Abstract
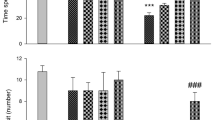
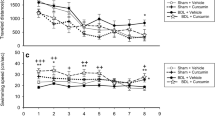
Cholestasis is a bile flow reduction that is induced following Bile Duct Ligation (BDL). Cholestasis impairs memory and induces apoptosis. Apoptosis consists of two pathways: intrinsic and extrinsic. The intrinsic pathway is modulated by BCL-2 (B cell lymphoma-2) family proteins. BCL-2 (a pro-survival BCL-2 protein) has anti-apoptotic effect, while BAD (BCL-2-associated death) and BAX (BCL-2-associated X), the other members of BCL-2 family have pro-apoptotic effect. Furthermore, TFAM (mitochondrial transcriptional factor A) is involved in transcription and maintenance of mitochondrial DNA and PGC-1α (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1α) is a master regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis. On the other hand, NeuroAid is a Traditional Chinese Medicine with neuroprotective and anti-apoptosis effects. In this study, we evaluated the effect of cholestasis on spatial memory and expression of BCL-2, BAD, BAX, TFAM, and PGC-1α in the hippocampus of rats. Additionally, we assessed the effect of NeuroAid on cholestasis-induced cognitive and genetic alterations. Cholestasis was induced by BDL surgery and NeuroAid was injected intraperitoneal at the dose of 0.4 mg/kg. Furthermore, spatial memory was evaluated using Morris Water Maze (MWM) apparatus. The results showed cholestasis impaired spatial memory, increased the expression of BAD and BAX, decreased the expression of TFAM and PGC-1α, and did not alter the expression of BCL-2. Also, NeuroAid decreased the expression of BAD and BAX and increased the expression of TFAM, PGC-1α, and BCL-2. In conclusion, cholestasis impaired spatial memory and increased the expression of pro-apoptotic genes. Also, cholestasis decreased the expression of TFAM and PGC-1α. Interestingly, NeuroAid restored the effects of cholestasis.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data will be made available on the reasonable request.
References
Boyer JL (2013) Bile formation and secretion. Compr Physiol 3(3):1035–1078. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/cphy.c120027
Wang K (2015) Molecular mechanisms of hepatic apoptosis regulated by nuclear factors. Cell Signal 27(4):729–738. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.11.038
Aktas C, Kanter M, Erboga M, Mete R, Oran M (2014) Melatonin attenuates oxidative stress, liver damage and hepatocyte apoptosis after bile-duct ligation in rats. Toxicol Ind Health 30(9):835–844. doi:https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233712464811
Motteleb AE, Ibrahim DM, Elshazly I SM (2017) Sildenafil protects against bile duct ligation induced hepatic fibrosis in rats: Potential role for silent information regulator 1 (SIRT1). Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 335:64–71. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2017.09.021
Yokota S, Ono Y, Nakao T, Zhang P, Michalopoulos GK, Khan Z (2018) Partial bile duct ligation in the mouse: a controlled model of localized obstructive cholestasis. J Vis Exp. https://doi.org/10.3791/56930
Lleo A, Marzorati S, Anaya JM, Gershwin ME (2017) Primary biliary cholangitis: a comprehensive overview. Hepatol Int 11(6):485–499. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-017-9830-1
Sirpal S, Chandok N (2017) Primary sclerosing cholangitis: diagnostic and management challenges. Clin Exp Gastroenterol 10:265–273. doi:https://doi.org/10.2147/CEG.S105872
Santamaria E, Rodriguez-Ortigosa CM, Uriarte I, Latasa MU, Urtasun R, Alvarez-Sola G, Barcena-Varela M, Colyn L, Arcelus S, Jimenez M, Deutschmann K, Peleteiro-Vigil A, Gomez-Cambronero J, Milkiewicz M, Milkiewicz P, Sangro B, Keitel V, Monte MJ, Marin JJG, Fernandez-Barrena MG, Avila MA, Berasain C (2018) The epidermal growth factor receptor ligand amphiregulin protects from cholestatic liver injury and regulates bile acids synthesis. Hepatology. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.30348
