Abstract
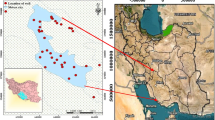
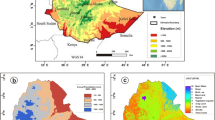
Excessive exploitation of groundwater has hitherto led to a significant land subsidence in a considerable number of plains in Iran. The compaction of aquifer layers ends up with changes in aquifer parameters, including hydraulic conductivity (Kx), specific yield (Sy), and compressibility (α). Accordingly, a precise estimation of aquifer parameters, Kx, Sy, and α seems essential for future water resources planning and management. In this study, an innovative inversion solution based on the combination of lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) and genetic algorithm (GA) was developed to determine the aquifer parameters, Kx, Sy, and α in Darab plain (in Fars province, Iran), which is highly subject to land subsidence. Herein, a newly developed LBM for unconfined groundwater flow was employed by incorporating the amount of subsidence measured by synthetic aperture radar interferometry (InSAR) spanning from 2010 to 2016. In order to optimize the aquifer parameters, the whole process of inverse modeling is replicated on the annual basis from 2010 to 2016 which leads to the temporal estimation of the aquifer parameters. Due to the compaction occurring in the aquifer system, a declining temporal trend is observed in the aquifer parameters in most parts of the plain. By fitting a function to time-dependent aquifer parameters, Kx, Sy, and α, their corresponding values and consequently the amount of subsidence in the near future, i.e., 2017, are predicted. The small average relative error (~ 3.5%) between the predicted land subsidence and the InSAR measurements demonstrates the high performance of the proposed inverse modeling approach.
Graphical abstract























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelaziz R, Merkel B (2015) Sensitivity analysis of transport modeling in a fractured gneiss aquifer. J Afr Earth Sci 103:121–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2014.12.003
Albu AF, Evtushenko YG, Zubov VI (2020) Choice of finite-difference schemes in solving coefficient inverse problems. Comput Math Math Phys 60:1589–1600. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0965542520100048
Ansumali S, Karlin IV, Arcidiacono S, Abbas A, Prasianakis NI (2007) Hydrodynamics beyond navier-stokes: exact solution to the lattice Boltzmann hierarchy. Phys Rev Lett 98:124502. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.98.124502
Anwar SH, Sukop MC (2008) Lattice Boltzmann simulation of solute transport in heterogeneous porous media with conduits to estimate macroscopic continuous time random walk model parameters. Int J Comput Fluid Dyn 8(8):213–221
Aral MM, Guan J, Maslia ML (2001) Identification of contaminant source location and release history in aquifers. J Hydrol Eng 6:225–234. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1084-0699(2001)6:3(225)
Arsyad MA, Ihsan N, Tiwow VA, Ahmar AS (2017) Model of groundwater flow using Boltzmann lattice-gas automation method in Maros karst region, Indonesia. Drink Water Eng Sci Discuss 5(10):65–72. https://doi.org/10.5194/dwes-2016-9
Ayaz MD (2017) Groundwater pollution source identification using genetic algorithm based optimization model. Int J Comput Sci 5:65–72. https://doi.org/10.26438/ijcse/v5i10.6572
Barati Moghaddam M, Mazaheri M, Samani JMV (2021) Inverse modeling of contaminant transport for pollution source identification in surface and groundwaters: a review. Groundw Sustain Dev 15:100651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2021.100651
Budinski L, Fabian J, Stipić M (2015) Lattice Boltzmann method for groundwater flow in non-orthogonal structured lattices. Comput Math with Appl 70:2601–2615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.camwa.2015.09.027
Cheng Z, Ning Z, Wang Q, Zeng Y, Qi R, Huang L, Zhang W (2019) The effect of pore structure on non-darcy flow in porous media using the lattice Boltzmann method. J Pet Sci Eng 172:391–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2018.09.066
Dehghani M, Valadan Zoej MJ, Hooper A, Hanssen RF, Entezam I, Saatchi S (2013) Hybrid conventional and persistent scatterer SAR interferometry for land subsidence monitoring in the Tehran basin. Iran ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 79:157–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2013.02.012
Fattahi E, Waluga C, Wohlmuth B, Rüde U, Manhart M, Helmig R (2016) Lattice boltzmann methods in porous media simulations: 339 from laminar to turbulent flow. Comput Fluids 140:247–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compfluid.2016.10.007
Garcia L, Shigidi A (2007) Using neural networks for parameter estimation in ground water. J Hydrol 318:215–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2005.05.028
Gentry RW, Larsen D, Ivey S (2003) Efficacy of genetic algorithm to investigate small scale aquitard leakage. J Hydraul Eng 129(7):527–535. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2003)129:7(527)
