Abstract
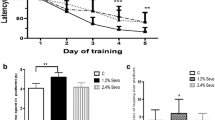
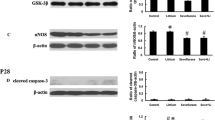
General anesthetics interfere with dendritic development and synaptogenesis, resulting in cognitive impairment in the developing animals. RhoA signal pathway plays important roles in dendritic development by regulating cytoskeleton protein such as tubulin and actin. However, it’s not clear whether RhoA pathway is involved in inhaled general anesthetics sevoflurane-induced synaptic development abnormalities and long-term cognitive dysfunction. Rats at postnatal day 7 (PND7) were injected intraperitoneally with RhoA pathway inhibitor Y27632 or saline 20 min before exposed to 2.8% sevoflurane for 4 h. The apoptosis-related proteins and RhoA/CRMP2 pathway proteins in the hippocampus were measured 6 h after sevoflurane exposure. Cognitive functions were evaluated by the open field test on PND25 rats and contextual fear conditioning test on PND32-33 rats. The dendritic morphology and density of dendritic spines in the pyramidal neurons of hippocampus were determined by Golgi staining and the synaptic plasticity-related proteins were also measured on PND33 rats. Long term potentiation (LTP) from hippocampal slices was recorded on PND34-37 rats. Sevoflurane induced caspase-3 activation, decreased the ratio of Bcl-2/Bax and increased TUNEL-positive neurons in hippocampus of PND7 rats, which were attenuated by inhibition of RhoA. However, sevoflurane had no significant effects on activity of RhoA/CRMP2 pathway. Sevoflurane disturbed dendritic morphogenesis, reduced the number of dendritic spines, decreased proteins expression of PSD-95, drebrin and synaptophysin, inhibited LTP in hippocampal slices and impaired memory ability in the adolescent rats, while inhibition of RhoA activity did not rescue the changes above induced by sevoflurane. RhoA signal pathway did not participate in sevoflurane-induced dendritic and synaptic development abnormalities and cognitive dysfunction in developing rats.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CRMP2:
-
Collapsin response mediator protein 2
- PND7:
-
Postnatal day 7
- LTP:
-
Long term potentiation
References
Jevtovic-Todorovic V, Hartman RE, Izumi Y, Benshoff ND, Dikranian K, Zorumski CF et al (2003) Early exposure to common anesthetic agents causes widespread neurodegeneration in the developing rat brain and persistent learning deficits. J Neurosci 23(3):876–882
Kong F, Xu L, He D, Zhang X, Lu H (2011) Effects of gestational isoflurane exposure on postnatal memory and learning in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 670(1):168–174
Satomoto M, Satoh Y, Terui K, Miyao H, Takishima K, Ito M et al (2009) Neonatal exposure to sevoflurane induces abnormal social behaviors and deficits in fear conditioning in mice. Anesthesiology 110(3):628–637
Brambrink AM, Evers AS, Avidan MS, Farber NB, Smith DJ, Zhang X et al (2010) Isoflurane-induced neuroapoptosis in the neonatal rhesus macaque brain. Anesthesiology 112(4):834–841
Briner A, De Roo M, Dayer A, Muller D, Habre W, Vutskits L (2010) Volatile anesthetics rapidly increase dendritic spine density in the rat medial prefrontal cortex during synaptogenesis. Anesthesiology 112(3):546–556
De Roo M, Klauser P, Briner A, Nikonenko I, Mendez P, Dayer A et al (2009) Anesthetics rapidly promote synaptogenesis during a critical period of brain development. PLoS ONE 4(9):e7043
Xiao H, Liu B, Chen Y, Zhang J (2016) Learning, memory and synaptic plasticity in hippocampus in rats exposed to sevoflurane. Int J Dev Neurosci 48:38–49
Briner A, Nikonenko I, De Roo M, Dayer A, Muller D, Vutskits L (2011) Developmental stage-dependent persistent impact of propofol anesthesia on dendritic spines in the rat medial prefrontal cortex. Anesthesiology 115(2):282–293
Head BP, Patel HH, Niesman IR, Drummond JC, Roth DM, Patel PM (2009) Inhibition of p75 neurotrophin receptor attenuates isoflurane-mediated neuronal apoptosis in the neonatal central nervous system. Anesthesiology 110(4):813–825
Lunardi N, Ori C, Erisir A, Jevtovic-Todorovic V (2010) General anesthesia causes long-lasting disturbances in the ultrastructural properties of developing synapses in young rats. Neurotox Res 17(2):179–188
