5, 1–6 (1997)
Diethelm, K., Ford, N.J.: Analysis of fractional differential equations. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 265, 229–248 (2002)
Diethelm, K., Ford, N.J., Freed, A.D.: A predictor-corrector approach for the numerical solution of fractional differential equations. Nonlinear Dynam. 29, 3–22 (2002)
Naik, P.A., Zu, J., Owolabi, K.M.: Modeling the mechanics of viral kinetics under immune control during primary infection of HIV-1 with treatment in fractional order. Phys. A 545, 123816 (2020)
Ghori, M.B., Naik, P.A., Zu, J., Eskandari, Z., Naik, M.: Global dynamics and bifurcation analysis of a fractional-order SEIR epidemic model with saturation incidence rate. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 45(7), 3665–3688 (2022)
Yavuz, M., Bonyah, E.: New approaches to the fractional dynamics of schistosomiasis disease model. Phys. A 525, 373–393 (2019)
Owolabi, K.M., Atangana, A.: Numerical approximation of nonlinear fractional parabolic differential equations with Caputo-Fabrizio derivative in Riemann-Liouville sense. Chaos Soliton Fract. 99, 171–179 (2017)
Yavuz, M., Ozdemir, N.: A different approach to the European option pricing model with new fractional operator. Math. Model. Nat. Phenom. 13(1), 12 (2018)
Gallegos, J.A., Mermoud, M.A.D.: Boundedness and convergence on fractional order systems. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 296, 815–826 (2016)
Teka, W.W., Upadhyay, R.K., Mondal, A.: Spiking and bursting patterns of fractional-order Izhikevich model. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 56, 161–176 (2018)
Camacho, N.A., Mermoud, M.A.D., Gallegos, J.A.: Lyapunov functions for fractional order systems. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 19(9), 2951–2957 (2014)
Carvalho, A., Pinto, C.M.A., Baleanu, D.: HIV/HCV coinfection model: a fractional-order perspective for the effect of the HIV viral load. Adv. differ. equ. 2018(1), 2 (2018)
Carvalho, A., Pinto, C.M.A.: The burden of the HIV viral load and of cell-to-cell spread in HIV/HCV coinfection. IFAC-PapersOnLine 51(2), 367–372 (2018)
Wyatt, A., Levy, D.: Modeling the effect of memory in the adaptive immune response. Bull. Math. Biol. 82(9), 124 (2020)
Kim, C.H.: FOXP3 and Its Role in the Immune System. In: Maiese, K. (ed.) Forkhead Transcription Factors. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. Springer, New York (2009)
Sturmlechner, I., Jain, A., Mu, Y., Weyand, C.M., Goronzy, J.J.: T cell fate decisions during memory cell generation with aging. Semin. Immunol. 69, 101800 (2023)
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Scientific Research Project for High-Level Talents of Youjiang Medical University for Nationalities, Baise, Guangxi, China under grant number yy2023rcky002. AM is a Canada Research Chair (Tier 1) in Theoretical and Computational Biology (CRC-2022-00147). The work of AM was partially supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC), Discovery Grants Program (RGPIN-2023-05231). The funding bodies did not play any role in the design of the study and in writing the manuscript.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known Conflict of interest or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Naik, P.A., Yeolekar, B.M., Qureshi, S. et al. Modeling and analysis of the fractional-order epidemic model to investigate mutual influence in HIV/HCV co-infection. Nonlinear Dyn (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-024-09653-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-024-09653-1