Geza M, Poeter E, McCray J (2009) Quantifying predictive uncertainty for a mountain-watershed model. J Hydrol 376:170–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.07.025
Gharibi F, Ashrafizaadeh M (2020) Darcy and inertial fluid flow simulations in porous media using the non-orthogonal central moments lattice Boltzmann method. J Pet Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2020.107572
Ghate A (2020) Inverse optimization in semi-infinite linear programs. Oper Res Lett 48(3):278–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orl.2020.02.007
Gladrow DW (1994) A lattice boltzmann equation for diffusion. J Stat Phys 79:1023–1032. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02181215
Guzy A, Malinowska AA (2020) State of the art and recent advancements in the modelling of land subsidence induced by groundwater withdrawal. Water 12(7):2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12072051
Han K, Zuo R, Ni P, Xue Z, Xu D, Wang J, Zhang D (2020) Application of a genetic algorithm to groundwater pollution source identification. J Hydrol 589:125343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125343
Hana K, Zuoa R, Nia P, Xuea Zh, Xua D, Wanga J, Zhang D (2020) Application of a genetic algorithm to groundwater pollution source identification. J Hydrol 589:125343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125343
Hekmatzadeh AA, Adel A, Zarei F, Haghighi AT (2019) Probabilistic simulation of advection-reaction-dispersion equation using random lattice Boltzmann method. Int J Heat Mass Transf 144:118647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2019.118647
Hekmatzadeh AA, Keshavarzi H, Talebbeydokhti N, Torabi HA (2020) Lattice Boltzmann solution of advection-dominated mass transport problem: a comparison. Sci Iran 27(2):625–638. https://doi.org/10.24200/sci.2018.5616.1376
Hoffmann J, Leake SA, Galloway DL, Wilson AM (2003) MODFLOW-2000, groundwater model-user guide to the subsidence and aquifer-system compaction (SUB) package. USGS, open-file report 03–233, Tucson, Arizona
Kavousi A, Reimann T, Liedl R, Raeisi E (2020) Karst aquifer characterization by inverse application of MODFLOW-2005 CFPv2 discrete-continuum flow and transport model. J Hydrol 587:124922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.124922
Lei X, Qiao Y, Guo Z, Tian Y (2013) Stimulate the pollutants transport in tai lake with lattice Boltzmann method. Procedia Eng 61:315–317
Li PW, Fu ZJ, Gu Y, Song L (2019) The generalized finite difference method for the inverse cauchy problem in two-dimensional isotropic linear elasticity. Int J Solids Struct 174–175:69–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2019.06.001
Lin Y, Yang C, Choi C, Zhang W, Machida H, Norinaga K (2021) Lattice Boltzmann simulation of multicomponent reaction-diffusion and coke formation in a catalyst with hierarchical pore structure for dry reforming of methane. Chem Eng Sci 229:116105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2020.116105
Liu H, Zhou JG, Li M, Zhao Y (2013) Multi-block lattice Boltzmann simulations of solute transport in shallow water flows. Adv Water Resour 58:24–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2013.04.008
Lorza RL, García RE, Martinez RF, Calvo MAM (2018) Using genetic algorithms with multi-objective optimization to adjust finite element models of welded joints. Metals 8(4):230. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8040230
Lu D, Ye M, Hill MC, Poeter EP, Curtis GP (2014) A computer program for uncertainty analysis integrating regression and Bayesian methods. Environ Model Softw 60:45–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2014.06.002
Mahinthakumar GK, Sayeed M (2005) Hybrid genetic algorithm-local search methods for solving groundwater source identification inverse problems. J Water Res Plan 131:45–57. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9496(2005)131:1(45)
Mahmoudpour M, Khamehchiyan M, Nikudel MR, Ghassemi MR (2016) Numerical simulation and prediction of regional land subsidence caused by groundwater exploitation in the southwest plain of Tehran. Iran Eng Geo 201:6–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.12.004
Mishra SC, Lankadasu A, Beronov KN (2005) Application of the lattice Boltzmann method for solving the energy equation of a 2-D transient conduction–radiation problem. Int J Heat Mass Transf 48(17):3648–3659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2004.10.041
Mohammad AA (2011) Lattice Boltzmann method: Fundamentals and engineering applications with computer codes. Springer
Motagh M, Djamour Y, Walter TR, Wetzel HU, Zschau J, Arabi S (2007) Land subsidence in Mashhad valley, Northeast of Iran, results from InSAR leveling and GPS. J Geophys 168(2):518–526. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.03246.x
Ostad-Ali-Askari K, Shayannejad M, Ghorbanizadeh-Kharazi H (2017) Artificial neural network for modeling nitrate pollution of groundwater in Marginal area of Zayandeh-rood river, Isfahan. Iran KSCE J Civ Eng 21(1):134–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-016-0572-8