Hosseini N, Nasehi M, Radahmadi M, Zarrindast MR (2013) Effects of CA1 glutamatergic systems upon memory impairments in cholestatic rats. Behav Brain Res 256:636–645. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2013.08.018
Dastgheib M, Dehpour AR, Heidari M, Moezi L (2015) The effects of intra-dorsal hippocampus infusion of pregnenolone sulfate on memory function and hippocampal BDNF mRNA expression of biliary cirrhosis-induced memory impairment in rats. Neuroscience 306:1–9. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.08.018
Zarrindast MR, Hoseindoost S, Nasehi M (2012) Possible interaction between opioidergic and cholinergic systems of CA1 in cholestasis-induced amnesia in mice. Behav Brain Res 228(1):116–124. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2011.11.039
Javadi-Paydar M, Ghiassy B, Ebadian S, Rahimi N, Norouzi A, Dehpour AR (2013) Nitric oxide mediates the beneficial effect of chronic naltrexone on cholestasis-induced memory impairment in male rats. Behav Pharmacol 24(3):195–206. doi:https://doi.org/10.1097/FBP.0b013e3283618a8c
Gimenez-Garzo C, Salhi D, Urios A, Ruiz-Sauri A, Carda C, Montoliu C, Felipo V (2015) Rats with mild bile duct ligation show hepatic encephalopathy with cognitive and motor impairment in the absence of cirrhosis: effects of alcohol ingestion. Neurochem Res 40(2):230–240. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-014-1330-2
Newton JL, Hollingsworth KG, Taylor R, El-Sharkawy AM, Khan ZU, Pearce R, Sutcliffe K, Okonkwo O, Davidson A, Burt J, Blamire AM, Jones D (2008) Cognitive impairment in primary biliary cirrhosis: symptom impact and potential etiology. Hepatology 48(2):541–549. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.22371
Yilmaz Y, Ozdogan O (2009) Liver disease as a risk factor for cognitive decline and dementia: an under-recognized issue. Hepatology 49(2):698. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.22752
Pantiga C, Rodrigo LR, Cuesta M, Lopez L, Arias JL (2003) Cognitive deficits in patients with hepatic cirrhosis and in liver transplant recipients. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 15(1):84–89. doi:https://doi.org/10.1176/jnp.15.1.84
Weissenborn K, Heidenreich S, Giewekemeyer K, Ruckert N, Hecker H (2003) Memory function in early hepatic encephalopathy. J Hepatol 39(3):320–325
Magen I, Avraham Y, Ackerman Z, Vorobiev L, Mechoulam R, Berry EM (2010) Cannabidiol ameliorates cognitive and motor impairments in bile-duct ligated mice via 5-HT1A receptor activation. Br J Pharmacol 159(4):950–957. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00589.x
Palomero-Gallagher N, Bidmon HJ, Cremer M, Schleicher A, Kircheis G, Reifenberger G, Kostopoulos G, Haussinger D, Zilles K (2009) Neurotransmitter receptor imbalances in motor cortex and basal ganglia in hepatic encephalopathy. Cell Physiol Biochem 24(3–4):291–306. doi:https://doi.org/10.1159/000233254
Butterworth RF (1996) The neurobiology of hepatic encephalopathy. Semin Liver Dis 16(3):235–244. doi:https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-1007236
Shipovskaya AA, Dudanova OP (2018) Intrahepatic cholestasis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Ter Arkh 90(2):69–74. doi:https://doi.org/10.26442/terarkh201890269-74
Wang K (2014) Molecular mechanisms of liver injury: apoptosis or necrosis. Exp Toxicol Pathol 66(8):351–356. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etp.2014.04.004
Malhi H, Gores GJ, Lemasters JJ (2006) Apoptosis and necrosis in the liver: a tale of two deaths? Hepatology 43(2 Suppl 1):S31-44. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.21062
