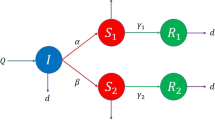
Abstract
Reaction–diffusion model is often used to describe the spatial distribution of network rumors. This paper establishes a reaction–diffusion rumor spreading model with media delay correction mechanism based on continuous space and discrete network space, respectively. By linearization, the condition of Turing instability under the influence of small delay is studied. The simulation results show when diffusion coefficient is extended periodically, the time stability of the pattern is broken, but the pattern type changes slightly. Finally, based on stable patterns, we estimate the unknown parameters of the system with the help of a statistical method, where the unknown parameters were set as infection rate \(\beta \) and cross-diffusion coefficient \(d_{21}\) for the system on the continuous space, as reconnection rate \(\rho \) and cross-diffusion coefficient \(d_{21}\) for the system on WS network. The final estimation error is within the ideal range.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the section of the numerical simulation.
References
Zhu, L.H., Guan, G., Li, Y.M.: Nonlinear dynamical analysis and control strategies of a network-based SIS epidemic model with time delay. Appl. Math. Model. 70, 512–531 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2019.01.037
Kawachi, K.: Deterministic models for rumor transmission. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 9, 1989–2028 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nonrwa.2007.06.004
Zhu, L.H., Zhao, H.Y., Wang, H.Y.: Partial differential equation modeling of rumor propagation in complex networks with higher order of organization. Chaos 29, 053106 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5090268
Li, W.Y., Tian, L.X., Gao, X.Y., Pan, B.R.: Impacts of information diffusion on green behavior spreading in multiplex networks. J. Clean. Prod. 222, 488–498 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.03.067
Zhu, L.H., Liu, W.S., Zhang, Z.D.: Delay differential equations modeling of rumor propagation in both homogeneous and heterogeneous networks with a forced silence function. Appl. Math. Comput. 370, 124925 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2019.124925
Jia, P.Q., Wang, C., Zhang, G.Y., Ma, J.F.: A rumor spreading model based on two propagation channels in social networks. Phys. A 524, 342–353 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2019.04.163
Xu, H., Li, T., Liu, X.D., Dong, J.: Spreading dynamics of an online social rumor model with psychological factors on scale-free networks. Phys. A 525, 234–246 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2019.03.037
Wan, C., Li, T., Sun, Z.C.: Global stability of a SEIR rumor spreading model with demographics on scale-free networks. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2017, 253 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13662-017-1315-y
Zhang, Y.H., Zhu, J.J.: Stability analysis of I2S2R rumor spreading model in complex networks. Phys. A 503, 862–881 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2018.02.087
Xia, C.Y., Wang, L., Sun, S.W., Wang, J.: An SIR model with infection delay and propagation vector in complex networks. Nonlinear Dyn. 69, 927–934 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-011-0313-y
Tian, Y., Ding, X.J.: Rumor spreading model with considering debunking behavior in emergencies. Appl. Math. Comput. 363, 124599 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2019.124599
Li, J.R., Jiang, H.J., Yu, Z.Y., Hu, C.: Dynamical analysis of rumor spreading model in homogeneous complex networks. Appl. Math. Comput. 359, 374–385 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2019.04.076
He, Z.B., Cai, Z.P., Yu, J.G., Wang, X.M., Sun, Y.C., Li, Y.S.: Cost-efficient strategies for restraining rumor spreading in mobile social networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 66, 2789–2800 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/tvt.2016.2585591
Zhu, L.H., Yang, F., Guan, G., Zhang, Z.D.: Modeling the dynamics of rumor diffusion over complex networks. Inf. Sci. 562, 240–258 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2020.12.071
Zan, Y.L.: DSIR double-rumors spreading model in complex networks. Chaos Solitons & Fractals 110, 191–202 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2018.03.021
Zhang, Y.M., Su, Y.Y., Li, W.G., Liu, H.O.: Interacting model of rumor propagation and behavior spreading in multiplex networks. Chaos Solitons & Fractals 121, 168–177 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2019.01.035
