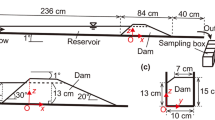
Abstract
The strong spatial nonuniformity of dam soil is a key factor for studying the safety and stability of landslide dams. In this paper, a 500 × 500 × 500 mm cubic model box was made, and the dam soil was deposited in it by layered deposition and different sliding angles to investigate the nonuniformity of the deposition. The depositional characteristics and particle size distribution (PSD) variations in different zones of different depositions were analyzed. Furthermore, based on the basic principle of grading entropy, the particle distributions of different depositions using the entropy parameter A−B coordinates were discussed. Finally, an index of nonuniformity Nd was proposed to quantitatively assess the nonuniformity degree of the deposition. We yielded that as the sliding angle increased, the deposition showed prominent sorting characteristics in the sliding direction. The coarser and finer particles were mainly concentrated in the front and back parts of the deposition, respectively. Compared with the traditional characteristic parameters, the grading entropy is more meticulous for characterizing the PSD curve. In the entropy parameter A−B coordinates, the points for the expected uniform deposition are more concentrated, which indicates that the nonuniformity of this deposition is smaller. The points of different zones for the sliding deposition are arch-shaped, and their distribution is more dispersed and directional in these coordinates, which indicates a greater nonuniformity of this deposition. For the sliding deposition, the index of nonuniformity Nd of different depositions tends to increase and then decrease with increasing sliding angle. The Nd of the deposition made by the sliding angle of 60° is the largest at 0.173. However, that of the expected uniform deposition is only 0.057. This study improves the understanding of spatial nonuniformity and aids the disaster prevention and mitigation of landslide dams.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arshad M, Nazir MS, O’Kelly BC (2020) Evolution of hydraulic conductivity models for sandy soils. Proc Inst Civ Eng Geotech Eng 173(2):97–114. https://doi.org/10.1680/jgeen.18.00062
Chang DS, Zhang LM (2013) Extended internal stability criteria for soils under seepage. Soils Found 53(4):569–583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sandf.2013.06.008
Chen S, Chen J, Liu H, Ma JX (2016) Grain size features and sedimentary environment of the sediments caused by outburst of barrier lake: a case study of the ancient barrier lake (Xuelongnang Lake). J Glaciol Geocryol 38(2):509–516. https://doi.org/10.7522/j.issn.1000-0240.2016.0057. in Chinese
Costa JE, Schuster RL (1988) The formation and failure of natural dams. Geol Soc Am Bull 100(7):1054–1068. https://doi.org/10.1130/0016-7606(1988)100%3c1054:TFAFON%3e2.3.CO;2
Fan XM, Westen CJ, Tang CX, Xu Q, Huang RQ, Wang GH (2015) The classification of damming landslides and landslide dams induced by the Wuchuan earthquake. Engineering Geology for society and territory, vol 2. Springer, Cham, pp 1143–1147. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-09057-3_201
Feng S, Vardanega PJ, Ibraim E, Widyatmoko I, Ojum C (2019) Permeability assessment of some granular mixtures. Géotechnique 69(7):646–654. https://doi.org/10.1680/jgeot.17.T.039
Heim A (1932) Landslides and human lives. Bitech Publishers, Vancouver, BC, pp 93–94
Imre E, Nagy L, Lőrincz J, Rahemi N, Schanz T (2015) Some comments on the entropy-based criteria for piping. Entropy 17(4):2281–2303. https://doi.org/10.3390/e17042281
Israr J, Zhang G (2021) Geometrical assessment of internal instability potential of granular soils based on grading entropy. Acta Geotech 16(6):1961–1970. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-020-01118-0
Istomina VS (1957) Filtration stability of soils. Gostroizdat, Moscow. Leningrad 15
Karpouza Μ, Chousianitis K, Bathrellos GD, Skilodimou HD, Kaviris G, Antonarakou A (2021) Hazard zonation mapping of earthquake-induced secondary effects using spatial multi-criteria analysis. Nat Hazards 109(1):637–669. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-021-04852-0
Li Y, Huang CM, Wang B, Tian X, Liu JJ (2017) A unified expression for grain size distribution of soils. Geoderma 288:105–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2016.11.011
Li X, Chen Q, Zhao CH, Zhou C, Wang C, Zhang QJ (2022) Depositing characteristics of landslide dams and advances in the model test for seepage failure. Pol J Environ Stud 31(6):1–15. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/151601
Liao HM, Yang XG, Lu GD, Tao J, Zhou JW (2019) Experimental study on the river blockage and landslide dam formation induced by rock slides. Eng Geol 261:105269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105269
Liu ZZ, Chen Q, Li X, Chen C, Zhou C, Wang C (2023) A review of the research on the failure potential of landslide dams caused by overtopping and seepage. Nat Hazards 116(2):1513–1538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-022-05726-9
Liu W, He S (2018) Dynamic simulation of a mountain disaster chain: landslides, barrier lakes, and outburst floods. Nat Hazards 90:757–775. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-017-3073-2
Lőrincz J (1986) Grading entropy of soils. University of Budapest, Budapest
Lőrincz J, Imre E, Gálos M, Trang QP, Rajkai K, Fityus S, Telekes G (2005) Grading entropy variation due to soil crushing. Int J Geomech 5(4):311–319. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1532-3641(2005)5:4(311)
Lőrincz J, Imre E, Fityus S, Trang PQ, Tarnal T, Talata I, Singh VP (2015) The grading entropy based criteria for structural stability of granular materials and filters. Entropy 17(5):2781–2811. https://doi.org/10.3390/e17052781
Manzella I, Labiouse V (2013) Empirical and analytical analyses of laboratory granular flows to investigate rock avalanche propagation. Landslides 10(1):23–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-011-0313-5
