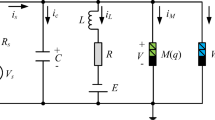
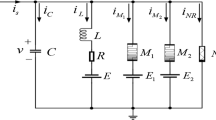
Abstract
Capacitive membrane and inductive channels enable the approach of neural activities in some equivalent neural circuits, and involvement of memristive term and magnetic flux can estimate the effect of electromagnetic induction. Based on the memristive neuron models, synaptic controllability and field coupling between neurons can be explored from physical aspect. Most of the biophysical neurons are defined in nonlinear oscillators, which can be mapped from the circuit equations under scale transformation, and the energy functions can be obtained in theoretical way. To enrich complex dynamics, specific terms are often introduced into the known models, and it requires the involvement of specific electric components for inducting special relation between the channel current and across voltage. Indeed, mathematical maps are effective to produce similar firing modes matching with neural activities in biological neurons. In this work, memristor is connected to a simple nonlinear circuit for building a memristive neuron, and its energy function is derived from two ways. Under linear transformation, the memristive neuron in oscillator form is converted into a memristive map, the energy function is confirmed, and an adaptive criterion is presented to regulate the intrinsic parameter, which the self-adaptive regulation property is released. The scheme provides clues to design discrete neuron models and understand its role of energy flow on the self-adaptive property and mode selection.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data are available under reasonable request.
References
Wang, Y., Zhang, D., Wang, L., et al.: Cluster synchronization induced by manifold deformation. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 32, 113118 (2022)
Fan, H., Kong, L.W., Lai, Y.C., et al.: Anticipating synchronization with machine learning. Phys. Rev. Res. 3, 023237 (2021)
He, Z., Yao, C., Liu, S., et al.: Transmission of pacemaker signal in a small world neuronal networks: temperature effects. Nonlinear Dyn. 106, 2547–2557 (2021)
Wu, Y., Ding, Q., Li, T., et al.: Effect of temperature on synchronization of scale-free neuronal network. Nonlinear Dyn. 111, 2693–2710 (2023)
Huang, W., Yang, L., Zhan, X., et al.: Synchronization transition of a modular neural network containing subnetworks of different scales. Front. Inf. Technol. Electron. Eng. 24, 1458–1470 (2023)
Xu, Q., Ding, S., Bao, H., et al.: Piecewise-linear simplification for adaptive synaptic neuron model. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 69, 1832–1836 (2021)
Bao, H., Zhang, J., Wang, N., et al.: Adaptive synapse-based neuron model with heterogeneous multistability and riddled basins. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 32, 123101 (2022)
Stepp, N., Plenz, D., Srinivasa, N.: Synaptic plasticity enables adaptive self-tuning critical networks. PLoS Comput. Biol. 11, e1004043 (2015)
Emelyanov, A.V., Nikiruy, K.E., Serenko, A.V., et al.: Self-adaptive STDP-based learning of a spiking neuron with nanocomposite memristive weights. Nanotechnology 31, 045201 (2019)
Hajian, D.N., Ramadoss, J., Natiq, H., et al.: Dynamics of Hindmarsh–Rose neurons connected via adaptive memristive synapse. Chin. J. Phys. 87, 311–329 (2024)
Ramakrishnan, B., Mehrabbeik, M., Parastesh, F., et al.: A new memristive neuron map model and its network’s dynamics under electrochemical coupling. Electronics 11, 153 (2022)
Shen, H., Yu, F., Wang, C., et al.: Firing mechanism based on single memristive neuron and double memristive coupled neurons. Nonlinear Dyn. 110, 3807–3822 (2022)
Yang, R., Huang, H.M., Guo, X.: Memristive synapses and neurons for bioinspired computing. Adv. Electron. Mater. 5, 1900287 (2019)
Zhang, Y., He, W., Wu, Y., et al.: Highly compact artificial memristive neuron with low energy consumption. Small 14, 1802188 (2018)
An, X., Qiao, S.: The hidden, period-adding, mixed-mode oscillations and control in a HR neuron under electromagnetic induction. Chaos Solitons Fractals 143, 110587 (2021)
Wu, F.Q., Ma, J., Zhang, G.: Energy estimation and coupling synchronization between biophysical neurons. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 63, 625–636 (2020)
