Abstract
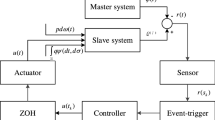
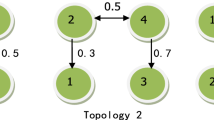
This article is concerned with the event-triggered quasi-synchronization for discrete Markov jump neural networks (MJNNs). Considering that the slave system cannot capture synchronously master system modes in real-world applications, a hidden Markov model is introduced to describe the resultant mode mismatches. To pursue a desired balance between the synchronization performance and the event-triggered transmission, a more general event-triggered protocol is constructed by developing the threshold parameter as a diagonal matrix. Subsequently, the sufficient condition for event-triggered quasi-synchronization of MJNNs is proposed with the assistance of Lyapunov techniques. Moreover, resorting to an iterative algorithm and the linear matrix inequality, the tighter error bound is obtained. Finally, a numerical example demonstrates effectiveness of the control scheme via a comparison of conservatism between the proposed approach and the existing one.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No data were used for the current study in this paper.
References
Ahn, C.K.: Switched exponential state estimation of neural networks based on passivity theory. Nonlinear Dyn. 67, 573–586 (2012)
Shen, H., Huang, Z., Yang, X., Wang, Z.: Quantized energy-to-peak state estimation for persistent dwell-time switched neural networks with packet dropouts. Nonlinear Dyn. 93(4), 2249–2262 (2018)
Lin, G., Li, H., Ahn, C.K., Yao, D.: Event-based finite-time neural control for human-in-the-loop UAV attitude systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3166531
Ni, Y., Wang, Z., Huang, X., Ma, Q., Shen, H.: Intermittent sampled-data control for local stabilization of neural networks subject to actuator saturation: a work-interval-dependent functional approach. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3180076
Li, C., Wu, S., Feng, G.G., Liao, X.: Stabilizing effects of impulses in discrete-time delayed neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 22(2), 323–329 (2011)
Li, C., Feng, G., Huang, T.: On hybrid impulsive and switching neural networks. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cyber. Part B (Cybernetics) 38(6), 1549–1560 (2008)
Stamov, G., Gospodinova, E., Stamova, I.: Practical exponential stability with respect to h-manifolds of discontinuous delayed Cohen–Grossberg neural networks with variable impulsive perturbations. Math. Model. Control 1, 26–34 (2021)
Tino, P., Cernansky, M., Benuskova, L.: Markovian architectural bias of recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 15(1), 6–15 (2004)
Shen, H., Zhu, Y., Zhang, L., Park, J.H.: Extended dissipative state estimation for Markov jump neural networks with unreliable links. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 28(2), 346–358 (2016)
Tao, J., Wu, Z.G., Su, H., Wu, Y., Zhang, D.: Asynchronous and resilient filtering for Markovian jump neural networks subject to extended dissipativity. IEEE Trans. Cyber. 49(7), 2504–2513 (2018)
Wang, J., Xing, M., Cao, J., Park, J.H., Shen, H.: \({H}_\infty \) bipartite synchronization of double-layer markov switched cooperation-competition neural networks: a distributed dynamic event-triggered mechanism. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. (2021)
Yao, L., Wang, Z., Huang, X., Li, Y., Ma, Q., Shen, H.: Stochastic sampled-data exponential synchronization of Markovian jump neural networks with time-varying delays. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 34(2), 909–920 (2023)
Mirollo, R.E., Strogatz, S.H.: Synchronization of pulse-coupled biological oscillators. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 50(6), 1645–1662 (1990)
Xu, Z., Li, C., Han, Y.: Impulsive consensus of nonlinear multi-agent systems via edge event-triggered control. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 31(6), 1995–2004 (2019)
Wang, X., Wang, H., Li, C., Huang, T., Kurths, J.: Consensus seeking in multiagent systems with Markovian switching topology under aperiodic sampled data. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cyber Syst 50(12), 5189–5200 (2018)
Chen, C., Xie, K., Lewis, F.L., Xie, S., Davoudi, A.: Fully distributed resilience for adaptive exponential synchronization of heterogeneous multiagent systems against actuator faults. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 64(8), 3347–3354 (2018)
Wang, X., Wang, H., Huang, T., Kurths, J.: Neural-network-based adaptive tracking control for nonlinear multiagent systems: the observer case. IEEE Trans. Cyber. 53(1), 138–150 (2023)
Ahmed, I., Rehan, M., Iqbal, N., Ahn, C.K.: A novel event-triggered consensus approach for generic linear multi-agents under heterogeneous sector-restricted input nonlinearities. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSE.2022.3232779
Zhou, X., Cheng, J., Cao, J., Ragulskis, M.: Asynchronous dissipative filtering for nonhomogeneous Markov switching neural networks with variable packet dropouts. Neural Netw. 130, 229–237 (2020)
Zhang, L., Zhong, J., Lu, J.: Intermittent control for finite-time synchronization of fractional-order complex networks. Neural Netw. 144, 11–20 (2021)
Hansel, D., Sompolinsky, H.: Synchronization and computation in a chaotic neural network. Phys. Rev. Lett. 68(5), 718 (1992)
Cao, J., Wan, Y.: Matrix measure strategies for stability and synchronization of inertial BAM neural network with time delays. Neural Netw. 53, 165–172 (2014)
Zhang, F., Zeng, Z.: Asymptotic stability and synchronization of fractional-order neural networks with unbounded time-varying delays. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cyber. Syst. 51(9), 5547–5556 (2019)
Li, H., Li, C., Ouyang, D., Nguang, S.K.: Impulsive synchronization of unbounded delayed inertial neural networks with actuator saturation and sampled-data control and its application to image encryption. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 32(4), 1460–1473 (2020)
