Abstract
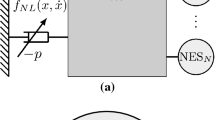
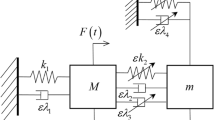
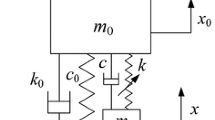
The main focus of this study is the development of an adapted complex variable method with respect to the equilibrium point in bistable nonlinear energy sink (NES), which is mainly investigated in the vicinity of 1:1 resonance. A simplified chaos trigger model is established to describe the distance between the stable phase cycle and the pseudo-separatrix. An analytical expression can predict the excitation threshold for chaos occurrence. The relative positions between the chaos trigger threshold line and the slow invariant manifold structure can interpret the distribution of response regimes under growing harmonic excitation. The degeneration of the response regimes can be demonstrated by the qualitative analysis method, which helps to classify the bistable NES. The experiment confirms the analytical result of intra-well oscillation in the frequency domain. The characteristic response regimes of weak, modest, and strong bistable NES are identified by the experimental results.




























Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Vakakis, A.F., Gendelman, O.V., Bergman, L.A., McFarland, M.D., Kerschen, G., Lee, Y.S.: Nonlinear Targeted Energy Transfer in Mechanical and Structural Systems. Springer, Amsterdam (2009)
Vakakis, A.F., Gendelman, O.V.: Energy pumping in nonlinear mechanical oscillators: partii-resonance capture. J. Appl. Mech. 68(1), 42–48 (2001)
Gendelman, O.V., Manevitch, L.I., Vakakis, A., M’Closkey, R.: Energy pumping in nonlinear mechanical oscillators: part I—dynamics of the under-lying Hamiltonian systems. ASME J. Appl. Mech. 68(1), 34–41 (2001)
Starosvetsky, Y., Gendelman, O.V.: Strongly modulated response in forced 2DOF oscillatory system with essential mass and potential asymmetry. Physica D 237(13), 1719–1733 (2008)
Starosvetsky, Y., Gendelman, O.: Response regimes of linear oscillator coupled to nonlinear energy sink with harmonic forcing and frequency detuning. J. Sound Vib. 315(3), 746–765 (2008)
Starosvetsky, Y., Gendelman, O.: Attractors of harmonically forced linear oscillator with attached nonlinear energy sink. II: optimization of a nonlinearvibration absorber. Nonlinear Dyn. 51(1–2), 47–57 (2008)
Vaurigaud, B., Savadkoohi, A.T., Lamarque, C.H.: Targeted energy transfer with parallel nonlinear energy sinks. Part I: design theory and numerical results. Nonlinear Dyn. 66(4), 763–780 (2011)
McFarland, D.M., Kerschen, G., Kowtko, J.J., et al.: Experimental investigation of targeted energy transfers in strongly and nonlinearly coupled oscillators. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 118(2), 791–799 (2005)
Bellet, R., Cochelin, B., Herzog, P., et al.: Experimental study of targeted energy transfer from an acoustic system to a nonlinear membrane absorber. J. Sound Vib. 329(14), 2768–2791 (2020)
AL-Shudeifat, M.A.: Nonlinear energy sinks with piecewise-linear nonlinearities. Int. J. Nonlinear Mech. 14(12), 124501 (2019)
Saeed, A.S., AL-Shudeifat, M.A., Vakakis, A.F.: Rotary-oscillatory nonlinear energy sink of robust performance. Int. J. Nonlinear Mech. 117, 103249 (2019)
Li, T., Gourc, E., Seguy, S., et al.: Dynamics of two vibro-impact nonlinear energy sinks in parallel under periodic and transient excitations. Int. J. Nonlinear Mech. 90, 100–110 (2017)
Qiu, D., Seguy, S., Paredes, M.: Design criteria for optimally tuned vibro-impact nonlinear energy sink. J. Sound Vib. 442, 497–513 (2019)
Qiu, D., Seguy, S., Paredes, M.: Tuned nonlinear energy sink with conical spring: design theory and sensitivity analysis. J. Mech. Des. 140(1), 011404 (2018)
Al-Shudeifat, M.A.: Highly efficient nonlinear energy sink. Nonlinear Dyn. 76(4), 1905–1920 (2014)
Al-Shudeifat, M.A., Wierschem, N., Quinn, D.D., et al.: Numerical and experimental investigation of a highly effective single-sided vibro-impact non-linear energy sink for shock mitigation. Int. J. Nonlinear Mech. 52, 96–109 (2013)
Chen, Y.Y., Qian, Z.C., Zhao, W., et al.: A magnetic bi-stable nonlinear energy sink for structural seismic control. J. Sound Vib. 473, 115233 (2020)