Elmore S (2007) Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol 35(4):495–516. doi:https://doi.org/10.1080/01926230701320337
Pistritto G, Trisciuoglio D, Ceci C, Garufi A, D’Orazi G (2016) Apoptosis as anticancer mechanism: function and dysfunction of its modulators and targeted therapeutic strategies. Aging 8(4):603–619. doi:https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.100934
Giam M, Huang DC, Bouillet P (2008) BH3-only proteins and their roles in programmed cell death. Oncogene 27(Suppl 1):S128–S136. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.50
Zhang L, Zhou Y, Chen K, Shi P, Li Y, Deng M, Jiang Z, Wang X, Li P, Xu B (2017) The pan-Bcl2 Inhibitor AT101 Activates the Intrinsic Apoptotic Pathway and Causes DNA Damage in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Stem-Like Cells. Target Oncol 12(5):677–687. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11523-017-0509-2
Ashkenazi A, Fairbrother WJ, Leverson JD, Souers AJ (2017) From basic apoptosis discoveries to advanced selective BCL-2 family inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discov 16(4):273–284. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2016.253
Yap JL, Chen L, Lanning ME, Fletcher S (2017) Expanding the Cancer Arsenal with Targeted Therapies: Disarmament of the Antiapoptotic Bcl-2 Proteins by Small Molecules. J Med Chem 60(3):821–838. doi:https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b01888
Shoshan-Barmatz V, Mizrachi D, Keinan N (2013) Oligomerization of the mitochondrial protein VDAC1: from structure to function and cancer therapy. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 117:303–334. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-386931-9.00011-8
Wang T, Yang Z, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Wang L, Zhang S, Jia L (2018) Caspase cleavage of Mcl-1 impairs its anti-apoptotic activity and proteasomal degradation in non-small lung cancer cells. Apoptosis 23(1):54–64. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-017-1436-5
Vogtle FN, Burkhart JM, Rao S, Gerbeth C, Hinrichs J, Martinou JC, Chacinska A, Sickmann A, Zahedi RP, Meisinger C (2012) Intermembrane space proteome of yeast mitochondria. Mol Cell Proteomics 11(12):1840–1852. doi:https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M112.021105
Han X, Cong H (2017) Enterovirus 71 induces apoptosis by directly modulating the conformational activation of pro-apoptotic protein Bax. J Gen Virol 98(3):422–434. doi:https://doi.org/10.1099/jgv.0.000705
Zhang R, Wang J (2018) HuR stabilizes TFAM mRNA in an ATM/p38-dependent manner in ionizing irradiated cancer cells. Cancer Sci 109(8):2446–2457. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13657
Malboosi N, Nasehi M, Hashemi M, Vaseghi S, Zarrindast MR (2020) The neuroprotective effect of NeuroAid on morphine-induced amnesia with respect to the expression of TFAM, PGC-1alpha, DeltafosB and CART genes in the hippocampus of male Wistar rats. Gene 742:144601. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2020.144601
Kunkel GH, Kunkel CJ, Ozuna H, Miralda I, Tyagi SC (2019) TFAM overexpression reduces pathological cardiac remodeling. Mol Cell Biochem 454(1–2):139–152. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-018-3459-9
Coskun P, Wyrembak J, Schriner SE, Chen HW, Marciniack C, Laferla F, Wallace DC (2012) A mitochondrial etiology of Alzheimer and Parkinson disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1820(5):553–564. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2011.08.008
Chaturvedi RK, Flint Beal M (2013) Mitochondrial diseases of the brain. Free Radic Biol Med 63:1–29. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.03.018
