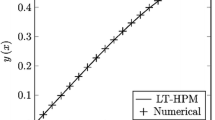
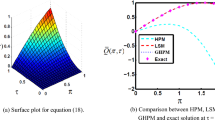
Abstract
Homotopy perturbation method (HPM) is one of the most popular semi-analytical methods to solve a nonlinear differential equation. However, in HPM, there is no strict rule for the choice of its linear operator, and its series solution may not always converges. In this study, firstly, we define the linear operator as an auxiliary linear operator (\({\mathcal {L}}_a\)), in the frame of homotopy analysis method (HAM). Then we generalize this \({\mathcal {L}}_a\) based on the auxiliary roots of \({\mathcal {L}}_a=0\). Finally, using the optimization technique (on minimization of the residual error) we determine the best-fitted optimal \({\mathcal {L}}_a\) for a problem. By doing this we ensure and accelerate the convergence of our semi-analytical homotopy perturbation series solution. Thereby we rename the HPM as Optimal and Modified Homotopy Perturbation Method (OMHPM). We consider three strongly nonlinear differential equations of nonlinear dynamical phenomena associated with the fluid dynamics to certify our technique. The dependencies of the form of the optimal \({\mathcal {L}}_a\) and the convergence of the solution (obtained by HPM, Optimal HAM and OMHPM) on the values of parameters (involved in the scale transformation), initial/boundary conditions and artificial controlling parameters (involved in optimal HAM) are explored here. It is reported that our OMHPM is highly accurate and efficient than HPM, optimal HAM and Domain decomposition optimal HAM. Moreover, OMHPM is simple and can be applied to directly to any singular/non-singular highly nonlinear ordinary differential equations without any decomposition, special/scale transformation, linearization, artificial controlling parameters and discretization. An attempt is made to apply our optimal auxiliary linear operator onto the optimal HAM for possible fastest convergence.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of supporting data
Not applicable.
References
Jafarimoghaddam, A., Rosca, N.C., Rosca, A.V., Pop, I.: The universal Blasius problem: New results by Duan–Rach Adomian Decomposition Method with Jafarimoghaddam contraction mapping theorem and numerical solutions. Math. Comput. Simul. 187, 60–76 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matcom.2021.02.014
Liao, S.J.: Proposed homotopy analysis technique for the solution of nonlinear problems. Ph.D. dissertation, Shanghai Jiaotong University, China (1992)
Liao, S.J., Tan, Y.: A general approach to obtain series solution of nonlinear differential equations. Stud. Appl. Math. 119, 297–355 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9590.2007.00387.x
Liao, S.J.: An Optimal Homotopy analysis approach for strongly nonlinear differential equations. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 15, 2003–2016 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnsns.2009.09.002
Odibat, Z.: On the optimal selection of the linear operator and the initial approximation in the application of the homotopy analysis method to nonlinear fractional differential equations. Appl. Numer. Math. 137, 203–212 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apnum.2018.11.003
Xu, H., Lin, Z.L., Liao, S.J., Wu, J.Z., Majdalani, J.: Homotopy based solutions of the Navier–Stokes equations for a porous channel with orthogonally moving walls. Phys. Fluids 22, 053601 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3392770
VanGorder, R.A., Vajravelu, K.: On the selection of auxiliary functions, operators and convergence control parameters in the application of the Homotopy Analysis Method to nonlinear differential equations: a general approach. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 14, 4078–4089 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnsns.2009.03.008
He, J.H.: Homotopy perturbation technique. J. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 178, 257–262 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-7825(99)00018-3
He, J.H.: Comparison of homotopy perturbation method and homotopy analysis method. Appl. Math. Comput. 156, 527–539 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2003.08.008
Esmaeilpour, M., Ganji, D.D.: Application of He’s homotopy perturbation method to boundary layer flow and convection heat transfer over a flat plate. Phys. Lett. A 372, 33–38 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physleta.2007.07.002
Jalili, P., Jalili, B., Shateri, A., Ganji, D.D.: A novel fractional analytical technique for the time-space fractional equations appearing in oil pollution. Int. J. Eng. 35, 2386–2394 (2022). https://doi.org/10.5829/ije.2022.35.12c.15
Pasha, S.A., Nawaz, Y., Arif, M.S.: The modified homotopy perturbation method with an auxiliary term for the nonlinear oscillator with discontinuity. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control (2018). https://doi.org/10.1177/0962144X18820454
Mahmood, B., Yousif, M.: A novel analytical solution for the modified Kawahara equation using the residual power series method. Nonlinear Dyn. 89, 1233–1238 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-017-3512-3
Zhang, R.F., Bilige, S.: Bilinear neural network method to obtain the exact analytical solutions of nonlinear partial differential equations and its application to p-gBKP equation. Nonlinear Dyn. 95, 3041–3048 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-04739-z
Zhang, R.F., Li, M.C., Cherraf, A., Vadyala, S.R.: The interference wave and the bright and dark soliton for two integro-differential equation by using BNNM. Nonlinear Dyn. 111, 8637–8646 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-08257-5
Liao, S.J.: An explicit, totally analytic approximate solution for Blasius viscous flow problems. Int. J. Non Linear Mech. 34, 759–778 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7462(98)00056-0
Liao, S.J.: Homotopy analysis method in nonlinear differential equations. New York, London, chapter-3 (2012). https://numericaltank.sjtu.edu.cn/KeyArticles/HAM2nd.pdf
Yabushita, K., Yamashita, M., Tsuboi, K.: An analytic solution of projective motion with the quadratic resistance law using homotopy analysis method. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 40, 8403–8416 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1088/1751-8113/40/29/015
Marinca, V., Herisanu, N.: The optimal homotopy asymptotic method for solving Blasius equation. Appl. Math. Comput. 231, 134–139 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2013.12.121