Gourc, E., Seguy, S., Michon, G., et al.: Quenching chatter instability in turning process with a vibro-impact nonlinear energy sink. J. Sound Vib. 355, 392–406 (2015)
Manevitch, L.I.: The description of localized normal modes in a chain of nonlinear coupled oscillators using complex variables. Nonlinear Dyn. 25(1), 95–109 (2001)
Manevitch, L.I., Sigalov, G., Romeo, F., et al.: Dynamics of a linear oscillator coupled to a bistable light attachment: analytical study. J. Appl. Mech. 81(4), 041011 (2014)
Romeo, F., Sigalov, G., Bergman, L.A., et al.: Dynamics of a linear oscillator coupled to a bistable light attachment: numerical study. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 10(1), 011007 (2015)
Bitar, D., Savadkoohi, A.T., Lamarque, C.H., et al.: Extended complexification method to study nonlinear passive control. Nonlinear Dyn. 99(2), 1433–1450 (2020)
Qiu, D., Li, T., Seguy, S., et al.: Efficient targeted energy transfer of bistable nonlinear energy sink: application to optimal design. Nonlinear Dyn. 92(2), 443–461 (2018)
Qiu, D., Paredes, M., Seguy, S.: Variable pitch spring for nonlinear energy sink: application to passive vibration control. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 233, 611–622 (2019)
Wu, Z., Seguy, S., Paredes, M.: Basic constraints for design optimization of cubic and bistable NES. J. Vib. Acoust. 144, 1–51 (2021)
Fang, X., Wen, J., Yin, J., et al.: Highly efficient continuous bistable nonlinear energy sink composed of a cantilever beam with partial constrained layer damping. Nonlinear Dyn. 87(4), 2677–2695 (2017)
Benacchio, S., Malher, A., Boisson, J., et al.: Design of a magnetic vibration absorber with tunable stiffnesses. Nonlinear Dyn. 85(2), 893–911 (2016)
Pennisi, G., Mann, B.P., Naclerio, N., et al.: Design and experimental study of a nonlinear energy sink coupled to an electromagnetic energy harvester. J. Sound Vib. 437, 340–357 (2018)
Pirrera, A., Avitabile, D., Weaver, P.M.: Bistable plates for morphing structures: a refined analytical approach with high-order polynomials. Int. J. Solids Struct. 47(25–26), 3412–3425 (2010)
Johnson, D.R., Thota, M., Semperlotti, F., et al.: On achieving high and adaptable damping via a bistable oscillator. Smart Mater. Struct. 22(11), 115027 (2013)
Iurasov, V., Mattei, P.O.: Bistable nonlinear damper based on a buckled beam configuration. Nonlinear Dyn. 99(3), 1801–1822 (2020)
Romeo, F., Manevitch, L.I., Bergman, L.A., et al.: Transient and chaotic low-energy transfers in a system with bistable nonlinearity. Chaos 25(5), 053109 (2015)
Farshidianfar, A., Saghafi, A.: Global bifurcation and chaos analysis in nonlinear vibration of spur gear systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 75(4), 783–806 (2014)
Dekemele, K., Van Torre, P., Loccufier, M.: Performance and tuning of a chaotic bi-stable NES to mitigate transient vibrations. Nonlinear Dyn. 98(3), 1831–1851 (2019)
Wolf, A., Swift, J.B., Swinney, H.L., Vastano, J.A.: Determining Lyapunov exponents from a time series. Physica D 16(3), 285–317 (1985)
Govorukhin, V.: Calculation Lyapunov exponents for ode. https://nl.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/4628-calculation-lyapunov-exponents-for-ode (2004)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the Chinese Scholarship Council under Grant No. 201801810128 for their financial support. The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Funding
The authors acknowledge the Chinese Scholarship Council under Grant No. 201801810128 for their financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The authors declare that all procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of COPE. This manuscript is only submitted to the journal ‘Nonlinear Dynamics’. The authors declare that this study is complete, unsplit and original.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Z., Seguy, S. & Paredes, M. Qualitative analysis of the response regimes and triggering mechanism of bistable NES. Nonlinear Dyn 109, 323–352 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07609-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07609-x