McDougall JR, Imre E, Barreto D, Kelly D, Laloui L (2014) Volumetric consequences of particle loss by grading entropy. Bio-and Chemo-Mechanical Processes in Geotechnical Engineering: Géotechnique Symposium in Print 2013. ICE Publishing 136–140. doi: https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.SIP13.T.002
Mei S, Chen S, Zhong QM, Shan Y (2021) Effects of grain size distribution on Landslide Dam breaching—insights from recent cases in China. Front Earth Sc-Switz 9:245. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2021.658578
O’Kelly BC, Nogal M (2020) Determination of soil permeability coefficient following an updated grading entropy method. Geotech Res 7(1):58–70. https://doi.org/10.1680/jgere.19.00036
Peng M, Zhang LM (2012) Analysis of human risks due to dam break floods—part 2: application to Tangjiashan landslide dam failure. Nat Hazards 64:1899–1923. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-012-0336-9
Renyi A (1961) On measures of entropy and information. In: Proceedings of the fourth Berkeley symposium on mathematical statistics and probability. University of California Press, Berkeley, pp 547–561
Shi BX (2020) Analysis on the typical characteristics of barrier dam. Hydro Sci Cold Zone Eng 3(4):1–8. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-3305.2020.04.002. in Chinese
Sun Y, Zheng C (2017) Breakage and shape analysis of ballast aggregates with different size distributions. Particuology 35:84–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.partic.2017.02.004
Wang GH, Huang RQ, Kamai T, Zhang FY (2013) The internal structure of a rockslide dam induced by the 2008 Wenchuan (Mw 7.9) earthquake, China. Eng Geol 156:28–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.01.004
Wang GH, Huang RQ, Lourenco SD, Kamai T (2014) A large landslide triggered by the 2008 Wenchuan (M8.0) earthquake in Donghekou area: phenomena and mechanisms. Eng Geol 182:148–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.07.013
Wang GH, Furuya G, Zhang F, Doi I, Watanable N, Wakai A, Marui H (2016) Layered internal structure and breaching risk assessment of the Higashi–Takezawa landslide dam in Niigata, Japan. Geomorphology 267:48–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2016.05.021
Wang SY, Liu J (2013) Modeling the risk assessment of landslide-dammed lakes based on the emergency response measures in Wenchuan earthquake, 2008, China. Nat Hazards 67:523–547. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-013-0584-3
Xu Q, Fan XM, Huang RQ (2009) Landslide dams triggered by the Wenchuan Earthquake, Sichuan Province, south west China. Bull Eng Geol Environ 68:373–386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-009-0214-1
Yang Y, Cao SY, Yang KJ, Li WP (2015) Experimental study of breach process of landslide dams by overtopping and its initiation mechanisms. J Hydrodyn 27(6):872–883. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-6058(15)60550-9
Youssef AM, Abu-Abdullah MM, AlFadail EA, Skilodimou HD, Bathrellos GD (2021) The devastating flood in the arid region a consequence of rainfall and dam failure: case study, Al-Lith flood on 23th November 2018, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Z Geomorphol 63(1):115–136. https://doi.org/10.1127/zfg/2021/0672
Zhang LM, Xu Y, Huang RQ, Chang DS (2011) Particle flow and segregation in giant landslide event triggered by the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake, Sichuan, China. Nat Hazard Earth Sys 11:1153–1162. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-11-1153-2011
Zhang LM, Xiao T, He J, Chen C (2019) Erosion-based analysis of breaching of Baige landslide dams on the Jinsha river, China, in 2018. Landslides 16:1965–1979. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-019-01247-y
Zhang QZ, Pan Q, Cheng Y, Luo ZJ, Shi ZM, Zhou YY (2019) Characteristics of landslide-debris flow accumulation in mountainous areas. Heliyon 5(9):e02463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02463
Zhang G, Wang HY, Israr J, Ma WG, Yang YZ, Ren KL (2022) A fractal entropy-based effective particle model used to deduce hydraulic conductivity of granular soils. Fractal Fract 6(9):474. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract6090474
Zhang WT, Liu JF, Li DL, You Y, Yang HQ (2023) Evaluation of comprehensive treatment effect of geotechnical and ecological engineering for debris flow: case of Wenchuan County, Sichuan Province. Nat Hazards 116(1):769–794. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-022-05698-w
Zheng G, Xu Q, Peng SQ (2019) Mechanism analysis of the accumulation characteristics of rock avalanche. J Eng Geol 27(4):842–852. https://doi.org/10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2018-241. in Chinese
Zhong QM, Chen SS, Wang L, Shan YB (2020) Back analysis of breaching process of Baige landslide dam. Landslides 17:1681–1692. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-020-01398-3
Zhou YY, Shi ZM, Zhang QZ, Jang B, Wu CZ (2019) Damming process and characteristics of landslide-debris avalanches. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 121:252–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2019.03.014
Zhu XH, Peng JB, Liu BX, Jiang C, Guo J (2020) Influence of textural properties on the failure mode and process of landslide dams. Eng Geol 271:105613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105613
Funding
This research was substantially supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41977239), the Sichuan Science and Technology Program (Grant No. 2022YFS0539).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Qun Chen had the idea for the manuscript. Xing Li collated and analyzed the references, and provided a first draft. Zhaozhao Liu and Chen Chen critically revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Chen, Q., Liu, Z. et al. Spatial nonuniformity of landslide dam deposition and its quantitative characterization. Nat Hazards 120, 581–599 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-023-06227-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-023-06227-z