Villena JA (2015) New insights into PGC-1 coactivators: redefining their role in the regulation of mitochondrial function and beyond. FEBS J 282(4):647–672. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.13175
Pedros I, Petrov D, Allgaier M, Sureda F, Barroso E, Beas-Zarate C, Auladell C, Pallas M, Vazquez-Carrera M, Casadesus G, Folch J, Camins A (2014) Early alterations in energy metabolism in the hippocampus of APPswe/PS1dE9 mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1842(9):1556–1566. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.05.025
Onyango IG, Khan SM, Bennett JP Jr (2017) Mitochondria in the pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 22:854–872
Reisi P, Eidelkhani N, Rafiee L, Kazemi M, Radahmadi M, Alaei H (2017) Effects of doxepin on gene expressions of Bcl-2 family, TNF-alpha, MAP kinase 14, and Akt1 in the hippocampus of rats exposed to stress. Res Pharm Sci 12(1):15–20. doi:https://doi.org/10.4103/1735-5362.199042
Murthy SR, Thouennon E, Li WS, Cheng Y, Bhupatkar J, Cawley NX, Lane M, Merchenthaler I, Loh YP (2013) Carboxypeptidase E protects hippocampal neurons during stress in male mice by up-regulating prosurvival BCL2 protein expression. Endocrinology 154(9):3284–3293. doi:https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2013-1118
Moretti M, Budni J, Dos Santos DB, Antunes A, Daufenbach JF, Manosso LM, Farina M, Rodrigues AL (2013) Protective effects of ascorbic acid on behavior and oxidative status of restraint-stressed mice. J Mol Neurosci 49(1):68–79. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-012-9892-4
Manczak M, Kandimalla R, Yin X, Reddy PH (2018) Hippocampal mutant APP and amyloid beta-induced cognitive decline, dendritic spine loss, defective autophagy, mitophagy and mitochondrial abnormalities in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 27(8):1332–1342. doi:https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddy042
Tsai MC, Chang CP, Peng SW, Jhuang KS, Fang YH, Lin MT, Tsao TC (2015) Therapeutic efficacy of Neuro AiD (MLC 601), a traditional Chinese medicine, in experimental traumatic brain injury. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 10(1):45–54. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-014-9570-0
Chan HY, Stanton LW (2016) A pharmacogenomic profile of human neural progenitors undergoing differentiation in the presence of the traditional Chinese medicine NeuroAiD. Pharmacogenomics J 16(5):461–471. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2016.21
Lorivel T, Gandin C, Veyssiere J, Lazdunski M, Heurteaux C (2015) Positive effects of the traditional Chinese medicine MLC901 in cognitive tasks. J Neurosci Res 93(11):1648–1663. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.23591
Quintard H, Borsotto M, Veyssiere J, Gandin C, Labbal F, Widmann C, Lazdunski M, Heurteaux C (2011) MLC901, a traditional Chinese medicine protects the brain against global ischemia. Neuropharmacology 61(4):622–631. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.05.003
Gandin C, Widmann C, Lazdunski M, Heurteaux C (2016) MLC901 Favors Angiogenesis and Associated Recovery after Ischemic Stroke in Mice. Cerebrovasc Dis 42(1–2):139–154. doi:https://doi.org/10.1159/000444810
Heurteaux C, Gandin C, Borsotto M, Widmann C, Brau F, Lhuillier M, Onteniente B, Lazdunski M (2010) Neuroprotective and neuroproliferative activities of NeuroAid (MLC601, MLC901), a Chinese medicine, in vitro and in vivo. Neuropharmacology 58(7):987–1001. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2010.01.001
Chopp M, Li Y, Zhang ZG (2009) Mechanisms underlying improved recovery of neurological function after stroke in the rodent after treatment with neurorestorative cell-based therapies. Stroke 40(3 Suppl):S143–S145. doi:https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.533141
