Abstract
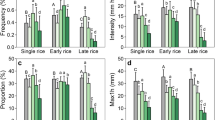
Based on the data of monthly precipitation and rice productivity at 61 meteorological stations in Jiangsu during 1966–2010, the possible impact of dryness/wetness variability on rice productivity was explored in this paper. Principal component analysis was applied to the climate-induced rice productivity index (CRPI) series and divided Jiangsu into six sub-regions—south, northwest, east, middle, southwest and northernmost. Mann–Kendall trend test for monthly Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) series in each sub-regions shows that most of Jiangsu was dominated by wetter tendency in August and drier tendency in September. CRPI had stronger negative correlation with monthly SPI series in the majority of sub-regions. Especially, the SPI in October, March, July and August had significantly negative linear relationship with CRPI in south Jiangsu, northwest Jiangsu, middle Jiangsu and southwest Jiangsu, respectively, which indicated the obvious unfavourable impact of extreme wetness episodes on rice productivity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abolverdi J, Ferdosifar G, Khalili D et al (2016) Spatial and temporal changes of precipitation concentration in Fars province, southwestern Iran. Meteorol Atmos Phys 128(2):181–196
Bannayan M, Lotfabadi SS, Sanjani S et al (2011) Effects of precipitation and temperature on crop production variability in northeast Iran. Int J Biometeorol 55(3):387–401
Caloiero T, Coscarelli R, Ferrari E et al (2015) Analysis of dry spells in southern Italy (Calabria). Water 7(6):3009–3023
Du ZX, Liu J, Liu WC (2012) Risk analysis of the high temperature heat damage in the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze river based on information diffusion. Meteorol Environ Sci 35(2):8–14 (in Chinese with English abstract)
EI-Maayar M, Lange MA (2013) A methodology to infer crop yield response to climate variability and change using long-term observations. Atmos 4:365–382
Gocic M, Trajkovic S (2014) Spatio-temporal patterns of precipitation in Serbia. Theor Appl Climatol 117(3–4):419–431
He ZX, Gong DY (2002) Interdepartmental change in western Pacific subtropical high and climatic effects. J Geogr Sci 12(2):202–209
Hua W, Chen H, Li X (2015a) Effects of future land use change on the regional climate in China. Sci China Earth Sci 58(10):1840–1848
Hua W, Chen H, Sun S, Zhou L (2015b) Assessing climatic impacts of future land use and land cover change projected with the CanESM2 model. Int J Climatol 35(12):3661–3675
Huang YY, Wang HJ, Fan K et al (2014) The western Pacific subtropical high after the 1970s: westward or eastward shift? Clim Dyn 44(7–8):2035–2047
Huang J, Xue Y, Su S, Zhang J (2015) Spatial and temporal variability of drought during 1960–2012 in Inner Mongolia, north China. Quatern Int 355:134–144
Jeong DI, St-Hilaire A, Ouarda TBMJ, Gachon P (2012) Multisite statistical downscaling model for daily precipitation combined by multivariate multiple linear regression and stochastic weather generator. Clim Change 114(3–4):567–591
Li C, Wang R (2016) Recent changes of precipitation in Gansu, Northwest China: an index-based analysis. Theor Appl Climatol. doi:10.1007/s00704-016-1783-0
Li XK, Li YC, Lu JW et al (2012) Effect of different factors on lodging of rice after flood and waterlogging induced by consecutive rainfall. J Nat Disasters 21(6):99–103 (in Chinese with English abstract)
McKee TB, Does ken NJ, Kleist J (1993) The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time steps. In: 8th conference on applied climatology, Anaheim, CA
Patel NR, Chopra P, Dadhwa VK (2007) Analyzing spatial patterns of meteorological drought using standardized precipitation index. Meteorol Appl 14(4):329–336
Rad AM, Khalili D, Kamgar-Haghighi AA, Zand-Parsa S, Banimahd SA (2016) Assessment of seasonal characteristics of streamflow droughts under semiarid conditions. Nat Hazards 82(3):1541–1564
Raja R, Nayak AK, Panda BB et al (2014) Monitoring of meteorological drought and its impact on rice (Oryza sativa L.) productivity in Odisha using standardized precipitation index. Arch Agron Soil Sci 60(12):1701–1715
Raziei T, Bordi I, Pereira LS (2008) A precipitation-based regionalization for Western Iran and regional drought variability. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 12(6):1309–1321
