Abstract
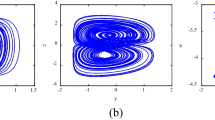
Linear time-delay feedback method makes the stable system generate the infinite-dimensional hyper-chaos, which possesses more than one positive Lyapunov exponent, infinite-dimensional, a wider chaotic parameter range, and multi-attractors, including the single-scroll attractor, the double-scroll attractor, and the composite multi-scroll attractor. The infinite-dimensional hyper-chaotic multi-attractors Chen system generated by linear time-delay feedback (HCMACS) is used for image encryption. Firstly, the state time sequences of the infinite-dimensional HCMACS are preprocessed to achieve the ideal statistical property. Secondly, two random matrices generated by random number generators are used to expand the image size. Finally, the preprocessed chaotic sequences are used to confuse and diffuse the expanded digital image to obtain the encrypted image. The special feature of the proposed method is the theoretically infinite-dimensional secret key space. Results of analysis and computer simulation indicate that the encryption algorithm has good encryption performance, which can effectively resist various attacks.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
El-Latif, A.A.A., Li, L., Wang, N., Han, Q., Niu, X.M.: A new approach to chaotic image encryption based on quantum chaotic system, exploiting color spaces. Signal Process. 93, 2986–3000 (2013)
Xiao, D., Liao, X.F., Wong, K.W.: An efficient entire chaos-based scheme for deniable authentication. Chaos Solitons Fract. 23(4), 1327–1331 (2005)
Hua, Z., Zhou, Y., Pun, C.M., Chen, C.P.: 2D Sine logistic modulation map for image encryption. Inf. Sci. 297, 80–942015 (2015)
Natiq, H., Al-Saidi, N.M.G., Said, M.R.M., Kilicman, A.: A new hyper-chaotic map and its application for image encryption. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 133(1), 6 (2018)
Zhang, Y.Q., Wang, X.Y.: A new image encryption algorithm based on non-adjacent coupled map lattices. Appl. Soft Comput. 26, 10–202015 (2015)
Boriga, R., DăscăLescu, A.C., Priescu, I.: A new hyperchaotic map and its application in an image encryption scheme. Signal Process. 29(8), 887–901 (2014)
Zhang, W., Wong, K.W., Yu, H., Zhu, Z.L.: An image encryption scheme using reverse 2-dimensional chaotic map and dependent diffusion. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 18(8), 2066–2080 (2013)
Wang, X.Y., Teng, L., Qin, X.: A novel colour image encryption algorithm based on chaos. Signal Process. 92(4), 1101–1108 (2012)
Solak, E., Cokal, C., Yildiz, O.T., Biyikoglu, T.: Cryptanalysis of Fridrich’s chaotic image encryption. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 20(5), 1405–1413 (2010)
Short, K.M.: Steps toward unmasking secure communications. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 4(4), 959–977 (1994)
Arroyo, D., Rhouma, R., Alvarez, G., Li, S.J., Fernandez, V.: On the security of a new image encryption scheme based on chaotic map lattices. Chaos 18(3), 033112 (2008)
Awad, A., Assad, S.E., Wang, Q.X., Vladeanu, C.: Comparative study of 1-D chaotic generators for digital data encryption. Int. J. Comput. Sci. 35(4), 05 (2008)
Zhou, H., Ling, X.T.: Problems with the chaotic inverse system encryption approach. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. I 44(3), 268–271 (1997)
Alvarez, G., Li, S.: Some basic cryptographic requirements for chaos-based cryptosystems. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 16(08), 2129–2151 (2006)
Li, S., Mou, X., Cai, Y., et al.: On the security of a chaotic encryption scheme: problems with computerized chaos in finite computing precision. Comput. Phys. Commun. 153(1), 52–58 (2003)
Ye, G.: Image scrambling encryption algorithm of pixel bit based on chaos map. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 31(5), 347–354 (2010)
Rhouma, R., Solak, E., Belghith, S.: Cryptanalysis of a new substitution-diffusion based image cipher. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 15(7), 1887–1892 (2010)
Arroyo, D., Li, S.J., Amigó, J.M., Alvarez, G., Rhouma, R.: Comment on Image encryption with chaotically coupled chaotic maps. Phys. D 239(12), 1002–1006 (2010)