Xie, Y., Yao, Z., Hu, X., et al.: Enhance sensitivity to illumination and synchronization in light-dependent neurons. Chin. Phys. B 30, 120510 (2021)
Sun, G., Yang, F., Ren, G., et al.: Energy encoding in a biophysical neuron and adaptive energy balance under field coupling. Chaos Solitons Fractals 169, 113230 (2023)
Wu, F., Guo, Y., Ma, J., et al.: Synchronization of bursting memristive Josephson junctions via resistive and magnetic coupling. Appl. Math. Comput. 455, 128131 (2023)
Wu, F., Yao, Z.: Dynamics of neuron-like excitable Josephson junctions coupled by a metal oxide memristive synapse. Nonlinear Dyn. 111, 13481–13497 (2023)
Zhang, H., Wang, L., Zhang, P., et al.: Estimation of biophysical properties of cell exposed to electric field. Chin. Phys. B 30, 038702 (2021)
Stubbe, M., Gimsa, J.: Maxwell’s mixing equation revisited: characteristic impedance equations for ellipsoidal cells. Biophys. J. 109, 194–208 (2015)
Maswiwat, K., Wachner, D., Gimsa, J.: Effects of cell orientation and electric field frequency on the transmembrane potential induced in ellipsoidal cells. Bioelectrochemistry 74, 130–141 (2008)
Ma, J.: Biophysical neurons, energy, and synapse controllability: a review. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 24, 109–129 (2023)
Njitacke, Z.T., Takembo, C.N., Awrejcewicz, J., et al.: Hamilton energy, complex dynamical analysis and information patterns of a new memristive FitzHugh–Nagumo neural network. Chaos Solitons Fractals 160, 112211 (2022)
Hou, B., Hu, X., Guo, Y., et al.: Energy flow and stochastic resonance in a memristive neuron. Phys. Scr. 98, 105236 (2023)
Yang, F., Ren, G., Tang, J.: Dynamics in a memristive neuron under an electromagnetic field. Nonlinear Dyn. 111, 21917–22193 (2023)
Yamakou, M.E.: Chaotic synchronization of memristive neurons: Lyapunov function versus Hamilton function. Nonlinear Dyn. 101, 487–500 (2020)
Jia, J., Yang, F., Ma, J.: A bimembrane neuron for computational neuroscience. Chaos Solitons Fractals 173, 113689 (2023)
Yang, F., Guo, Q., Ma, J.: A neuron model with nonlinear membranes. Cogn. Neurodyn. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-023-10017-5
Guo, Y., Wu, F., Yang, F., et al.: Physical approach of a neuron model with memristive membranes. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 33, 113106 (2023)
Mladenov, V., Kirilov, S.: Analysis of the mutual inductive and capacitive connections and tolerances of memristors parameters of a memristor memory matrix. In: 2013 European Conference on Circuit Theory and Design (ECCTD), pp. 1–4. IEEE (2013)
Mladenov, V.: Analysis and simulations of hybrid memory scheme based on memristors. Electronics 7, 289 (2018)
Mladenov, V.: A modified tantalum oxide memristor model for neural networks with memristor-based synapses. In: 2020 9th International Conference on Modern Circuits and Systems Technologies (MOCAST), pp. 1–4. IEEE (2020)
Yang, X., Taylor, B., Wu, A., et al.: Research progress on memristor: from synapses to computing systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 69, 1845–1857 (2022)
Ascoli, A., Weiher, M., Herzig, M., et al.: Graph coloring via locally-active memristor oscillatory networks. J. Low Power Electron. Appl. 12, 22 (2022)
Chen, S., Zhang, T., Tappertzhofen, S., et al.: Electrochemical-memristor-based artificial neurons and synapses-fundamentals, applications, and challenges. Adv. Mater. 35, 2301924 (2023)
Messaris, I., Ascoli, A., Demirkol, A.S., et al.: High frequency response of non-volatile memristors. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 70, 566–578 (2022)
Jiang, B., Ke, S.W., Tao, Z.P., et al.: In-depth analysis of core–shell filaments in nonvolatile NbOx memristive device as an artificial synapse for multifunctional bionic applications. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 66, 3596–3603 (2023)
Bao, H., Chen, Z.G., Cai, J.M., et al.: Memristive cyclic three-neuron-based neural network with chaos and global coexisting attractors. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 65, 2582–2592 (2022)
Li, X.J., Wang, X., Li, P., et al.: Ternary combinational logic gates design based on tri-valued memristors. Front. Phys. 11, 1292336 (2023)
Wang, X., Zhang, X., Dong, C., et al.: Design and application of memristive balanced ternary univariate logic circuit. Micromachines 14, 1895 (2023)
