Abstract
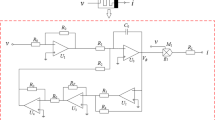
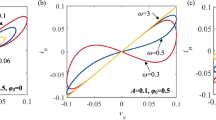
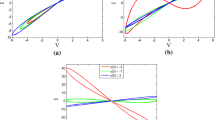
In this paper, a new type of non-volatile locally active memristor with bi-stability is proposed by injecting appropriate voltage pulses to realize a switching mechanism between two stable states. It is found that the memristive parameters of the new memristor can affect the local activity, which has been rarely reported, and this phenomenon is explained based on mathematical analyses and numerical simulations. Then, a locally active memristive coupled neuron model is constructed using the proposed memristor as a connecting synapse. The parameter-associated dynamical behaviors are revealed by bifurcation plots, phase plane portraits and dynamical evolution maps. Moreover, the bi-stability phenomenon of the new coupled neuron model is disclosed by local attraction basins, and the periodic burster and multi-scroll chaotic burster are found if a multi-level pulse current is used to imitate a periodical external stimulus on the neurons. The Hamiltonian energy function is calculated and analyzed with or without external excitation. Finally, the neuronal circuit is designed and implemented, which can mimic electrical activity of the neurons and is useful for physical applications. The experimental results captured from the analog circuit are consistent well with the numerical simulation results.























Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
Data will be made available on reasonable request.
References
Chua, L.: Memristor-the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory 18(5), 507–519 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCT.1971.1083337
Corinto, F., Forti, M.: Memristor circuits: bifurcations without parameters. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I 64(6), 1540–1551 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/tcsi.2016.2642112
Corinto, F., Forti, M.: Memristor circuits: flux-charge analysis method. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I 63(11), 1997–2009 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/tcsi.2016.2590948
Minati, L., Gambuzza, L.V., Thio, W.J., Sprott, J.C., Frasca, M.: A chaotic circuit based on a physical memristor. Chaos Solitons Fractals 138, 109990 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2020.109990
Chen, M., Sun, M., Bao, H., Hu, Y., Bao, B.: Flux-charge analysis of two-memristor-based chua’s circuit: dimensionality decreasing model for detecting extreme multistability. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 67(3), 2197–2206 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/tie.2019.2907444
Chen, M., Ren, X., Wu, H., Xu, Q., Bao, B.: Interpreting initial offset boosting via reconstitution in integral domain. Chaos Solitons Fractals 131, 109554 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2019.109544
Chua, L.: Local activity is the origin of complexity. Int. J. Bifurcation Chaos 15(11), 3435–3456 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218127405014337
Chua, L.: If it’s pinched it’s a memristor. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 29(10), 104001 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1088/0268-1242/29/10/104001
Yu, Y., Bao, H., Shi, M., Bao, B., Chen, Y., Chen, M.: Complex dynamical behaviors of a fractional-order system based on a locally active memristor. Complexity 2019, 1–13 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/2051053
Lin, H., Wang, C., Hong, Q., Sun, Y.: A multi-stable memristor and its application in a neural network. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II 67(12), 3472–3476 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/tcsii.2020.3000492
Liang, Y., Wang, G., Chen, G., Dong, Y., Yu, D., Iu, H.H.-C.: S-type locally active memristor-based periodic and chaotic oscillators. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I 67(12), 1–14 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/tcsi.2020.3017286
Dong, Y., Wang, G., Chen, G., Shen, Y., Ying, J.: A bistable nonvolatile locally-active memristor and its complex dynamics. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 84, 105203 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnsns.2020.105203
Zhu, M., Wang, C., Deng, Q., Hong, Q.: Locally active memristor with three coexisting pinched hysteresis loops and its emulator circuit. Int. J. Bifurcation Chaos 30(13), 2050184 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1142/s0218127420501849
Liang, Y., Lu, Z., Wang, G., Dong, Y., Yu, D., Iu, H.H.-C.: Modeling simplification and dynamic behavior of n-shaped locally-active memristor based oscillator. IEEE Access 8, 75571–75585 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2020.2988029
Ying, J., Wang, G., Dong, Y., Yu, S.: Switching characteristics of a locally-active memristor with binary memories. Int. J. Bifurcation Chaos 29(11), 1930030 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1142/s0218127419300301
Bao, H., Hu, A., Liu, W., Bao, B.: Hidden bursting firings and bifurcation mechanisms in memristive neuron model with threshold electromagnetic induction. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn Syst. 31(2), 502–511 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2019.2905137
Bao, H., Zhu, D., Liu, W., Xu, Q., Chen, M., Bao, B.: Memristor synapse-based morris-lecar model: bifurcation analyses and fpga-based validations for periodic and chaotic bursting/spiking firings. Int. J. Bifurcation Chaos 30(03), 2050045 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1142/s0218127420500455
Chen, C., Bao, H., Chen, M., Xu, Q., Bao, B.: Non-ideal memristor synapse-coupled bi-neuron Hopfield neural network: Numerical simulations and breadboard experiments. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 111, 152894 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aeue.2019.152894
Lin, H., Wang, C.: Influences of electromagnetic radiation distribution on chaotic dynamics of a neural network. Appl. Math. Comput. 369, 124840 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2019.124840
Bao, B., Qian, H., Wang, J., Xu, Q., Chen, M., Wu, H., Yu, Y.: Numerical analyses and experimental validations of coexisting multiple attractors in Hopfield neural network. Nonlinear Dyn. 90(4), 2359–2369 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-017-3808-3
