Abstract
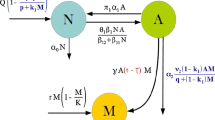
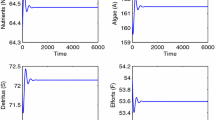
The ecological dynamic models of algal bloom in existence are of poor environmental adaptability and hard to reflect nonlinear dynamic change of algal bloom formation mechanism. To solve this problem, time variable is applied to mechanism-based model according to algal bloom nonlinear dynamic in this paper, and mechanism feature of algal bloom is represented by time function model and effecting function model. Data-driven modeling approaches including tabu search and genetic algorithm are also adopted to optimize structure and parameter for the time-varying nonlinear modeling to improve environmental adaptability and accuracy of the model. High-precision numerical solutions of the optimized time-varying nonlinear model is obtained by fourth-order Adams predictor–corrector method. This method finally realizes effective prediction of algal bloom.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zaiwen, L., Siying, L., Xiaoyi, W., et al.: Forecast methods for algal bloom in rivers and lakes. Water Resour. Prot. 05, 42–47 (2008)
Upadhyay, R.K., Roy, P., Datta, J.: Complexdynamics of ecological systems under nonlinear harvesting: Hopf bifurcation and Turing instability. Nonlinear Dyn. 79, 2251–2270 (2015)
Chakraborty, K., Manthena, V.: Modelling and analysis of spatio-temporal dynamics of a marine ecosystem. Nonlinear Dyn. 81, 1895–1906 (2015)
Wang, S.L., Jin, X.L., Huang, Z.L.: Break-out of dynamic balance of nonlinear ecosystems using first passage failure theory. Nonlinear Dyn. 80, 1403–1411 (2015)
Issa, R.: Modelling algae transport in coastal areas with a shallow water equation model including wave effects. J. Hydro Environ. Res. 210, 215–223 (2010)
Lopes, J.F., Almeida, M., et al.: Modeling the ecological patterns of a temperate lagoon in a very wet spring season. Ecol. Model. 221, 2302–2322 (2010)
Komatsu, E., Takehiko, F., et al.: Modeling of P-dynamics and algal growth in a stratified reservoir-mechanisms of P-cycle in water and interaction between overlying water and sediment. Ecol. Model. 197, 331–349 (2006)
Xiaoyi, W., Lina, T., Zaiwen, L., et al.: Formation mechanism of cyanobacteria bloom in urban Lake Reserboir. CIESC J. 05, 1492–1497 (2012)
Li, W., Zaiwen, L., et al.: Water bloom prediction and factor analysis based on multidimensional time series analysis. Huagong Xuebao/CIESC J. 64, 4649–4655 (2013)
Dagang, L., Xiaoyi, W., Zaiwen, L., et al.: Research on water-bloom prediction based on process neural network. Comput. Appl. Chem. 02, 173–176 (2011)
Xinyu, Ma., Yan, Shi, Xiaoyi, Wang, et al.: Research of water bloom prediction based on bagging ensemble learning. Comput. Appl. Chem. 02, 140–144 (2014)
Jianping, W., Shengtong, C., Haifeng, J.: Parameter optimization of water quality model: implementation of genetic algorithm and its control parameters analysis. Environ. Sci. 03, 61–65 (2005)
Jin, Ma., Bingshu, Wang, Liping, Li, et al.: Study of parameter optimization using genetic algorithm for mechanism model of superheater. J. Syst. Simul. 09, 2433–2436 (2008)
Xu, F., Jorgensen, S.E., Tao, S., et al.: Modeling the effects of macrophyte restoration on water quality and ecosystem of Lake Chao. Ecol. Model 117, 239–260 (1999)
Jin Xue-Bo, D., Jing-Jing, B.J.: Maneuvering target tracking by adaptive statistics model. J. China Univ. Posts Telecommun. 20, 108–114 (2013)
Jin, X.B., Wang, J.F., Zhang, H.Y., Cao, L.H.: ANFIS model for time series prediction. Appl. Mech. Mater. 385–386, 1411–1414 (2013)
Xue-Bo, J., Xiao-Feng, L., Yan, Shi, Li, Wang: Data driven modeling under irregular sampling. In: Proceedings of the 32nd Chinese Control Conference, pp. 4731–4734 (2013)
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (51179002), Major Project of Beijing Municipal Education Commission science and technology development plans (KZ 201510011011), and General Project of Beijing Municipal Education Commission science and technology development plans (SQKM 201610011009). Those supports are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Wang, X., Xu, J. et al. Time-varying nonlinear modeling and analysis of algal bloom dynamics. Nonlinear Dyn 84, 371–378 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-015-2552-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-015-2552-9