Abstract
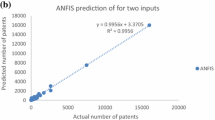
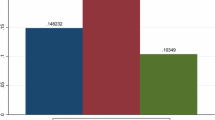
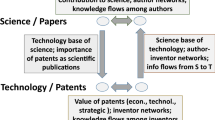
The number of granted patents, as an innovation output at macro level, may be influenced by different factors. In this study the total number of granted European patents was analyzed based on key science and economic factors, i.e. innovation potential indicators. Nine input factors were considered: total number of researchers in the higher education sector, total number of researchers in the government sector, total number of researchers in the business enterprise sector, research and development (R&D) expenditure in the higher education sector, R&D expenditure in the government sector, human resources in science and technology, employment rate, unemployment rate and gross domestic expenditure on R&D. The main goal was to determine which factor has the highest impact on the number of the granted patents. The total number of the granted patents belongs to the electrical engineering, instruments, chemistry, mechanical engineering and other fields. Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) was used as the searching methodology. In general the total number of researchers in the business enterprise sector is the most influential factor for the total number of granted patents.



Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
12 November 2019
The Editor-in-Chief has retracted this article (Markovi�� 2018) because validity of the content of this article cannot be verified.
References
Andergassen R, Nardini F, Ricottilli M (2015) Emergence and resilience in a model of innovation and network formation. Netw Spat Econ 15(2):293–311
Audretsch DB (2004) Sustaining Innovation and Growth: Public Policy Support for Entrepreneurship. Ind Innov 11(3):167–191
Audretsch D, Feldman M (1996) R&D spillovers and the geography of innovative production. Am Econ Rev 86:630–640
Bass SD, Kurgan LA (2010) Discovery of factors influencing patent value based on machine learning in the field of nanotechnology. Scientometrics 82(2)
Batabyal AA, Beladi H (2017) Patent Protection in a Model of Economic Growth in Multiple Regions. Netw Spat Econ 17:255–268
Batabyal AA, Nijkamp P (2014) Innovation, decentralization, and planning in a multi-region model of Schumpeterian Economic Growth. Netw Spat Econ 14(3-4):605–628. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11067-014-9258-2
Bottazzi L, Giovanni P (2002) Innovation and Spillovers in Regions: Evidence from European Patent Data. Eur Econ Rev 47:687–710
Budescu DV (1993) Dominance Analysis: A New Approach to the Problem of Relative Importance of Predictors in Multiple Regression. Psychol Bull 114:542–551
Capello R, Lenzi C (2013) Territorial patterns on innovation and economic growth in European Regions. Growth Chang 44(2):195–227
Coto-Millán P, Fernández XL, Pesquera MÁ, Agüeros M (2016) Impact of logistics on technical efficiency of world production (2007–2012). Netw Spat Econ 16(4):981–995
Freeman C (1969) Measurement of output of research and experimental development, a review paper. UNESCO, Paris. http://unesdoc.unesco.org/images/0013/001317/131744eo.pdf
Gössling T, Rutten R (2007) Innovation in regions. Eur Plan Stud 15(2):253–270
Grömping U (2006) Relative importance for linear regression in R: The Package relaimpo. J Stat Softw 17:1. Available at http://www.jstatsoft.org/v17/i01/. (2007)
Grömping U (2007) Estimators of Relative Importance in Linear Regression Based on Variance Decomposition. Am Stat 61:139–147
Grömping U (2009) Variable Importance Assessment in Regression: Linear Regression versus Random Forest. Am Stat 63(4):308–319. https://doi.org/10.1198/tast.2009.08199
Hu M-C, Mathews JA (2008) China’s national innovative capacity. Res Policy 37:1465–1479
Jang J-SR (1993) ANFIS: Adaptive-Network-based Fuzzy Inference Systems. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 23:665–685
Markovic D (2017) Comparative analysis of the most influential parameters that impact innovations in two EU states: Romania as “Modest Innovator” and Italy as “Moderate Innovator”, DSCIM 2017, pp. 58–62
Meek VL, Teichler U, Kearney M-L (2009) Higher education, research and innovation: changing dynamics, report on the UNESCO forum on higher education, research and knowledge, 2001–2009. https://www.unikassel.de/einrichtungen/fileadmin/datas/einrichtungen/incher/T_18__UNESCO_Forum_Report__2009.pdf
OECD (1963) Frascati manual, the measurement of scientific and technical activities, proposed standard practice for surveys on research and development. OECD. https://www.oecd.org/sti/inno/Frascati-1963.pdf
OECD (2013) Main science and technology indicators, Volume 2013/1. OECD. http://www.oecd.org/sti/2013_1_documentation_e.pdf
Prodan I (2005) Influence of research and development expenditures on number of patent aplications: selected case studies in OECD countries and Central Europe, 1981–2001. Appl Econ Int Dev 5-4. AEID
Rahimi AM (2017) Determination of the main influencing factors on road fatalities using an integrated neuro-fuzzy algorithm. Lat Am J Solids Struct, Print version ISSN 1679-7817, On-line version ISSN 1679–7825
Soete B, Stephan A (2004) Introduction: Entrepreneurship, Innovation and Growth. Ind Innov 11(3):161–165
Westland JC, Hao JX, Xiao X, Shan S (2016) Substitutes, Complements and Network Effects in Instant Messaging Services. Netw Spat Econ 16(2):525–543
Zoltan A, Audretsch D (1989) Patents as a Measure of Innovative Activity. Kyklos 42:171–180. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-6435.1989.tb00186.x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The Editor-in-Chief has retracted this article [1] because validity of the content of this article cannot be verified. This article showed evidence of authorship manipulation. The author does not agree to this retraction.
References
1. Marković, D. Netw Spat Econ (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11067-017-9373-y
About this article
Cite this article
Marković, D. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Appraisal of Science and Economic Factors on Total Number of Granted Patents. Netw Spat Econ 18, 1019–1026 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11067-017-9373-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11067-017-9373-y