Maruf, M.H., Ashrafi, M.S.I., Shihavuddin, A.S.M., et al.: Design and comparative analysis of memristor-based transistor-less combinational logic circuits. Int. J. Electron. 109, 1291–1306 (2022)
Wang, X.Y., Dong, C.T., Wu, Z.R., et al.: A review on the design of ternary logic circuits. Chin. Phys. B 30, 128402 (2021)
Maan, A.K., Jayadevi, D.A., James, A.P.: A survey of memristive threshold logic circuits. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 28, 1734–1746 (2016)
Guo, Y., Xie, Y., Ma, J.: How to define energy function for memristive oscillator and map. Nonlinear Dyn. 111, 21903–21915 (2023)
Ma, J.: Energy function for some maps and nonlinear oscillators. Appl. Math. Comput. 463, 128379 (2024)
Niven, J.E.: Neuronal energy consumption: biophysics, efficiency and evolution. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 41, 129–135 (2016)
Sotero, R.C., Trujillo-Barreto, N.J.: Biophysical model for integrating neuronal activity, EEG, fMRI and metabolism. Neuroimage 39, 290–309 (2008)
Yu, T., Sejnowski, T.J., Cauwenberghs, G.: Biophysical neural spiking, bursting, and excitability dynamics in reconfigurable analog VLSI. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 5, 420–429 (2011)
Wu, F.Q., Guo, Y.T., Ma, J.: Energy flow accounts for the adaptive property of functional synapses. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 66, 3139–3152 (2023)
Yang, F., Xu, Y., Ma, J.: A memristive neuron and its adaptability to external electric field. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 33, 023110 (2023)
Fox, R.F., Gatland, I.R., Roy, R., et al.: Fast, accurate algorithm for numerical simulation of exponentially correlated colored noise. Phys. Rev. A 38, 5938 (1988)
Ginoux, J.M., Meucci, R., Euzzor, S., et al.: Torus breakdown in a two-stroke relaxation memristor. Chaos Solitons Fractals 153, 111594 (2021)
Sharma, P.K., Prasad, S.S., Tasneem, S., et al.: Resistive tunable memristor emulator model and its application. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 160, 154500 (2023)
Sun, J., Yang, J., Xiao, X., et al.: Emotion-based behavioral inhibition and self-repairing memristive circuit. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 157, 154424 (2022)
Prasad, S.S., Kumar, P., Raj, N., et al.: A compact floating and grounded memristor model using single active element. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 157, 154426 (2022)
Yang, Y., Ma, M., Li, Z., et al.: A memristive non-smooth dynamical system with coexistence of bimodule periodic oscillation. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 153, 154279 (2022)
Zhong, H., Li, G., Xu, X.: A generic voltage-controlled discrete memristor model and its application in chaotic map. Chaos Solitons Fractals 161, 112389 (2022)
Peng, Y., Sun, K., He, S.: A discrete memristor model and its application in Hénon map. Chaos Solitons Fractals 137, 109873 (2020)
Bao, H., Gu, Y., Xu, Q., et al.: Parallel bi-memristor hyperchaotic map with extreme multistability. Chaos Solitons Fractals 160, 112273 (2022)
Ren, L., Mou, J., Banerjee, S., et al.: A hyperchaotic map with a new discrete memristor model: design, dynamical analysis, implementation and application. Chaos Solitons Fractals 167, 113024 (2023)
Lai, Q., Yang, L.: Discrete memristor applied to construct neural networks with homogeneous and heterogeneous coexisting attractors. Chaos Solitons Fractals 174, 113807 (2023)
Acknowledgements
This project is partially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 12072139.
Funding
Funding was provided by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 12072139).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yanni Li and Mi Lv calculated all the numerical results and provided formal analysis. Jun Ma suggested this investigation and provided complete proof and wrote this manuscript. Xikui Hu verified the proof and numerical approach.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest with this publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Lv, M., Ma, J. et al. A discrete memristive neuron and its adaptive dynamics. Nonlinear Dyn 112, 7541–7553 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-024-09361-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-024-09361-w