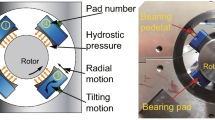
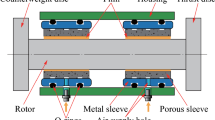
Abstract
Porous tilting pad bearings (PTPBs) combine the advantages of tilting pad and porous gas bearings and can be used in rotary motion and precision machine tools. This research mathematically investigates the dynamic characteristics of a rotor supported by PTPBs. A nonlinear rotor dynamics model that considers the unsteady gas film as well as translational and angular gyroscopic motions is established in this paper. The predicted results agree well with the experimental data when the rotor accelerates to ~ 30 krpm. Subsynchronous responses with large vibration amplitude are observed at high rotational speeds. The subsynchronous vibrations are related to both the fluid circumferential average velocity and eccentricity ratio. Meanwhile, the nonlinear dynamic responses of the system are analyzed by using waterfall plots, fast Fourier transforms, rotor orbits, Poincaré maps, and bifurcation diagrams. The results suggest that the adaptive motions of pads can enhance the stability of the system and increase the onset speed of the instability. Given that the eccentricity ratio increases along with the rotor mass (within a certain scale) and the pressure ratio of unload pads, the system stability is enhanced at the same time. Both the preload of PTPBs and pad installation can influence the system stability. Those PTPBs without preload and those pads with loads in between can also benefit the stability of the system. The findings of this work can help designers avoid subsynchronous vibrations at high rotational speeds.































Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \( W \) :
-
Pad width (m)
- \( L \) :
-
Pad axial length (m)
- \( r_{0} ,\;r_{\text{d}} \) :
-
Pad radius and rotor diameter (m)
- \( \varTheta_{\text{p}} \) :
-
Pad arc angle (rad)
- \( \theta_{s} ,\;\theta_{e} \) :
-
Pad leading edge and pad trailing edge (rad)
- \( \theta_{\text{p}} \) :
-
Angular position of pivot (rad)
- \( r_{\text{p}} \) :
-
The preload of the pads
- \( \xi \) :
-
Pad tilting angle (rad)
- \( I_{\text{pad}} \) :
-
Moment of inertia of pad (kg m2)
- \( p_{\text{a}} ,\;p_{\text{s}} \) :
-
Ambient and supply pressures (pa)
- \( p \) :
-
Pressure (pa)
- \( P \) :
-
Dimensionless pressure (\( p/p_{\text{a}} \))
- \( r,\;\theta ,\;z \) :
-
Coordinates in the \( r \), \( \theta \), and \( z \) directions
- \( R,\;Z \) :
-
Dimensionless coordinates in the \( r \) and \( z \) directions
- \( C \) :
-
Nominal clearance (m)
- \( h,\;H \) :
-
Film thickness (m) and dimensionless film thickness (\( h/C \))
- \( e_{x} ,\;e_{y} \) :
-
Components of rotor eccentricity
- \( \omega \) :
-
Angular velocity of shaft (rad/s)
- \( m_{\text{r}} \) :
-
Mass flow rates in the \( r \) direction
- \( x,\;y \) :
-
x and y axes
- \( F_{x} ,\;F_{y} \) :
-
Forces acting on shaft along the x and y axes caused by gas pressure (N)
- \( M_{\xi } \) :
-
Tilting moment (N m)
- \( K_{\xi } \) :
-
Tilting stiffness of the pivot (N m/rad)
- \( \eta \) :
-
Porosity of porous materials
- \( k \) :
-
Permeability of porous materials (m2)
- \( \mu ,\;\rho \) :
-
Gas viscosity (Pa s) and density (kg/m3)
- \( \Re \) :
-
Air gas constant (J/kg K)
- \( T \) :
-
Temperature of the supply gas (K)
- \( m_{s} \) :
-
Rotor mass (kg)
- \( F_{bx} ,\;F_{by} \) :
-
Dynamic forces of PTPBs in x- and y- directions (N)
- \( F_{ux} ,\;F_{uy} \) :
-
Imbalance forces in x- and y- directions (N)
- \( I_{\text{t}} \) :
-
Translational torque of the rotor inertia (kg m2)
- \( I_{\text{p}} \) :
-
Polar moment of the rotor inertia (kg m2)
