Abstract
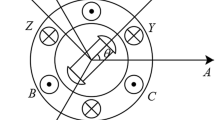
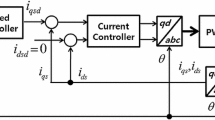
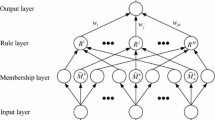
High precision motion control of permanent magnet linear motors (PMLMs) is limited by undesired nonlinear dynamics, parameter variations, and unstructured uncertainties. To tackle these problems, this paper presents a neural-network-based adaptive robust precision motion control scheme for PMLMs. The presented controller contains a robust feedback controller and an adaptive compensator. The robust controller is designed based on the robust integral of the sign of the error method, and the adaptive compensator consists of a neural network component and a parametric component. Moreover, a composite learning law is designed for the parameter adaption in the compensator to further enhance the control performance. Rigorous stability analysis is provided by using the Lyapunov theory, and asymptotic tracking is theoretically achieved. The effectiveness of the proposed method is verified by comparative simulations and experiments on a PMLM-driven motion stage.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Gajek, J., Awrejcewicz, J.: Mathematical models and nonlinear dynamics of a linear electromagnetic motor. Nonlinear Dyn. 94(1), 377–396 (2018)
Liu, Z.Z., Luo, F.L., Rahman, M.A.: Robust and precision motion control system of linear-motor direct drive for high-speed xy table positioning mechanism. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 52(5), 1357–1363 (2005)
Gordon, S., Hillery, M.T.: Development of a high-speed cnc cutting machine using linear motors. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 166(3), 321–329 (2005)
Kim, K., Choi, Y.M., Gweon, D.G., Lee, M.G.: A novel laser micro/nano-machining system for fpd process. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 201(1–3), 497–501 (2008)
Komada, S., Ishida, M., Ohnishi, K., Hori, T.: Disturbance observer-based motion control of direct drive motors. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 6(3), 553–559 (1991)
Tan, K.K., Lee, T.H., Dou, H.F., Chin, S.J., Zhao, S.: Precision motion control with disturbance observer for pulsewidth-modulated-driven permanent-magnet linear motors. IEEE Trans. Magn. 39(3), 1813–1818 (2003)
Alter, D., Tsao, T.C.: Control of linear motors for machine tool feed drives: Design and implementation of \(h_{\infty }\) optimal feedback control. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Contr. 118(4), 649–656 (1996)
Zheng, J., Wang, H., Man, Z., Jin, J., Fu, M.: Robust motion control of a linear motor positioner using fast nonsingular terminal sliding mode. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 20(4), 1743–1752 (2014)
Sun, G., Ma, Z.: Practical tracking control of linear motor with adaptive fractional order terminal sliding mode control. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 22(6), 2643–2653 (2017)
Sun, G., Wu, L., Kuang, Z., Ma, Z., Liu, J.: Practical tracking control of linear motor via fractional-order sliding mode. Automatica 94, 221–235 (2018)
Du, H., Chen, X., Wen, G., Yu, X., Lü, J.: Discrete-time fast terminal sliding mode control for permanent magnet linear motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 65(12), 9916–9927 (2018)
Li, J., Du, H., Cheng, Y., Wen, G., Chen, X., Jiang, C.: Position tracking control for permanent magnet linear motor via fast nonsingular terminal sliding mode control. Nonlinear Dyn. 97(4), 2595–2605 (2019)
Xu, D., Ding, B., Jiang, B., Yang, W., Shi, P.: Nonsingular fast terminal sliding mode control for permanent magnet linear synchronous motor via high-order super-twisting observer
Hou, Q., Ding, S., Yu, X.: Composite super-twisting sliding mode control design for pmsm speed regulation problem based on a novel disturbance observer. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. (2020)
Hou, Q., Ding, S.: Gpio based super-twisting sliding mode control for pmsm. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II: Exp. Briefs 68(2), 747–751 (2020)
Hou, Q., Ding, S., Yu, X., Mei, K.: A super-twisting-like fractional controller for spmsm drive system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. (2021)
Liu, X., Zhen, S., Sun, H., Zhao, H.: A novel model-based robust control for position tracking of permanent magnet linear motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 67(9), 7767–7777 (2019)
Tan, K., Huang, S., Lee, T.: Robust adaptive numerical compensation for friction and force ripple in permanent-magnet linear motors. IEEE Trans. Magn. 38(1), 221–228 (2002)
Lee, T.H., Tan, K.K., Huang, S.: Adaptive friction compensation with a dynamical friction model. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 16(1), 133–140 (2010)