Quintard H, Lorivel T, Gandin C, Lazdunski M, Heurteaux C (2014) MLC901, a Traditional Chinese Medicine induces neuroprotective and neuroregenerative benefits after traumatic brain injury in rats. Neuroscience 277:72–86. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.06.047
Bergasa NV, Alling DW, Vergalla J, Jones EA (1994) Cholestasis in the male rat is associated with naloxone-reversible antinociception. J Hepatol 20(1):85–90
Rastegar H, Homayoun H, Afifi M, Rezayat M, Dehpour AR (2002) Modulation of cholestasis-induced antinociception by CCK receptor agonists and antagonists. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 12(2):111–118
Tag CG, Sauer-Lehnen S, Weiskirchen S, Borkham-Kamphorst E, Tolba RH, Tacke F, Weiskirchen R (2015) Bile duct ligation in mice: induction of inflammatory liver injury and fibrosis by obstructive cholestasis. J Vis Exp. https://doi.org/10.3791/52438
Villar-Lorenzo A, Rada P, Rey E, Maranon P, Arroba AI, Santamaria B, Saiz J, Ruperez FJ, Barbas C, Garcia-Monzon C, Valverde AM, Gonzalez-Rodriguez A (2019) Insulin receptor substrate 2 (IRS2) deficiency delays liver fibrosis associated with cholestatic injury. Dis Model Mech. https://doi.org/10.1242/dmm.038810
Vartak N, Damle-Vartak A, Richter B, Dirsch O, Dahmen U, Hammad S, Hengstler JG (2016) Cholestasis-induced adaptive remodeling of interlobular bile ducts. Hepatology 63(3):951–964. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.28373
Mohammadian Z, Eidi A, Mortazavi P, Tavangar MM, Asghari A (2015) Effects of folic acid on dyslipidemia and serum homocysteine in a rat model of cholestasis and hepatic fibrosis. Pol J Pathol 66(1):49–56. doi:https://doi.org/10.5114/pjp.2015.51153
Vorhees CV, Williams MT (2006) Morris water maze: procedures for assessing spatial and related forms of learning and memory. Nat Protoc 1(2):848–858. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.116
Vaseghi S, Babapour V, Nasehi M, Zarrindast MR (2019) Synergistic but not additive effect between ACPA and lithium in the dorsal hippocampal region on spatial learning and memory in rats: Isobolographic analyses. Chem Biol Interact 315:108895. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2019.108895
Vaseghi S, Babapour V, Nasehi M, Zarrindast MR (2018) The role of CA1 CB1 receptors on lithium-induced spatial memory impairment in rats. EXCLI J 17:916–934. doi:https://doi.org/10.17179/excli2018-1511
Nadimi H, Djazayery A, Javanbakht MH, Dehpour A, Ghaedi E, Derakhshanian H, Mohammadi H, Mousavi SN, Djalali M (2020) Effect of vitamin D supplementation on CREB-TrkB-BDNF pathway in the hippocampus of diabetic rats. Iran J Basic Med Sci 23(1):117–123. doi:https://doi.org/10.22038/IJBMS.2019.38170.9068
Kordestani-Moghadam P, Nasehi M, Khodagholi F, Vaseghi S, Zarrindast MR, Khani M (2020) The fluctuations of metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5 (mGluR5) in the amygdala in fear conditioning model of male Wistar rats following sleep deprivation, reverse circadian and napping. Brain Res 1734:146739. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2020.146739
Aghaei I, Shabani M, Doustar N, Nazeri M, Dehpour A (2014) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma activation attenuates motor and cognition impairments induced by bile duct ligation in a rat model of hepatic cirrhosis. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 120:133–139. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2014.03.002
Swain MG (2001) Cytokines and neuroendocrine dysregulation in obstructive cholestasis: pathophysiological implications. J Hepatol 35(3):416–418