- \( M_{{{\text{b}}\xi }} ,\;M_{{{\text{b}}\psi }} \) :
-
Rotor rotational moments caused by bearings
- \( M_{u\xi } ,\;M_{u\psi } \) :
-
Rotor rotational moments caused by imbalance mass of the rotor (N m)
- \( Z_{{u\_{\text{left}}}} ,\;Z_{{u\_{\text{right}}}} \) :
-
The axial distances between the imbalance locations and the rotor mass center (m)
- \( Z_{{b\_{\text{lef}}t}} ,\;Z_{{b\_{\text{right}}}} \) :
-
The axial distances between the PTPB locations and the rotor mass center (m)
- \( \phi_{\text{left}} ,\;\phi_{\text{right}} \) :
-
The imbalance phase angles at the different sides of the rotor (rad)
- \( M_{\text{left}} \) :
-
The imbalance mass at the left side of the rotor (kg)
- \( U_{\text{left}} \) :
-
Imbalance radius at the left side of the rotor (m)
- \( \omega_{\text{ins}} \) :
-
Onset speed of the instability
- \( \lambda \) :
-
Fluid circumferential average velocity ratio
- \( \omega_{\text{sys}} \) :
-
System natural frequency (Hz)
References
Majumdar, B.C.: Externally pressurized gas bearings: a review. Wear 62(2), 299–314 (1980)
Sneck, H.J.: A survey of gas-lubricated porous bearings. J. Tribol. 90(4), 804–809 (1968)
Miyatake, M., Yoshimoto, S., Sato, J.: Whirling instability of a rotor supported by aerostatic porous journal bearings with a surface-restricted layer. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 220(2), 95–103 (2006)
Sneck, H., Yen, K.: The externally pressurized, porous wall, gas-lubricated journal bearing. ASLE Trans. 7(3), 288–298 (1964)
Sneck, H.J., Elwell, R.: The externally pressurized, porous wall, gas-lubricated journal bearing. II. ASLE Trans. 8(4), 339–345 (1965)
Sneck, H., Yen, K.: The externally pressurized, porous wall, gas-lubricated journal bearing-III. ASLE Trans. 10(3), 339–347 (1967)
Mori, H., et al.: Theoretical analysis of externally pressurized porous journal gas bearings: 1st report. Earth Obs. Champ 33(254), 1718–1726 (1967)
Mori, H., Yabe, H., Yamakage, H.: Theoretical analysis of externally pressurized porous journal gas bearings: 2nd report. Earth Obs. Champ 12(54), 1512–1518 (1969)
Mori, H., Yabe, H.: Theoretical investigation of externally pressurized gas-lubricated porous journal bearing with surface-loading effect. J. Tribol. 95(2), 195–203 (1973)
Majumdar, B.C.: Analysis of externally pressurized porous gas journal bearings—I. Wear 33(1), 25–35 (1975)
Majumdar, B.C.: Whirl instability of externally pressurized gas-lubricated porous journal bearings. Wear 40(2), 141–153 (1976)
Gargiulo, E.P.: Porous wall gas lubricated journal bearings: experimental investigation. J. Tribol. 101(4), 466–473 (1979)
Gargiulo, E.P.: Porous wall gas lubricated journal bearings: theoretical investigation. J. Tribol. 101(4), 458–465 (1979)
Wang, C.-C., Lee, R.-M., Yau, H.-T., Lee, T.-E.: Nonlinear analysis and simulation of active hybrid aerodynamic and aerostatic bearing system. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Active Control 38, 1401 (2018)
Wang, C., Lo, C., Chen, C.O.: Nonlinear dynamic analysis of a flexible rotor supported by externally pressurized porous gas journal bearings. J. Tribol.-Trans. Asme 124(3), 553–561 (2002)
Wang, C.C.: Nonlinear dynamic behavior and bifurcation analysis of a rigid rotor supported by a relatively short externally pressurized porous gas journal bearing system. Acta Mech. 183(1–2), 41–60 (2006)
Wang, C.C., Chen, C.O.K.A.: Bifurcation analysis of self-acting gas journal bearings. J. Tribol. 123(4), 755–767 (2001)
Khan, N.S., et al.: Thin film flow of a second grade fluid in a porous medium past a stretching sheet with heat transfer. Alexandria Eng. J. 57(2), 1019–1031 (2017)