Cokal, C., Solak, E.: Cryptanalysis of a chaos-based image encryption algorithm. Phys. Lett. A 373(15), 1357–1360 (2009)
Wang, S., Kuang, J., Li, J., et al.: Chaos-based secure communications in a large community. Phys. Rev. E 66(2), 065202 (2002)
Ren, H.P., Liu, D., Han, C.Z.: Anticontrol of chaos via direct time delay feedback. Acta Phys. Sin-Ch. ED. 55(06), 2694–08 (2006)
Ren, H.P., Li, W.C.: Heteroclinic orbits in Chen circuit with time delay. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 15(10), 3058–3066 (2010)
Ren, H.P., Bai, C., Tian, K., Grebogi, C.: Dynamics of delay induced composite multi-scroll attractor and its application in encryption. Int. J. Nonlin. Mech. 94, 334–342 (2017)
Ren, H.P., Bai, C., Huang, Z.Z.: Secure communication with hyper-chaotic Chen system. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 14(5), 1750076 (2017)
Chen, G.R., Tetsushi, U.: Yet another chaotic attractor. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 9(07), 1465–1466 (1999)
Tetsushi, U., Chen, G.R.: Bifurcation analysis of Chen’s equation. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 10(08), 1917–1931 (2000)
Lu, J., Chen, G., Zhang, S.: Dynamical analysis of a new chaotic attractor. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 12(05), 1001–1015 (2002)
Zhou, Y.C., Bao, L., Chen, C.P.: A new 1D chaotic system for image encryption. Signal Process. 97(7), 172–182 (2014)
Wu, Y., Yang, G.L., Jin, H.X., Noonan, P.J.: Image encryption using the two-dimensional logistic chaotic map. J. Electron. Image 21(1), 013014 (2012)
Chen, J.X., Zhu, Z.L., Zhang, L.B., Zhang, Y.S., Yang, B.Q.: Exploiting self-adaptive permutation-diffusion and DNA random encoding for secure and efficient image encryption. Signal Process. 142(1), 340–353 (2018)
Ye, G.D., Pan, C., Huang, X.L., Mei, Q.X.: An efficient pixel-level chaotic image encryption algorithm. Nonlinear Dyn. 94(1), 745–756 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This paper was supported in part by the Shaanxi Provincial Special Support Program for Science and Technology Innovation Leader.
Funding
The funding was provided partially by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 60804040).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix: The sensitivity of the initial conditions of HCMACS
Appendix: The sensitivity of the initial conditions of HCMACS
Since time delay is introduced, HCMACS generates hyper-chaos with theoretically infinite dimension in the sense that a continuum of initial conditions over the interval \(-\tau \le t < 0\) is required to specify the dynamical behavior, that is, when \(t > 0\), the behavior of the system is not only dependent on the states at time 0, but also related to the state on [\(-\tau \), 0]. So the initial state space of the system is infinite dimensional.
HCMACS is sensitively dependent on the state on [\(-0.3, 0\)]. To show this point, assume \(\tau = 0.3\), \(a = 35\), \(b = 3\), \(c = 18.5\), \(k = 3.8\), \(x(0) = 0.1\), \(y(0) = 0.1\), and \(z (0) = 0.1\), the state of z(t) for \(-\tau \le t < 0\) is given as two slightly different cases:
- (1)
\(z(t) = 0\) for \(-\tau \le t < 0\).
- (2)
\(z(t) = 0\) for \(-\tau \le t < -0.0195\) and \(-0.0195< t < 0\), while, \(z(-0.0195) = 2^{-32}\).
The time domain waveforms of the state x of the system for slightly different initial condition are given in Fig. 14. From Fig. 14, we can see that two time sequences are quite different. The cross-correlation of the time sequences with different initial conditions is given in Fig. 15, from which, we know that the cross-correlation is near zero. This indicates that the system is sensitive on the initial condition in the time-delay continuum. Therefore, the time-delay continuum can be used as key to expand the key space.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, CF., Ren, HP. Image encryption based on hyper-chaotic multi-attractors. Nonlinear Dyn 100, 679–698 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-05526-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-05526-5