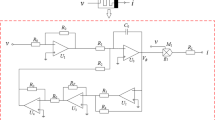
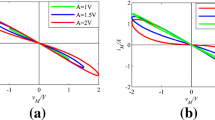
Abstract
Transition of firing modes via synapse is a crucial step in neural coding. The neuron/synapse-like circuits have been proposed to simulate neural behaviors and functions. Despite a few researches of the mimicking neuron inspired on Josephson junction, the dynamical explanation of neuron-like junction is still unclear. We explore the dynamics in the Josephson junction composed of capacitor, nonlinear resistor and supercurrent component. The biophysical mechanism of neuron-like excitability in the junction is further interpreted by using frequency-current curve and two-parameter bifurcation plane. We propose the coupled model with memristive synaptic connection between two junctions to replace the synaptic coupling and neurons bridged for information exchange. It is found that the multiple modes are induced and controlled by the memristive synapse with plasticity. Meanwhile, the firing states of the two junctions with memristive synapse become synchronized under the suitable choices of parameters. These could help in the development of brain-like system with the Josephson junctions and memristive devices.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Gosak, M., Milojević, M., Duh, M., Skok, K., Perc, M.: Networks behind the morphology and structural design of living systems. Phys. Life Rev. 41, 1–21 (2022)
Majhi, S., Perc, M., Ghosh, D.: Dynamics on higher-order networks: a review. J. R. Soc. Interface. 19, 20220043 (2022)
Ma, J.: Biophysical neurons, energy, and synapse controllability: a review. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A. 24, 109–129 (2023)
Trenchard, H., Perc, M.: Energy saving mechanisms, collective behavior and the variation range hypothesis in biological systems: a review. BioSystems. 147, 40–66 (2016)
Shilnikov, A., Cymbalyuk, G.: Transition between tonic spiking and bursting in a neuron model via the blue-sky catastrophe. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 048101 (2005)
Izhikevich, E.M.: Neural excitability, spiking and bursting. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos. 10, 1171–1266 (2000)
Morozova, E.O., Zakharov, D., Gutkin, B.S., Lapish, C.C., Kuznetsov, A.: Dopamine neurons change the type of excitability in response to stimuli. PLoS Comput. Biol. 12, e1005233 (2016)
Bard Ermentrout, G., Terman, D.H.: Mathematical Foundations of Neuroscience. Springer, New York (2010)
Mahowald, M., Douglas, R.: A silicon neuron. Nature 354, 515–518 (1991)
Wang, N., Zhang, G.S., Bao, H.: Bursting oscillations and coexisting attractors in a simple memristor-capacitor-based chaotic circuit. Nonlinear Dyn. 97, 1477–1494 (2019)
Xu, L., Qi, G.Y., Ma, J.: Modeling of memristor-based Hindmarsh-Rose neuron and its dynamical analyses using energy method. Appl. Math. Model. 101, 503–516 (2022)
Ren, G., Xu, Y., Wang, C.: Synchronization behavior of coupled neuron circuits composed of memristors. Nonlinear Dyn. 88, 893–901 (2017)
Zhang, G., Ma, J., Alsaedi, A., Ahmad, B., Alzahrani, F.: Dynamical behavior and application in Josephson junction coupled by memristor. Appl. Math. Comput. 321, 290–299 (2018)
Bao, H., Zhang, Y., Liu, W., Bao, B.: Memristor synapse-coupled memristive neuron network: synchronization transition and occurrence of chimera. Nonlinear Dyn. 100, 937–950 (2020)
Zhang, G., Wu, F.Q., Hayat, T., Ma, J.: Selection of spatial pattern on resonant network of coupled memristor and Josephson junction. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 65, 79–90 (2018)
Krzysteczko, P., Münchenberger, J., Schäfers, M., Reiss, G., Thomas, A.: The memristive magnetic tunnel junction as a nanoscopic synapse-neuron system. Adv. Mater. 24, 762–766 (2012)
Zhang, T., Yang, K., Xu, X., Cai, Y., Yang, Y., Huang, R.: Memristive devices and networks for brain-inspired computing. Phys. Status Solidi Rapid Res. Lett. 13, 1900029 (2019)
Najem, J.S., Taylor, G.J., Weiss, R.J., Hasan, M.S., Rose, G., Schuman, C.D., Belianinov, A., Collier, C.P., Sarles, S.A.: Memristive ion channel-doped biomembranes as synaptic mimics. ACS Nano 12, 4702–4711 (2018)