Lin, H., Wang, C., Tan, Y.: Hidden extreme multistability with hyperchaos and transient chaos in a Hopfield neural network affected by electromagnetic radiation. Nonlinear Dyn. 99(3), 2369–2386 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-019-05408-5
Zhang, G., Wang, C., Alzahrani, F., Wu, F., An, X.: Investigation of dynamical behaviors of neurons driven by memristive synapse. Chaos Solitons Fractals 108, 15–24 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2018.01.017
Tan, Y., Wang, C.: A simple locally active memristor and its application in HR neurons. Chaos 30(5), 053118 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5143071
Lin, H., Wang, C., Sun, Y., Yao, W.: Firing multistability in a locally active memristive neuron model. Nonlinear Dyn. 100(4), 3667–3683 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-05687-3
Njitacke, Z.T., Doubla, I.S., Mabekou, S., Kengne, J.: Hidden electrical activity of two neurons connected with an asymmetric electric coupling subject to electromagnetic induction: Coexistence of patterns and its analog implementation. Chaos Solitons Fractals 137, 109785 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2020.109785
Xu, Q., Zhu, D.: FPGA-based Experimental Validations of Electrical Activities in Two Adjacent FitzHugh-Nagumo Neurons Coupled by Memristive Electromagnetic Induction. IETE Technical Review 1–15 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/02564602.2020.1800526
Chen, C., Chen, J., Bao, H., Chen, M., Bao, B.: Coexisting multi-stable patterns in memristor synapse-coupled Hopfield neural network with two neurons. Nonlinear Dyn. 95(4), 3385–3399 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-019-04762-8
Zhang, G., Ma, J., Alsaedi, A., Ahmad, B., Alzahrani, F.: Dynamical behavior and application in Josephson Junction coupled by memristor. Appl. Math. Comput. 321, 290–299 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2017.10.054
Wu, F., Ma, J., Zhang, G.: Energy estimation and coupling synchronization between biophysical neurons. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 63(4), 625–636 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-019-9670-1
Xu, Y., Jia, Y., Ma, J., Alsaedi, A., Ahmad, B.: Synchronization between neurons coupled by memristor. Chaos Solitons Fractals 104, 435–442 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2017.09.002
Bao, H., Zhang, Y., Liu, W., Bao, B.: Memristor synapse-coupled memristive neuron network: synchronization transition and occurrence of chimera. Nonlinear Dyn. 100(1), 937–950 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-05529-2
Parker, J.E., Short, K.M.: Sigmoidal synaptic learning produces mutual stabilization in chaotic FitzHugh-Nagumo model. Chaos 30(6), 063108 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0002328
Wang, S., He, S., Rajagopal, K., Karthikeyan, A., Sun, K.: Route to hyperchaos and chimera states in a network of modified Hindmarsh-Rose neuron model with electromagnetic flux and external excitation. Europ. Phys. J. Special Topics 229(6–7), 929–942 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2020-900247-7
Bao, B., Hu, A., Xu, Q., Bao, H., Wu, H., Chen, M.: AC-induced coexisting asymmetric bursters in the improved Hindmarsh-Rose model. Nonlinear Dyn. 92(4), 1695–1706 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-4155-8
Bao, H., Hu, A., Liu, W.: Bipolar pulse-induced coexisting firing patterns in two-dimensional hindmarsh-rose neuron model. Int. J. Bifurcation Chaos 29(01), 1950006 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1142/s0218127419500068
QuanXu, Z.S., Bao, H., Chen, M., Bao, B.: Two-neuron-based non-autonomous memristive Hopfield neural network: numerical analyses and hardware experiments. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 96, 66–74 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aeue.2018.09.017
Lin, H., Wang, C., Yao, W., Tan, Y.: Chaotic dynamics in a neural network with different types of external stimuli. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 90, 105390 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnsns.2020.105390
Yang, Y., Ma, J., Xu, Y., Jia, Y.: Energy dependence on discharge mode of Izhikevich neuron driven by external stimulus under electromagnetic induction. Cognit. Neurodyn. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-020-09596-4
Wang, Y., Wang, C., Ren, G., Tang, J., Jin, W.: Energy dependence on modes of electric activities of neuron driven by multi-channel signals. Nonlinear Dyn. 89(3), 1967–1987 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-017-3564-4
Chua, L.: Everything you wish to know about memristors but are afraid to ask. Radioengineering 24(2), 319–368 (2015). https://doi.org/10.13164/re.2015.0319
Mannan, Z.I., Adhikari, S.P., Kim, H., Chua, L.: Global dynamics of Chua Corsage Memristor circuit family: fixed-point loci, Hopf bifurcation, and coexisting dynamic attractors. Nonlinear Dyn. 99(4), 3169–3196 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-05476-y
Hong, Q., Xie, Q., Xiao, P.: A novel approach for generating multi-direction multi-double-scroll attractors. Nonlinear Dyn. 87(2), 1015–1030 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-016-3094-5
Qi, G., Hu, J.: Modelling of both energy and volume conservative chaotic systems and their mechanism analyses. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 84, 105171 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnsns.2020.105171
Cang, S., Wu, A., Wang, Z., Chen, Z.: Four-dimensional autonomous dynamical systems with conservative flows: two-case study. Nonlinear Dyn. 89(4), 2495–2508 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-017-3599-6
Ma, J., Wu, F., Jin, W., Zhou, P., Hayat, T.: Calculation of Hamilton energy and control of dynamical systems with different types of attractors. Chaos 27(5), 053108 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4983469
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin (No. 18JCYBJC87700), the New Generation Artificial Intelligence Technology Major Project of Tianjin (18ZXZNSY00270) and South African National Research Foundation Grants (Nos. 114911 and 132797).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, R., Wang, Z. & Dong, E. A new locally active memristive synapse-coupled neuron model. Nonlinear Dyn 104, 4459–4475 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-06574-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-06574-1