Hosseini N, Alaei H, Zarrindast MR, Nasehi M, Radahmadi M (2014) Cholestasis progression effects on long-term memory in bile duct ligation rats. Adv Biomed Res 3:215. doi:https://doi.org/10.4103/2277-9175.143263
Cauli O, Lopez-Larrubia P, Rodrigues TB, Cerdan S, Felipo V (2007) Magnetic resonance analysis of the effects of acute ammonia intoxication on rat brain. Role of NMDA receptors. J Neurochem 103(4):1334–1343. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04878.x
Jover R, Rodrigo R, Felipo V, Insausti R, Saez-Valero J, Garcia-Ayllon MS, Suarez I, Candela A, Compan A, Esteban A, Cauli O, Auso E, Rodriguez E, Gutierrez A, Girona E, Erceg S, Berbel P, Perez-Mateo M (2006) Brain edema and inflammatory activation in bile duct ligated rats with diet-induced hyperammonemia: A model of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis. Hepatology 43(6):1257–1266. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.21180
Keller JN, Guo Q, Holtsberg FW, Bruce-Keller AJ, Mattson MP (1998) Increased sensitivity to mitochondrial toxin-induced apoptosis in neural cells expressing mutant presenilin-1 is linked to perturbed calcium homeostasis and enhanced oxyradical production. J Neurosci 18(12):4439–4450
Stewart SM, Campbell RA, McCallon D, Waller DA, Andrews WS (1992) Cognitive patterns in school-age children with end-stage liver disease. J Dev Behav Pediatr 13(5):331–338
Huang LT, Chen CC, Sheen JM, Chen YJ, Hsieh CS, Tain YL (2010) The interaction between high ammonia diet and bile duct ligation in developing rats: assessment by spatial memory and asymmetric dimethylarginine. Int J Dev Neurosci 28(2):169–174. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2009.11.006
Nasehi M, Piri M, Abbolhasani K, Zarrindast MR (2013) Involvement of opioidergic and nitrergic systems in memory acquisition and exploratory behaviors in cholestatic mice. Behav Pharmacol 24(3):180–194. doi:https://doi.org/10.1097/FBP.0b013e3283618aab
Forton DM, Patel N, Prince M, Oatridge A, Hamilton G, Goldblatt J, Allsop JM, Hajnal JV, Thomas HC, Bassendine M, Jones DE, Taylor-Robinson SD (2004) Fatigue and primary biliary cirrhosis: association of globus pallidus magnetisation transfer ratio measurements with fatigue severity and blood manganese levels. Gut 53(4):587–592
Burak KW, Le T, Swain MG (2002) Increased sensitivity to the locomotor-activating effects of corticotropin-releasing hormone in cholestatic rats. Gastroenterology 122(3):681–688
Bearn J, Allain T, Coskeran P, Munro N, Butler J, McGregor A, Wessely S (1995) Neuroendocrine responses to d-fenfluramine and insulin-induced hypoglycemia in chronic fatigue syndrome. Biol Psychiatry 37(4):245–252. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-3223(94)00121-I
Nasehi M, Mohammadi A, Ebrahimi-Ghiri M, Hashemi M, Zarrindast MR (2019) MLC901 during sleep deprivation rescues fear memory disruption in rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-018-01612-z
Chen CLH, Sharma PR, Tan BY, Low C, Venketasubramanian N (2019) The Alzheimer’s disease THErapy with NEuroaid (ATHENE) study protocol: Assessing the safety and efficacy of Neuroaid II (MLC901) in patients with mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease stable on cholinesterase inhibitors or memantine-A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Alzheimers Dement (N Y) 5:38–45. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trci.2018.12.001
Lee WT, Hsian CCL, Lim YA (2017) The effects of MLC901 on tau phosphorylation. Neuroreport 28(16):1043–1048. doi:https://doi.org/10.1097/WNR.0000000000000884
Friberg H, Wieloch T, Castilho RF (2002) Mitochondrial oxidative stress after global brain ischemia in rats. Neurosci Lett 334(2):111–114