Raziei T, Saghafian B, Paulo AA, Pereira LS, Bordi I (2009) Spatial patterns and temporal variability of drought in western Iran. Water Resour Manag 23(3):439–455
Ren YF, Gao P, Wang CY (2010) Impacts of high temperature stress on rice and the causes in Jiangsu province. J Nat Disaster 19:101–107 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Santos JF, Pulido-Calvo I, Portela MM (2010) Spatial and temporal variability of droughts in Portugal. Water Resour Res 46(3):W03503
Shen CH (2015) Meteorological effects on rice yields in Jiangsu Province. Acta Ecologica Sin 35(12):4155–4167 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Subash N, Ram Mohan HS (2011) Trend detection in rainfall and evaluation of standardized precipitation index as a drought assessment index for rice–wheat productivity over IGR in India. Int J Climatol 31(11):1694–1709
Sun S, Sun G, Caldwell P, McNulty S, Cohen E, Xiao J, Zhang Y (2015) Drought impacts on ecosystem functions of the US National Forests and Grasslands: part II assessment results and management implications. For Ecol Manage 353:269–279
Tosunoglu F, Can I (2016) Application of copulas for regional bivariate frequency analysis of meteorological droughts in Turkey. Nat Hazards 82(3):1457–1477
Wang XL, Feng Y (2013) RHtestsV4 user manual. Climate Research Division, ASTD
Wang R, Li C (2016) Spatiotemporal analysis of precipitation trends during 1961–2010 in Hubei province, central China. Theor Appl Climatol 124(1–2):385–399
Wang P, Zhang Z, Song X et al (2014) Temperature variations and rice yields in China: historical contributions and future trends. Clim Change 124(4):777–789
Wang P, Zhan Z, Chen Y et al (2015a) How much yield loss has been caused by extreme temperature stress to the irrigated rice production in China? Clim Change 134(4):635–650
Wang H, Chen Y, Pan Y, Li W (2015b) Spatial and temporal variability of drought in the arid region of China and its relationships to teleconnection indices. J Hydrol 523:283–296
Wang Y, Xu Y, Lei C et al (2016) Spatio-temporal characteristics of precipitation and dryness/wetness in Yangtze river delta, Eastern China, during 1960–2012. Atmos Res 172:196–205
Xiao M, Zhang Q, Singh VP (2015) Influences of ENSO, NAO, IOD and PDO on seasonal precipitation regimes in the Yangtze river basin China. Int J Climatol 35(12):3556–3567
Yu K, Song J, Ping Gao (2010) Characteristics of heat damage for rice in Jiangsu province. J Meteorol Sci 4:530–533 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang Z, Zhang Q, Xu C, Liu C, Jiang T (2009) Atmospheric moisture budget and floods in the Yangtze River basin China. Theor Appl Climatol 95(3–4):331–340
Zhang Z, Tao H, Zhang Q, Zhang J, Forher N, Hörmann G (2010) Moisture budget variations in the Yangtze river Basin, China, and possible associations with large-scale circulation. Stoch Env Res Risk Assess 24(5):579–589
Zhang Z, Zhang Q, Chen X, Zhang J, Zhou J (2011) Statistical properties of moisture transport in East Asia and their impacts on wetness/dryness variations in North China. Theoret Appl Climatol 104(3–4):337–347
Zhao J, Guo J, Mu J (2015) Exploring the relationships between climatic variables and climate-induced yield of spring maize in Northeast China. Agric Ecosyst Environ 207:79–90
Zhou LM, Zhang F, Liu CA (2015) Improved yield by harvesting water with ridges and sub grooves using buried and surface plastic mulchs in a semiarid area of China. Soil Tillage Res 150:21–29
Acknowledgments
This paper was mainly supported by Natural Science Fund for Colleges and Universities in Jiangsu Province (16KJB170008), China Special Fund for Meteorological Research in the Public Interest (Major projects) (GYHY201506001-6), Public welfare projects ‘key technology and demonstration for the vegetation recovery and reconstruction in open-pit mines’ (No. 201504406), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No: 31300420) and Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu (Nos. BK20130987 and BK20151525).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, J., Zhang, F., Xue, Y. et al. Recent changes of extreme dryness/wetness pattern and its possible impact on rice productivity in Jiangsu Province, southeast China. Nat Hazards 84, 1967–1979 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2529-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2529-0