Kumar, R., Koundal, R., Shehzad, S.A.: Modified homotopy perturbation approach for the system of fractional partial differential equations: a utility of fractional Wronskian. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 45, 809–826 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/mma.7815
Odibat, Z.M.: A new modification of the homotopy perturbation method for linear and nonlinear operators. Appl. Math. Comput. 189, 746–753 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-008-0165-x
Sajid, M., Hayat, T.: Comparison of HAM and HPM in nonlinear heat conduction and convection equation. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 9, 2296–2301 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nonrwa.2007.08.007
Liao, S.J.: Comparison between the homotopy analysis method and homotopy perturbation method. Appl. Math. Comput. 169, 1186–1194 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2004.10.058
Turyilmazoglu, M.: Some issues on HPM and HAM method: a convergence scheme. Math. Comput. Model. 53, 1929–1936 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcm.2011.01.022
Ashrafi, T.G., Hoseinzadeh, S., Sohani, A., Shahverdian, M.H.: Applying homotopy perturbation method to provide an analytical solution for Newtonian fluid flow on a porous flat plate. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 44, 7017–7030 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/mma.7238
Ganji, D.D., Sahouli, A.R., Famouri, M.: A new modification of He’s homotopy perturbation method for rapid convergence of nonlinear undamped oscillators. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 30, 181–192 (2009)
Jalili, P., Ganji, D.D., Nourazar, S.S.: Hybrid semi analytical method for geothermal U shaped heat exchanger. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 12, 578–586 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csite.2018.07.010
Jalili, B., Jalili, P., Sadighi, S., Ganji, D.D.: Effect of magnetic and boundary parameters on flow characteristics analysis of micropolar ferrofluid through the shrinking sheet with effective thermal conductivity. Chin. J. Phys. 71, 136–150 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjph.2020.02.034
Blasius, H.: Grenzschichten in Flussigkeiten mit kleiner Reibung. Z. Math. Phys 56, 1–37 (1908)
Wang, L.: A new algorithm for solving classical Blasius equation. Appl. Math. Comput. 157, 1–9 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2003.06.011
Wazwaz, A.M.: The variational iteration method for solving two forms of Blasius equation on a half-infinite domain. Appl. Math. Comput. 188, 485–491 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2006.10.009
Roul, P., Madduri, H.: A new highly accurate domain decomposition optimal homotopy analysis method and its convergence for singular boundary value problems. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 41, 6625–6644 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/mma.5181
Roul, P., Biswal, D.: A new numerical approach for solving a class of singular two-point boundary value problems. Numer. Algorithm 75, 531–552 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11075-016-0210-z
Roul, P.: On the numerical solution of singular two-point boundary value problems: a domain decomposition homotopy perturbation approach. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 40, 7396–7409 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/mma.4536
Liang, S., Jeffrey, D.: Comparison of homotopy analysis method and homotopy perturbation method through an evolution equation. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 14, 4057–4064 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnsns.2009.02.016
Kolbig, K.S.: The complete Bell polynomials for certain arguments in terms of Stirling numbers of the first kind. Appl. Math. Comput. 51, 113–116 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-0427(94)00010-7
Bataller, R.C.: Numerical comparison of Blasius and Sakiadis Flows. Mathematica 26, 187–196 (2010). https://doi.org/10.11113/matematika.v26.n.562
Howarth, L.: On the solution of the laminar boundary layer equations. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 164, 547 (1938). https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.1938.0037
Asaithambi, A.: Solution of the Falkner–Skan equation by recursive evaluation of Taylor coefficients. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 176, 203–214 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cam.2004.07.013
Martínez, H.Y., Aguilar, J.F.G.: A new modified definition of Caputo–Fabrizio fractional-order derivative and their applications to the Multi Step Homotopy Analysis Method (MHAM). J. Comput. Appl. Math. 346, 247–260 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cam.2018.07.023
Odibat, Z., Momani, S., Xu, H.: A reliable algorithm of homotopy analysis method for solving nonlinear fractional differential equations. Appl. Math. Model. 34, 593–600 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2009.06.025
Acknowledgements
Authors are very grateful to anonymous referees for their valuable suggestions and comments which improved the paper. Also thankfully acknowledge support given by the DST-FIST, INDIA (Sanction Order No.: SR/FST/MS1/2018/21(C) dated-13/12/2019) for upgradation of research facility at the departmental level.
Funding
Govt. of West Bengal, INDIA supports scholarship to Mr. Roy for Ph.D. through the Swami Vivekananda Merit Cum Means Scholarship Scheme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TR has done mathematical calculation, developed the numerical code and partly written the manuscript, while DK Maiti conceived the problem, verified the results, and supervised the overall numerical computation and finalize the whole manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
We give our consent for the publication of identifiable details, which can include within the manuscript to be published in the Journal and Article.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Human and animal ethics
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Roy, T., Maiti, D.K. An optimal and modified homotopy perturbation method for strongly nonlinear differential equations. Nonlinear Dyn 111, 15215–15231 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-08662-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-08662-w