Moha Ou Maati H, Borsotto M, Chatelain F, Widmann C, Lazdunski M, Heurteaux C (2012) Activation of ATP-sensitive potassium channels as an element of the neuroprotective effects of the Traditional Chinese Medicine MLC901 against oxygen glucose deprivation. Neuropharmacology 63(4):692–700. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.05.035
Franke TF, Kaplan DR, Cantley LC (1997) PI3K: downstream AKTion blocks apoptosis. Cell 88(4):435–437
Ferrara N (2004) Vascular endothelial growth factor: basic science and clinical progress. Endocr Rev 25(4):581–611. doi:https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2003-0027
Bekinschtein P, Cammarota M, Medina JH (2014) BDNF and memory processing. Neuropharmacology 76:677–683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.04.024
Maass A, Duzel S, Brigadski T, Goerke M, Becke A, Sobieray U, Neumann K, Lovden M, Lindenberger U, Backman L, Braun-Dullaeus R, Ahrens D, Heinze HJ, Muller NG, Lessmann V, Sendtner M, Duzel E (2016) Relationships of peripheral IGF-1, VEGF and BDNF levels to exercise-related changes in memory, hippocampal perfusion and volumes in older adults. Neuroimage 131:142–154. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.10.084
Lomonosova E, Chinnadurai G (2008) BH3-only proteins in apoptosis and beyond: an overview. Oncogene 27(Suppl 1):S2–S19. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.39
Xiang H, Kinoshita Y, Knudson CM, Korsmeyer SJ, Schwartzkroin PA, Morrison RS (1998) Bax involvement in p53-mediated neuronal cell death. J Neurosci 18(4):1363–1373
Perez MJ, Macias RI, Marin JJ (2006) Maternal cholestasis induces placental oxidative stress and apoptosis. Protective effect of ursodeoxycholic acid. Placenta 27(1):34–41. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2004.10.020
Nasehi M, Torabinejad S, Hashemi M, Vaseghi S, Zarrindast MR (2020) Effect of cholestasis and NeuroAid treatment on the expression of Bax, Bcl-2, Pgc-1alpha and Tfam genes involved in apoptosis and mitochondrial biogenesis in the striatum of male rats. Metab Brain Dis 35(1):183–192. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-019-00508-y
Shi SH, Jiang L, Xie HY, Xu J, Zhu YF, Zheng SS (2015) The effect of secondary cholestasis on the CD68-positive and CD163-positive macrophage population, cellular proliferation, and apoptosis in rat testis. J Reprod Immunol 110:36–47. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jri.2015.03.008
Oh SH, Yun KJ, Nan JX, Sohn DH, Lee BH (2003) Changes in expression and immunolocalization of protein associated with toxic bile salts-induced apoptosis in rat hepatocytes. Arch Toxicol 77(2):110–115. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-002-0415-x
Tiao MM, Lin TK, Liou CW, Wang PW, Chen JB, Kuo FY, Huang CC, Chou YM, Chuang JH (2009) Early transcriptional deregulation of hepatic mitochondrial biogenesis and its consequent effects on murine cholestatic liver injury. Apoptosis 14(7):890–899. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-009-0357-3
Arduini A, Serviddio G, Escobar J, Tormos AM, Bellanti F, Vina J, Monsalve M, Sastre J (2011) Mitochondrial biogenesis fails in secondary biliary cirrhosis in rats leading to mitochondrial DNA depletion and deletions. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 301(1):G119–G127. doi:https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00253.2010
Serviddio G, Pereda J, Pallardo FV, Carretero J, Borras C, Cutrin J, Vendemiale G, Poli G, Vina J, Sastre J (2004) Ursodeoxycholic acid protects against secondary biliary cirrhosis in rats by preventing mitochondrial oxidative stress. Hepatology 39(3):711–720. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.20101
Kang D, Kim SH, Hamasaki N (2007) Mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM): roles in maintenance of mtDNA and cellular functions. Mitochondrion 7(1–2):39–44. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mito.2006.11.017