Jo, S.H., Chang, T., Ebong, I., Bhadviya, B.B., Mazumder, P., Lu, W.: Nanoscale memristor device as synapse in neuromorphic systems. Nano Lett. 10, 1297–1301 (2010)
Chang, T., Jo, S.H., Kim, K.H., Sheridan, P., Gaba, S., Lu, W.: Synaptic behaviors and modeling of a metal oxide memristive device. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 102, 857–863 (2011)
Moon, J., Ma, W., Shin, J.H., Cai, F., Du, C., Lee, S.H., Lu, W.D.: Temporal data classification and forecasting using a memristor-based reservoir computing system. Nat. Electron. 2, 480–487 (2019)
Wang, J., Zhuge, F.: Memristive synapses for brain-inspired computing. Adv. Mater. Technol. 4, 1800544 (2019)
Bao, B.C., Zhu, Y.X., Ma, J., Bao, H., Wu, H.G., Chen, M.: Memristive neuron model with an adapting synapse and its hardware experiments. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 64, 1107–1117 (2021)
Sahu, D.P., Jetty, P., Jammalamadaka, S.N.: Graphene oxide based synaptic memristor device for neuromorphic computing. Nanotechnology 32, 155701 (2021)
Wang, R., Mu, Z., Sun, H., Wang, Y.: Dual-mode memristor synaptic circuit design and application in image processing. Front. Phys. 9, 690944 (2021)
Maheshwar, P.S., Yang, C., Kim, H., Chua, L.: A voltage mode memristor bridge synaptic circuit with memristor emulators. Sensors. 12, 3587–3604 (2012)
Wu, F.Q., Guo, Y.T., Ma, J.: Reproduce the biophysical function of chemical synapse by using a memristive synapse. Nonlinear Dyn. 109, 2063–2084 (2022)
Guo, Y., Zhou, P., Yao, Z., Ma, J.: Biophysical mechanism of signal encoding in an auditory neuron. Nonlinear Dyn. 105, 3603–3614 (2021)
Liu, Y., Xu, W., jiang Ma, J., Alzahrani, F., Hobiny, A.: A new photosensitive neuron model and its dynamics. Front. Inf. Technol. Electron. Eng. 21, 1387–1396 (2020)
Xie, Y., Yao, Z., Hu, X., Ma, J.: Enhance sensitivity to illumination and synchronization in light-dependent neurons. Chinese Phys. B. 30, 120510 (2021)
Tagne, J.F., Edima, H.C., Njitacke, Z.T., Kemwoue, F.F., Mballa, R.N., Atangana, J.: Bifurcations analysis and experimental study of the dynamics of a thermosensitive neuron conducted simultaneously by photocurrent and thermistance. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 231, 993–1004 (2022)
Takembo, C.N., Mvogo, A., Ekobena Fouda, H.P., Kofané, T.C.: Effect of electromagnetic radiation on the dynamics of spatiotemporal patterns in memristor-based neuronal network. Nonlinear Dyn. 95, 1067–1078 (2019)
Takembo, C.N., Mvogo, A., Fouda, H.P.E., Kofané, T.C.: Wave pattern stability of neurons coupled by memristive electromagnetic induction. Nonlinear Dyn. 96, 1083–1093 (2019)
Xie, Y., Zhou, P., Ma, J.: Energy balance and synchronization via inductive-coupling in functional neural circuits. Appl. Math. Model. 113, 175–187 (2023)
Upadhyay, R.K., Sharma, S.K., Mondal, A., Mondal, A.: Emergence of hidden dynamics in different neuronal network architecture with injected electromagnetic induction. Appl. Math. Model. 111, 288–309 (2022)
Sun, J., Li, C., Lu, T., Akgul, A., Min, F.: A memristive chaotic system with hypermultistability and its application in image encryption. IEEE Access. 8, 139289–139298 (2020)
Yao, Z., Wang, C.: Control the collective behaviors in a functional neural network. Chaos, Solitons and Fractals. 152, 111361 (2021)
Tankou Tagne, A.S., Takembo, C.N., Ben-Bolie, H.G., Owona Ateba, P.: Localized nonlinear excitations in diffusive memristor-based neuronal networks. PLoS ONE 14, e0214989 (2019)
Mishra, A., Ghosh, S., Kumar Dana, S., Kapitaniak, T., Hens, C.: Neuron-like spiking and bursting in Josephson junctions: a review. Chaos 31, 052101 (2021)
Likharev, K.K.: Dynamics of Josephson Junctions and Circuits. Gordon and Breach, New York (1986)
Crotty, P., Schult, D., Segall, K.: Josephson junction simulation of neurons. Phys. Rev. E. 82, 011914 (2010)
Hens, C., Pal, P., Dana, S.K.: Bursting dynamics in a population of oscillatory and excitable Josephson junctions. Phys. Rev. E. 92, 022915 (2015)
Levi, M., Hoppensteadt, F.C., Miranker, W.L.: Dynamics of the Josephson junction. Q. Appl. Math. 36, 167–198 (1978)
Chalkiadakis, D., Hizanidis, J.: Dynamical properties of neuromorphic Josephson junctions. Phys. Rev. E. 106, 044206 (2022)