Wang, Y., Lu, J., Li, X., Liang, J.: Synchronization of coupled neural networks under mixed impulsive effects: a novel delay inequality approach. Neural Netw. 127, 38–46 (2020)
Shen, H., Li, F., Wu, Z.G., Park, J.H.: Finite-time \(l_2-l_\infty \) tracking control for Markov jump repeated scalar nonlinear systems with partly usable model information. Inf. Sci. 332, 153–166 (2016)
He, W., Qian, F., Lam, J., Chen, G., Han, Q.L., Kurths, J.: Quasi-synchronization of heterogeneous dynamic networks via distributed impulsive control: error estimation, optimization and design. Automatica 62, 249–262 (2015)
Rao, H., Xu, Y., Peng, H., Lu, R., Su, C.Y.: Quasi-synchronization of time delay Markovian jump neural networks with impulsive-driven transmission and fading channels. IEEE Trans. Cyber. 50(9), 4121–4131 (2019)
Yue, D., Tian, E., Han, Q.L.: A delay system method for designing event-triggered controllers of networked control systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 58(2), 475–481 (2012)
Zhang, J., Raissi, T.: Indefinite Lyapunov-Razumikhin functions-based stability and event-triggered control of switched nonlinear time-delay systems. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. II Express Briefs 68(10), 3286–3290 (2021)
Tao, J., Xu, M., Chen, D., Xiao, Z., Rao, H., Xu, Y.: Event-triggered resilient filtering with the interval type uncertainty for Markov jump systems. IEEE Trans. Cyber. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2022.3227446
Liu, W., Yang, X., Rakkiyappan, R., Li, X.: Dynamic analysis of delayed neural networks: event-triggered impulsive Halanay inequality approach. Neurocomputing 498, 98–107 (2022)
Tao, J., Xiao, Z., Chen, J., Lin, M., Lu, R., Shi, P., Wang, X.: Event-triggered control for Markov jump systems subject to mismatched modes and strict dissipativity. IEEE Trans. Cyber. 53(3), 1537–1546 (2023)
Gu, Z., Ahn, C.K., Yan, S., Xie, X., Yue, D.: Event-triggered filter design based on average measurement output for networked unmanned surface vehicles. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. II Express Briefs 69(9), 3804–3808 (2022)
Wang, J., Chen, M., Shen, H.: Event-triggered dissipative filtering for networked semi-Markov jump systems and its applications in a mass-spring system model. Nonlinear Dyn. 87(4), 2741–2753 (2017)
Wang, J., Zhang, X.M., Lin, Y., Ge, X., Han, Q.L.: Event-triggered dissipative control for networked stochastic systems under non-uniform sampling. Inf. Sci. 447, 216–228 (2018)
Dai, M., Xia, J., Xia, H., Shen, H.: Event-triggered passive synchronization for Markov jump neural networks subject to randomly occurring gain variations. Neurocomputing 331, 403–411 (2019)
Zhang, J., Zheng, G., Feng, Y., Chen, Y.: Event-triggered state-feedback and dynamic output-feedback control of positive Markovian jump systems with intermittent faults. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 68(2), 1039–1046 (2023)
Yan, L., Chen, W., Fang, X., Dai, H.: Event-triggered synchronization for second-order nodes in complex dynamical network with time-varying coupling matrices. Nonlinear Dyn. 98(3), 2227–2245 (2019)
Wen, S., Zeng, Z., Chen, M.Z., Huang, T.: Synchronization of switched neural networks with communication delays via the event-triggered control. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 28(10), 2334–2343 (2016)
Yang, J., Lu, J., Li, L., Liu, Y., Wang, Z., Alsaadi, F.E.: Event-triggered control for the synchronization of Boolean control networks. Nonlinear Dyn. 96(2), 1335–1344 (2019)
Xu, Y., Huang, Z., Rao, H., Lu, R., Huang, T.: Quasi-synchronization for periodic neural networks with asynchronous target and constrained information. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cyber Syst (2019)
Wang, S., Cao, Y., Guo, Z., Yan, Z., Wen, S., Huang, T.: Periodic event-triggered synchronization of multiple memristive neural networks with switching topologies and parameter mismatch. IEEE Trans. Cyber (2020)
Dong, S., Liu, M.: Adaptive fuzzy asynchronous control for nonhomogeneous Markov jump power systems under hybrid attacks. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 31(3), 1009–1019 (2023)
Li, F., Xu, S., Shen, H., Ma, Q.: Passivity-based control for hidden Markov jump systems with singular perturbations and partially unknown probabilities. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 65(8), 3701–3706 (2019)
Dong, S., Xie, K., Chen, G., Liu, M., Wu, Z.G.: Extended dissipative sliding-mode control for discrete-time piecewise nonhomogeneous Markov jump nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Cyber. 52(9), 9219–9229 (2021)
Wu, Z., Chen, J., Zhang, X., Xiao, Z., Tao, J., Wang, X.: Dynamic event-triggered synchronization of complex networks with switching topologies: asynchronous observer-based case. Appl. Math. Comput. 435, 127413 (2022)
Cheng, P., He, S., Luan, X., Liu, F.: Finite-region asynchronous \({H}_\infty \) control for 2D Markov jump systems. Automatica 129, 109590 (2021)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and Guangdong Province Key Laboratory of Intelligent Decision and Cooperative Control for supporting the authors’ study.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62276069,62121004), the Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou (202201010337), and the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2022A1515010271).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study. ZW and ZX contributed to conceptualization, visualization, validation, and methodology. Funding acquisition and supervision were performed by JT and XZ. The original draft was written by ZW. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Z., Xiao, Z., Zhang, X. et al. Event-Triggered quasi-synchronization of neural networks with hidden Markov model-based asynchronous target. Nonlinear Dyn 111, 16145–16157 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-08679-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-08679-1