Xu, L., Yao, B.: Adaptive robust precision motion control of linear motors with negligible electrical dynamics: theory and experiments. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 6(4), 444–452 (2001)
Xu, L., Yao, B.: Output feedback adaptive robust precision motion control of linear motors. Automatica 37(7), 1029–1039 (2001)
Chen, Z., Yao, B., Wang, Q.: \(\mu \)-synthesis-based adaptive robust control of linear motor driven stages with high-frequency dynamics: a case study. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 20(3), 1482–1490 (2014)
Otten, G., De Vries, T.J., Van Amerongen, J., Rankers, A.M., Gaal, E.W.: Linear motor motion control using a learning feedforward controller. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2(3), 179–187 (1997)
Gong, J., Yao, B.: Neural network adaptive robust control with application to precision motion control of linear motors. Int. J. Adapt. Control Sign. Process. 15(8), 837–864 (2001)
Wang, Z., Hu, C., Zhu, Y., He, S., Yang, K., Zhang, M.: Neural network learning adaptive robust control of an industrial linear motor-driven stage with disturbance rejection ability. IEEE Trans. Ind. Informat. 13(5), 2172–2183 (2017)
Xian, B., Dawson, D.M., Queiroz, M.S.D., Chen, J.: A continuous asymptotic tracking control strategy for uncertain nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 49(7), 1206–1211 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1109/TAC.2004.831148
Wang, S., Na, J., Ren, X.: Rise-based asymptotic prescribed performance tracking control of nonlinear servo mechanisms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern.: Syst. 48(12), 2359–2370 (2017)
Chen, S.L., Tan, K.K., Huang, S., Teo, C.S.: Modeling and compensation of ripples and friction in permanent-magnet linear motor using a hysteretic relay. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 15(4), 586–594 (2009)
Makkar, C., Dixon, W.E., Sawyer, W.G., Hu, G.: A new continuously differentiable friction model for control systems design. In: Proceedings of IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, pp. 600–605 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1109/AIM.2005.1511048
Na, J., Chen, Q., Ren, X., Guo, Y.: Adaptive prescribed performance motion control of servo mechanisms with friction compensation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 61(1), 486–494 (2013)
Chen, Z., Yao, B., Wang, Q.: Adaptive robust precision motion control of linear motors with integrated compensation of nonlinearities and bearing flexible modes. IEEE Trans. Ind. Informat. 9(2), 965–973 (2012)
Patre, P.M., MacKunis, W., Kaiser, K., Dixon, W.E.: Asymptotic tracking for uncertain dynamic systems via a multilayer neural network feedforward and rise feedback control structure. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 53(9), 2180–2185 (2008)
Yao, Z., Yao, J., Sun, W.: Adaptive rise control of hydraulic systems with multilayer neural-networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 66(11), 8638–8647 (2018)
Slotine, J.J.E., Li, W.: Composite adaptive control of robot manipulators. Automatica 25(4), 509–519 (1989)
Patre, P.M., Bhasin, S., Wilcox, Z.D., Dixon, W.E.: Composite adaptation for neural network-based controllers. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 55(4), 944–950 (2010)
Krstic, M., Kokotovic, P.V., Kanellakopoulos, I.: Nonlinear and Adaptive Control Design. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. (1995)
Patre, P.M., MacKunis, W., Makkar, C., Dixon, W.E.: Asymptotic tracking for systems with structured and unstructured uncertainties. In: Proceedings of the 45th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, pp. 441–446. IEEE (2006)
Wang, L., Chai, T., Zhai, L.: Neural-network-based terminal sliding-mode control of robotic manipulators including actuator dynamics. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 56(9), 3296–3304 (2009)
Yao, B., Tomizuka, M.: Adaptive robust control of mimo nonlinear systems in semi-strict feedback forms. Automatica 37(9), 1305–1321 (2001)
Funding
This document is the results of the research project funded in part by the National Science and Technology Major Project of China 2017ZX02101007-001, in part by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2021TQ0070) and in part by State Key Laboratory of ASIC & System (No. 2021KF007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, R., Ding, C., Xu, Y. et al. Neural-network-based adaptive robust precision motion control of linear motors with asymptotic tracking performance. Nonlinear Dyn 108, 1339–1356 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07258-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07258-0