Hu, C.K.: Spiking and bursting in Josephson junction. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Exp. Briefs. 53, 1031–1034 (2006)
Blackburn, J.A., Smith, H.J.T.: Dynamics of double-Josephson-junction interferometers. J. Appl. Phys. 49, 2452–2455 (1978)
Wiesenfeld, K., Colet, P., Strogatz, S.H.: Synchronization Transitions in a Disordered Josephson Series Array. Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 404–407 (1996)
Ray, A., Mishra, A., Ghosh, D., Kapitaniak, T., Dana, S.K., Hens, C.: Extreme events in a network of heterogeneous Josephson junctions. Phys. Rev. E. 101, 032209 (2020)
Zibold, T., Nicklas, E., Gross, C., Oberthaler, M.K.: Classical bifurcation at the transition from rabi to Josephson dynamics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 204101 (2010)
Zhang, Y., Wang, C.N., Tang, J., Ma, J., Ren, G.D.: Phase coupling synchronization of FHN neurons connected by a Josephson junction. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 63, 2328–2338 (2020)
Segall, K., Legro, M., Kaplan, S., Svitelskiy, O., Khadka, S., Crotty, P., Schult, D.: Synchronization dynamics on the picosecond time scale in coupled Josephson junction neurons. Phys. Rev. E. 95, 032220 (2017)
Marcus, P.M., Imry, Y., Ben-Jacob, E.: Characteristic modes and the transition to chaos of a resonant Josephson circuit. Solid State Commun. 41, 161–166 (1982)
Whan, C.B., Lobb, C.J.: Complex dynamical behavior in RCL-shunted Josephson tunnel junctions. Phys. Rev. E. 53, 405–413 (1996)
Zhou, Z.Y., Xiao, H., Wang, S., Fu, X.H., Yan, J.: Preparation and DC characteristics of MgB2/B/MgB2 josephson junctions. Acta Phys. Sin. 65, 180301 (2016)
Prescott, S.A., De Koninck, Y., Sejnowski, T.J.: Biophysical basis for three distinct dynamical mechanisms of action potential initiation. PLoS Comput. Biol. 4, e1000198 (2008)
Wu, F.Q., Gu, H.G., Jia, Y.B.: Bifurcations underlying different excitability transitions modulated by excitatory and inhibitory memristor and chemical autapses. Chaos, Solitons and Fractals. 153, 111611 (2021).
Tsumoto, K., Kitajima, H., Yoshinaga, T., Aihara, K., Kawakami, H.: Bifurcations in Morris-Lecar neuron model. Neurocomputing 69, 293–316 (2006)
Xing, M., Song, X., Yang, Z., Chen, Y.: Bifurcations and excitability in the temperature-sensitive Morris-Lecar neuron. Nonlinear Dyn. 100, 2687–2698 (2020)
Qiu, Q., Ma, R., Kurths, J., Zhan, M.: Swing equation in power systems: approximate analytical solution and bifurcation curve estimate. Chaos 30, 013110 (2020)
Skubov, D., Lukin, A., Popov, I.: Bifurcation curves for synchronous electrical machine. Nonlinear Dyn. 83, 2323–2329 (2016)
Hesse, J., Schleimer, J.-H., Maier, N., Schmitz, D., Schreiber, S.: Temperature elevations can induce switches to homoclinic action potentials that alter neural encoding and synchronization. Nat. Commun. 13, 3934 (2022)
Dana, S.K., Sengupta, D.C., Edoh, K.: Chaotic dynamics in Josephson junction. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst. I Fundam. Theory Appl. 48, 990–996 (2001)
Zhou, P., Zhang, X., Hu, X., Ren, G.: Energy balance between two thermosensitive circuits under field coupling. Nonlinear Dyn. 110, 1879–1895 (2022)
Zhou, P., Yao, Z., Ma, J., Zhu, Z.: A piezoelectric sensing neuron and resonance synchronization between auditory neurons under stimulus. Chaos, Solitons and Fractals. 145, 1107 (2021)
Xie, Y., Zhu, Z.G., Zhang, X.F., Ren, G.D.: Control of firing mode in nonlinear neuron circuit driven by photocurrent. Acta Phys. Sin. 70, 210502 (2021)
Zhang, Y., Xu, Y., Yao, Z., Ma, J.: A feasible neuron for estimating the magnetic field effect. Nonlinear Dyn. 102, 1849–1867 (2020)
Blackburn, J.A., Baker, G.L., Smith, H.J.T.: Intermittent synchronization of resistively coupled chaotic Josephson junctions. Phys. Rev. B. 62, 5931–5935 (2000)
Funding
This project is partially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 12072139.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, F., Yao, Z. Dynamics of neuron-like excitable Josephson junctions coupled by a metal oxide memristive synapse. Nonlinear Dyn 111, 13481–13497 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-08524-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-08524-5