Ostad-Ali-Askari K, Ghorbanizadeh KH, Zareian MJ (2019) Effect of management strategies on reducing negative impacts of climate change on water resources of the Isfahan-Borkhar aquifer using MODFLOW. River Res Appl 35(6):611–631. https://doi.org/10.1002/rra.3463
Peng Y, Zhou JG, Burrows R (2011) Modelling solute transport in shallow water with the lattice Boltzmann method. Comput Fluids 50(1):181–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compfluid.2011.07.008
Rahnama MB, Moafi H (2009) Investigation of land subsidence due to groundwater withdraw in Rafsanjan plain using GIS software. Arab J Geosci 2:241–246. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-009-0034-4
Regional Water Company of Fars (2016) Prohibition of water extraction from Darab Plain. Report code 2722 (in Persian)
Ru Z, Liu H, Xing L, Ding Y (2021) A well-balanced lattice Boltzmann model for the depth-averaged advection–diffusion equation with variable water depth. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 379:113745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2021.113745
Safdari Shadloo M (2019) Numerical simulation of compressible flows by lattice Boltzmann method. Numer Heat Transf A 75(3):167–182. https://doi.org/10.1080/10407782.2019.1580053
Servan-Camas B, Tsai FTC (2009) Saltater intrusion modeling in heterogeneous confined aquifers using two-relaxation-time lattice Boltzmann method. Adv Water Resour 32(4):620–631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2009.02.001
Seyedpour SM, Valizadeh I, Kirmizakis P, Doherty R, Ricken T (2021) Optimization of the groundwater remediation process using a coupled genetic algorithm-finite difference method. Water 13(3):383. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13030383
Sonnenborg T, Christensen B, Nyegaard P, Henriksen HJ, Refsgaard JC (2003) Transient modeling of regional groundwater flow using parameter estimates from steady-state automatic calibration. J Hydrol 273:188–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(02)00389-X
Sophia L, Bhattacharjya RK (2020) A ga based iterative model for identification of unknown groundwater pollution sources considering noisy data. Methods Metaheuristics Optim, Nature-Inspir. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-26458-1_17
Timothy CYC, Kaw N (2020) Inverse optimization for the recovery of constraint parameters. Eur J Oper Res 282(2):415–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2019.09.027
Xia X, Jiang S, Zhou N, Li X, Wang L (2019) Genetic algorithm hyper-parameter optimization using Taguchi design for groundwater pollution source identification. Water Supply 19(1):137–146. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2018.059
Yousefi R, Talebbeydokhti N, Afzali SH, Dehghani M (2019) Stress–strain analysis by genetic algorithm-based integration of longterm subsidence time series from different synthetic aperture radar platforms in Darab. Iran J Appl Remote Sens 13(2):024520. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.JRS.13.024520
Yousefi R, Talebbeydokhti N, Afzali SH, Hekmatzadeh AA (2021) A solution of unconfined groundwater flow with an innovative lattice Boltzmann method. Sci Iran 13(2):024520. https://doi.org/10.24200/sci.2021.55624.4321
Zhang M, Zhao W, Lin P (2019) Lattice Boltzmann method for general convection-diffusion equations: MRT model and boundary schemes. J Comput Phys 389:147–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2019.03.045
Zhou JG (2004) Lattice Boltzmann methods for shallow water flows. Springer, Berlin. https://doi.org/10.1002/fld.1489
Zhou JG (2007a) A lattice Boltzmann model for groundwater flows. Int J Mod Phys 18(06):973–991. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0129183107011078
Zhou JG (2007b) A rectangular lattice Boltzmann method for groundwater flows. Mod Phys Lett 21(09):531–542. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0217984907013080
Zhou JG (2011) Lattice Boltzmann method for advection and anisotropic dispersion equation. J Appl Mech 78(26):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4002572
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the Regional Water Company of Fars, Iran, for their contribution in collecting the groundwater information.
Funding
The authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest (such as honoraria; educational grants; participation in speakers’ bureaus; membership, employment, consultancies, stock ownership, or other equity interest; and expert testimony or patent-licensing arrangements), or non-financial interest (such as personal or professional relationships, affiliations, knowledge or beliefs) in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yousefi, R., Talebbeydokhti, N., Afzali, S.H. et al. Understanding the effects of subsidence on unconfined aquifer parameters by integration of Lattice Boltzmann Method (LBM) and Genetic Algorithm (GA). Nat Hazards 115, 1571–1600 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-022-05607-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-022-05607-1