Wang, J.L., Jiang, H.J., Ma, T.L., Hu, C.: Global dynamics of the multi-lingual SIR rumor spreading model with cross-transmitted mechanism. Chaos Solitons & Fractals 126, 148–157 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2019.05.027
Chierichetti, F., Giakkoupis, G., Lattanzi, S., Panconesi, A.: Rumor spreading and conductance. J. ACM 65, 17 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1145/3173043
Bodaghi, A., Goliaei, S., Salehi, M.: The number of followings as an influential factor in rumor spreading. Appl. Math. Comput 357, 167–184 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2019.04.005
Zhu, L., Wang, Y.G.: Rumor spreading model with noise interference in complex social networks. Phys. A 469, 750–760 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2016.11.119
Yang, L., Li, Z.W., Giua, A.: Containment of rumor spread in complex social networks. Inf. Sci. 506, 113–130 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2019.07.055
Lu, P.: Heterogeneity, judgment, and social trust of agents in rumor spreading. Appl. Math. Comput. 350, 447–461 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2018.10.079
Liu, W.P., Wu, X., Wu, Y., Zhu, X.F., Zhong, S.M.: Modeling cyber rumor spreading over mobile social networks: A compartment approach. Appl. Math. Comput. 343, 214–229 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2018.09.048
Wang, C., Tan, Z.X., Ye, Y., Wang, L., Kang, H.C., Xie, N.G.: A rumor spreading model based on information entropy. Sci. Rep. 7, 9615 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-09171-8
Falasco, G., Rao, R., Esposito, M.: Information thermodynamics of Turing patterns. Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 108301 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.121.108301
Yan, X.P., Zhang, C.H.: Turing instability and formation of temporal patterns in a diffusive bimolecular model with saturation law. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 43, 54–77 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nonrwa.2018.02.004
Lacitignola, D., Bozzini, B., Frittelli, M., Sgura, I.: Turing pattern formation on the sphere for a morphochemical reaction-diffusion model for electrodeposition. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numerical Simul. 48, 484–508 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnsns.2017.01.008
Huang, S.W., Yang, J.H., Yang, S.H., Yu, M.B., Kwong, D.L., Zelevinsky, T., Jarrahi, M., Wong, C.W.: Globally stable microresonator Turing pattern formation for coherent high-power THz radiation on-chip. Phys. Rev. X 7, 041002 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevX.7.041002
Rumbach, P., Lindsay, A.E., Go, D.B.: Turing patterns on a plasma-liquid interface. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 28, 105014 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6595/ab45e4
Buscarino, A., Corradino, C., Fortuna, L., Frasca, M.: Turing patterns via pinning control in the simplest memristive cellular nonlinear networks. Chaos 29, 103145 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5115131
Duan, M.R., Chang, L.L., Jin, Z.: Turing patterns of an SI epidemic model with cross-diffusion on complex networks. Phys. A 533, 122023 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2019.122023
Wang, W.M., Gao, X.Y., Cai, Y.L., Shi, H.B., Fu, S.M.: Turing patterns in a diffusive epidemic model with saturated infection force. J. Frankl. Inst. 355, 7226–7245 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfranklin.2018.07.014
Zheng, Q., Shen, J.: Turing instability in a gene network with cross-diffusion. Nonlinear Dyn. 78, 1301–1310 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-014-1516-9
Banerjee, M., Ghorai, S., Mukherjee, N.: Study of cross-diffusion induced Turing patterns in a ratio-dependent prey-predator model via amplitude equations. Appl. Math. Model. 55, 383–399 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2017.11.005
Tian, C., Ling, Z., Lin, Z.: Turing pattern formation in a predator-prey-mutualist system. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 12, 3224–3237 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nonrwa.2011.05.022
Chen, M., Wu, R., Chen, L.: Spatiotemporal patterns induced by Turing and Turing-Hopf bifurcations in a predator-prey system. Appl. Math. Comput. 380, 125300 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2020.125300
Pablo, M., Ramirez, S.A., Elston, T.C.: Particle-based simulations of polarity establishment reveal stochastic promotion of Turing pattern formation. Plos Comput. Biol. 14, e1006016 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006016