Khan, N.S., et al.: Thermophoresis and thermal radiation with heat and mass transfer in a magnetohydrodynamic thin-film second-grade fluid of variable properties past a stretching sheet. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 132(1), 11 (2017)
Khan, N.S., et al.: Magnetohydrodynamic nanoliquid thin film sprayed on a stretching cylinder with heat transfer. Appl. Sci. 7(3), 271 (2017)
Khan, N.S., Gul, T., Khan, M.A., Bonyah, E., Islam, S.: Mixed Convection in gravity-driven thin film non-Newtonian nanofluids flow with gyrotactic microorganisms. Results Phys. 7, S2211379717314596 (2017)
Zuhra, S., et al.: Flow and heat transfer in water based liquid film fluids dispensed with graphene nanoparticles. Results Phys. 7, S2211379717321277 (2018)
Palwasha, Z., et al.: Non-Newtonian nanoliquids thin-film flow through a porous medium with magnetotactic microorganisms. Appl. Nanosci. 8(6), 1523–1544 (2018)
Samina, Z., et al.: Magnetohydrodynamic second-grade nanofluid flow containing nanoparticles and gyrotactic microorganisms. Comput. Appl. Math. 37, 6332–6358 (2018)
Khan, N.S.: Bioconvection in second grade nanofluid flow containing nanoparticles and gyrotactic microorganisms. Braz. J. Phys. 48(3), 227–241 (2018)
Khan, N.S., et al.: Thin film flow of a second grade fluid in a porous medium past a stretching sheet with heat transfer. Alexandria Eng. J. 57, 1019–1031 (2017)
Khan, N.S.S.Z., Islam, S., Khan, I., Alkanhal, T.A., Tlili, I.: Entropy generation in MHD mixed convection non-Newtonian second-grade nanoliquid thin film flow through a porous medium with chemical reaction and stratification. Entropy 21, 139 (2017)
Palwasha, Z., et al.: Study of two-dimensional boundary layer thin film fluid flow with variable thermo-physical properties in three dimensions space. AIP Adv. 8(10), 105318 (2018)
Otsu, Y., Miyatake, M., Yoshimoto, S.: Dynamic characteristics of aerostatic porous journal bearings with a surface-restricted layer. J. Tribol.-Trans. Asme 133(1), 10 (2011)
Zhu, X.H., Andrés, L.S.: Rotordynamic performance of flexure pivot hydrostatic gas bearings for oil-free turbomachinery. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 129(4), 1020–1027 (2007)
Osborne, D.A., AndréS, L.S.: Experimental response of simple gas hybrid bearings for oil-free turbomachinery. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 128(3), 607–617 (2003)
Kim, D., Rimpel, A: Experimental and analytical studies on flexure pivot tilting pad gas bearings with dampers applied to radially compliant pads. In: ASME Turbo Expo 2009: Power for Land, Sea, and Air (2009)
Feng, K., et al.: Theoretical investigation on porous tilting pad bearings considering tilting pad motion and porous material restriction. Precis. Eng. 53, 26–37 (2018)
Wu, Y., et al.: Nonlinear dynamic analysis of a rotor-bearing system with porous tilting pad bearing support. Nonlinear Dyn. 94, 1391–1408 (2018)
Muszyńska, A.: Rotordynamics. Taylor & Francis, Milton Park (2005)
Vance, J.M., Zeidan, F., Murphy, B.: Machinery Vibration and Rotordynamics. Wiley, Hoboken (2010)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFB2000100), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51875185), and the Foundation of Hunan Province (2018JJ1006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
This work is original research and approved by all authors. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Deng, M., Feng, K. et al. Investigations on the nonlinear dynamic characteristics of a rotor supported by porous tilting pad bearings. Nonlinear Dyn 100, 2265–2286 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-05652-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-05652-0