Theilen NT, Kunkel GH, Tyagi SC (2017) The Role of Exercise and TFAM in Preventing Skeletal Muscle Atrophy. J Cell Physiol 232(9):2348–2358. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.25737
Nisoli E, Clementi E, Moncada S, Carruba MO (2004) Mitochondrial biogenesis as a cellular signaling framework. Biochem Pharmacol 67(1):1–15
Tiao MM, Lin TK, Chen JB, Liou CW, Wang PW, Huang CC, Chou YM, Huang YH, Chuang JH (2011) Dexamethasone decreases cholestatic liver injury via inhibition of intrinsic pathway with simultaneous enhancement of mitochondrial biogenesis. Steroids 76(7):660–666. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.steroids.2011.03.002
Wang P, Guo X, Zong W, Li Y, Liu G, Lv Y, Zhu Y, He S (2019) PGC-1alpha/SNAI1 axis regulates tumor growth and metastasis by targeting miR-128b in gastric cancer. J Cell Physiol. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.28193
Puigserver P, Spiegelman BM (2003) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1 alpha (PGC-1 alpha): transcriptional coactivator and metabolic regulator. Endocr Rev 24(1):78–90. doi:https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2002-0012
Peng K, Yang L, Wang J, Ye F, Dan G, Zhao Y, Cai Y, Cui Z, Ao L, Liu J, Zou Z, Sai Y, Cao J (2017) The Interaction of Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Fission/Fusion Mediated by PGC-1alpha Regulates Rotenone-Induced Dopaminergic Neurotoxicity. Mol Neurobiol 54(5):3783–3797. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9944-9
de Andrade DC, de Carvalho SN, Pinheiro D, Thole AA, Moura AS, de Carvalho L, Cortez EA (2015) Bone marrow mononuclear cell transplantation improves mitochondrial bioenergetics in the liver of cholestatic rats. Exp Cell Res 336(1):15–22. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2015.05.002
Heurteaux C, Widmann C, Moha ou Maati H, Quintard H, Gandin C, Borsotto M, Veyssiere J, Onteniente B, Lazdunski M (2013) NeuroAiD: properties for neuroprotection and neurorepair. Cerebrovasc Dis 35(Suppl 1):1–7. doi:https://doi.org/10.1159/000346228
Nasehi M, Torabinejad S, Hashemi M, Vaseghi S, Zarrindast MR (2019) Effect of cholestasis and NeuroAid treatment on the expression of Bax, Bcl-2, Pgc-1alpha and Tfam genes involved in apoptosis and mitochondrial biogenesis in the striatum of male rats. Metab Brain Dis. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-019-00508-y
Kernie SG, Erwin TM, Parada LF (2001) Brain remodeling due to neuronal and astrocytic proliferation after controlled cortical injury in mice. J Neurosci Res 66(3):317–326. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.10013
Johnson GV, Jope RS (1992) The role of microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP-2) in neuronal growth, plasticity, and degeneration. J Neurosci Res 33(4):505–512. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.490330402
Acknowledgements
Special thanks to Iranian National Center for Addiction Studies (INCAS), Tehran, Iran, for providing laboratory tools and rats.
Funding
There is no providing financial support to this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
P. Molaei conducted the experiments. S. Vaseghi and M. Hashemi wrote the manuscript and managed the literature search. M. Entezari analyzed data. M. Nasehi designed the study. All authors have approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Molaei, P., Vaseghi, S., Entezari, M. et al. The Effect of NeuroAid (MLC901) on Cholestasis-Induced Spatial Memory Impairment with Respect to the Expression of BAX, BCL-2, BAD, PGC-1α and TFAM Genes in the Hippocampus of Male Wistar Rats. Neurochem Res 46, 2154–2166 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03353-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03353-7