Cao, X., Jiang, W.H.: Turing-Hopf bifurcation and spatiotemporal patterns in a diffusive predator-prey system with Crowley-Martin functional response. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 43, 428–450 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nonrwa.2018.03.010
Tripathi, J.P., Abbas, S., Sun, G.Q., Jana, D., Wang, C.H.: Interaction between prey and mutually interfering predator in prey reserve habitat: pattern formation and the Turing-Hopf bifurcation. J. Frankl. Inst. 355, 7466–7489 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfranklin.2018.07.029
Chang, L.L., Liu, C., Sun, G.Q., Wang, Z., Jin, Z.: Delay-induced patterns in a predator-prey model on complex networks with diffusion. New J. Phys. 21, 073035 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/1367-2630/ab3078
Tian, C.R., Ling, Z., Zhang, L.: Delay-driven spatial patterns in a network-organized semiarid vegetation model. Appl. Math. Comput. 367, 124778 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2019.124778
Petit, J., Lauwens, B., Fanelli, D., Carletti, T.: Theory of Turing patterns on time varying networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 119, 148301 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.119.148301
Karig, D., Martini, K.M., Lu, T., DeLateur, N.A., Goldenfeld, N., Weiss, R.: Stochastic Turing patterns in a synthetic bacterial population. Proc. National Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 115, 6572–6577 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1720770115
Di Patti, F., Lavacchi, L., Arbel-Goren, R., Schein-Lubomirsky, L., Fanelli, D., Stavans, J.: Robust stochastic Turing patterns in the development of a one-dimensional cyanobacterial organism. Plos Biol. 16, e2004877 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.2004877
Scholes, N.S., Schnoerr, D., Isalan, M., Stumpf, M.: A comprehensive network atlas reveals that Turing patterns are common but not robust. Cell Syst. 9, 243–257 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cels.2019.07.007
Kazarnikov, A., Haario, H.: Statistical approach for parameter identification by Turing patterns. J. Theor. Biol. 501, 110319 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtbi.2020.110319
Zheng, M.M., Shao, B., Ouyang, Q.: Identifying network topologies that can generate turing pattern. J. Theor. Biol. 408, 88–96 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtbi.2016.08.005
Li, Y.M., Sun, Y.Y., Hua, J., Li, L.: Indirect adaptive type-2 fuzzy impulsive control of nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 23, 1084–1099 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2014.2346235
Zhang, F.X., Li, Y.M., Hua, J.: Direct adaptive fuzzy control of SISO nonlinear systems with input-output nonlinear relationship. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 20, 1069–1078 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-017-0414-y
Zhao, H.Y., Zhu, L.H.: Dynamic analysis of a reaction-diffusion rumor propagation model. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 6(26), 1650101 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218127416501017
Zhu, L.H., Zhao, H.Y.: Dynamical behaviors and control measures of rumor spreading model with consideration of network topology. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 48(10), 2064–2078 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/00207721.2017.1312628
Xia, Y.B., Zhang, Z.Z., Bi, Q.S.: Relaxation oscillations and the mechanism in a periodically excited vector field with pitchfork-Hopf bifurcation. Nonlinear Dyn. 101, 37–51 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-05795-0
Zhang, R., Wang, Y., Zhang, Z.Z., Bi, Q.S.: Nonlinear behaviors as well as the bifurcation mechanism in switched dynamical systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 79, 465–471 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-014-1679-4
Acknowledgements
This research is partly supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 12002135), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (Grant No. BK20190836) and Young Science and Technology Talents Lifting Project of Jiangsu Association for Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, L., He, L. Pattern dynamics analysis and parameter identification of time delay-driven rumor propagation model based on complex networks. Nonlinear Dyn 110, 1935–1957 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07717-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07717-8