Abstract
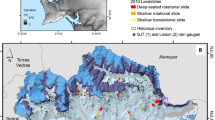
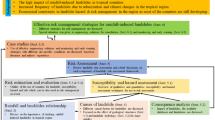
On February 17 2023, a landslide occurred on a highway slope along the Xiaolangdi Reservoir of the Yellow River, involving approximately 1,200 m3. This event directly resulted in road interruption and had profound social repercussions. This paper researches the landslide using a combination of field investigation, remote sensing imagery, laboratory tests, and numerical simulation. It traces the evolution of landslide occurrences influenced by human engineering activities and investigates the mechanisms by considering climatic factors, water levels fluctuations, and stress changes. The results indicate that: (1) fluctuations in water levels can reduce the stability coefficient of ancient landslides, albeit without directly triggering them. Moreover, alterations in soil stress induced by artificial excavation changes the distribution of the slope plastic zone, consequently altering potential sliding zones. (2) rainfall and temperature emerge as primary factors influencing the occurrence of accumulation landslides, it is particularly susceptible with the transition between winter and spring. (3) freeze-thaw action exerts significant pressure on sandstone bedding, which causes notable expansion deformation. Consequently, it is advisable to consider soil temperature and bedrock deformation when monitoring similar slopes.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dai Z, Zhang Y, Zhang C et al (2022) Interpreting the Influence of Reservoir Water Level Fluctuation on the Seepage and Stability of an ancient landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area: a case study of the Outang Landslide. Geotech Geol Eng 40:4551–4561
Deng M, Huang X, Yi Q et al (2023) Fifteen-year professional monitoring and deformation mechanism analysis of a large ancient landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Bull Eng Geol Environ 82:243
Dhakal S, Cui P, Su L et al (2020) Landslide susceptibility assessment at Kathmandu Kyirong Highway Corridor in pre-quake, co-seismic and post-quake situations. J Mt Sci 17:2652–2673
GBT50123-2019 Geotechnical test method standard. Ministry of Water Resources of the PRC, Beijing. (In Chinese)
GBT50266-2013 Standard for test methods of engineering rock mass. Ministry of Housing and Urban Rural Development of the PRC, Beijing. (In Chinese)
Han B, Tong B, Yan J et al (2018) The monitoring-based analysis on deformation-controlling factors and slope stability of reservoir landslide: hongyanzi landslide in the southwest of China. Geofluids 5:1–14
Hou T, Xu G, Zhang D et al (2022) Stability analysis of Gongjiacun landslide in the three Gorges Reservoir area under the action of reservoir water level fluctuation and rainfall. Nat Hazards 114:1647–1683
Hu S, Qiu H, Wang N et al (2022) Movement process, geomorphological changes, and influencing factors of a reactivated loess landslide on the right bank of the middle of the Yellow River. China Landslides 19:1265–1295
Hussain ML, Shafique M, Bacha AS et al (2021) Landslide inventory and susceptibility assessment using multiple statistical approaches along the Karakoram highway, northern Pakistan. J Mt Sci 18:583–598
Jie Y, Wei Y, Wang D et al (2021) Numerical study on settlement of high-fill airports in collapsible loess geomaterials: a case study of Lüliang Airport in Shanxi Province, China. J Cent South Univ 28:939–953
Keqiang H, Shangqing W, Wen D et al (2010) Dynamic features and effects of rainfall on landslides in the Three Gorges Reservoir region, China: using the Xintan landslide and the large Huangya landslide as the examples. Environ Earth Sci 59:1267–1274
Kong D, Miao C, Wu J et al (2017) Environmental impact assessments of the Xiaolangdi Reservoir on the most hyperconcentrated laden river, Yellow River, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:4337–4351
Lan H, Peng J, Zhu Y et al (2022) Research on geological and surfacial processes and major disaster effects in the Yellow River Basin. Sci China Earth Sci 65:234–256
Liu W, He S (2018) Dynamic simulation of a mountain disaster chain: landslides, barrier lakes, and outburst floods. Nat Hazards 90:757–775
Liu Y, Fan H, Wang L et al (2021) Monitoring of surface deformation in a low coherence area using distributed scatterers InSAR: case study in the Xiaolangdi Basin of the Yellow River, China. Bull Eng Geol Environ 80:25–39
Meng Z, Liyi C, Shanyong W et al (2020) Experimental study of the microstructure of loess on its macroscopic geotechnical properties of the Baozhong railway subgrade in Ningxia, China. Bull Eng Geol Environ 79:4829–4840
Tang H, Gong W, Li C et al (2019) A new framework for characterizing landslide deformation: a case study of the Yu-Kai highway landslide in Guizhou, China. Bull Eng Geol Environ 78:4291–4309
Wang FW, Zhang YM, Huo ZT et al (2004) The July 14, 2003 Qianjiangping landslide, Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Landslides 1:157–162
Wang L, Chen Y, Wang S et al (2022) Response of landslide deformation to rainfall based on multi-index monitoring: a case of the Tanjiawan landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Bull Eng Geol Environ 81:231
Wei Z, Yin G, Wang JG et al (2012) Stability analysis and supporting system design of a high-steep cut soil slope on an ancient landslide during highway construction of Tehran–Chalus. Environ Earth Sci 67:1651–1662
Xu Q, Fan XM, Huang RQ et al (2009) Landslide dams triggered by the Wenchuan Earthquake, Sichuan Province, South West China. Bull Eng Geol Environ 68:373–386
Yao Y, Zhang Y, Ma C et al (2022) Study on deformation of filling composite geological body in loess mountainous area. Nat Hazards 110:1469–1493
Yi X, Feng W, Wu M et al (2022) The initial impoundment of the Baihetan reservoir region (China) exacerbated the deformation of the Wangjiashan landslide: characteristics and mechanism. Landslides 19:1897–1912
Yin Y, Huang B, Zhang Q et al (2020) Research on recently occurred reservoir-induced Kamenziwan rockslide in Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Landslides 17:1935–1949
Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Xue S et al (2020) Stability analysis of a typical landslide mass in the Three Gorges Reservoir under varying reservoir water levels. Environ Earth Sci 79:42
Zhang Weibang (1990) The characteristics, governance goals, and research directions of the Loess Plateau. J Shanxi University: Nat Sci Ed S1:1–6 (In Chinese)
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by the Technology project of the Shanxi communications holding group (Grant No. 22-JKKJ-01, 22-JKKJ-05, 21-JKKJ-11). Shanxi transportation science research insititute Technology project (Grant No. 21-JKCF-58). Shanxi Provincial Basic Research Program (Grant No. 202203021222426, 202203021222428). National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52127815).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Chen, Y. Characteristics and mechanism of landslides on highway landfill along Xiaolangdi Reservoir of the Yellow River: a case study. Nat Hazards (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-024-06607-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-024-06607-z