Fifkova E, Delay RJ (1982) Cytoplasmic actin in neuronal processes as a possible mediator of synaptic plasticity. J Cell Biol 95(1):345–350
Matus A, Ackermann M, Pehling G, Byers HR, Fujiwara K (1982) High actin concentrations in brain dendritic spines and postsynaptic densities. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79(23):7590–7594
Matus A (2000) Actin-based plasticity in dendritic spines. Science 290(5492):754–758
Elia LP, Yamamoto M, Zang K, Reichardt LF (2006) p120 catenin regulates dendritic spine and synapse development through Rho-family GTPases and cadherins. Neuron 51(1):43–56
Govek EE, Newey SE, Akerman CJ, Cross JR, Van der Veken L, Van Aelst L (2004) The X-linked mental retardation protein oligophrenin-1 is required for dendritic spine morphogenesis. Nat Neurosci 7(4):364–372
Amano M, Nakayama M, Kaibuchi K (2010) Rho-kinase/ROCK: a key regulator of the cytoskeleton and cell polarity. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken) 67(9):545–554
Hall A, Lalli G (2010) Rho and Ras GTPases in axon growth, guidance, and branching. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2(2):a1818
Lemkuil BP, Head BP, Pearn ML, Patel HH, Drummond JC, Patel PM (2011) Isoflurane neurotoxicity is mediated by p75NTR-RhoA activation and actin depolymerization. Anesthesiology 114(1):49–57
Fukata Y, Itoh TJ, Kimura T, Menager C, Nishimura T, Shiromizu T et al (2002) CRMP-2 binds to tubulin heterodimers to promote microtubule assembly. Nat Cell Biol 4(8):583–591
Inagaki N, Chihara K, Arimura N, Menager C, Kawano Y, Matsuo N et al (2001) CRMP-2 induces axons in cultured hippocampal neurons. Nat Neurosci 4(8):781–782
Charrier E, Reibel S, Rogemond V, Aguera M, Thomasset N, Honnorat J (2003) Collapsin response mediator proteins (CRMPs): involvement in nervous system development and adult neurodegenerative disorders. Mol Neurobiol 28(1):51–64
Jin X, Sasamoto K, Nagai J, Yamazaki Y, Saito K, Goshima Y et al (2016) Phosphorylation of CRMP2 by Cdk5 regulates dendritic spine development of cortical neuron in the mouse hippocampus. Neural Plast 2016:6790743
Makihara H, Nakai S, Ohkubo W, Yamashita N, Nakamura F, Kiyonari H et al (2016) CRMP1 and CRMP2 have synergistic but distinct roles in dendritic development. Genes Cells 21(9):994–1005
Yamashita N, Ohshima T, Nakamura F, Kolattukudy P, Honnorat J, Mikoshiba K et al (2012) Phosphorylation of CRMP2 (collapsin response mediator protein 2) is involved in proper dendritic field organization. J Neurosci 32(4):1360–1365
Liu Y, Lin D, Liu C, Zhao Y, Shen Z, Zhang K et al (2017) Cyclin-dependent kinase 5/Collapsin response mediator protein 2 pathway may mediate sevoflurane-induced dendritic development abnormalities in rat cortical neurons. Neurosci Lett 651:21–29
Arimura N, Menager C, Kawano Y, Yoshimura T, Kawabata S, Hattori A et al (2005) Phosphorylation by Rho kinase regulates CRMP-2 activity in growth cones. Mol Cell Biol 25(22):9973–9984
Tao G, Zhang J, Zhang L, Dong Y, Yu B, Crosby G et al (2014) Sevoflurane induces tau phosphorylation and glycogen synthase kinase 3beta activation in young mice. Anesthesiology 121(3):510–527
Zheng H, Dong Y, Xu Z, Crosby G, Culley DJ, Zhang Y et al (2013) Sevoflurane anesthesia in pregnant mice induces neurotoxicity in fetal and offspring mice. Anesthesiology 118(3):516–526
Lu Y, Huang Y, Jiang J, Hu R, Yang Y, Jiang H et al (2016) Neuronal apoptosis may not contribute to the long-term cognitive dysfunction induced by a brief exposure to 2% sevoflurane in developing rats. Biomed Pharmacother 78:322–328
Schilling JM, Kassan A, Mandyam C, Pearn ML, Voong A, Grogman GG et al (2017) Inhibition of p75 neurotrophin receptor does not rescue cognitive impairment in adulthood after isoflurane exposure in neonatal mice. Br J Anaesth 119(3):465–471
Fredriksson A, Ponten E, Gordh T, Eriksson P (2007) Neonatal exposure to a combination of N-methyl-D-aspartate and gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor anesthetic agents potentiates apoptotic neurodegeneration and persistent behavioral deficits. Anesthesiology 107(3):427–436
Stratmann G, May LD, Sall JW, Alvi RS, Bell JS, Ormerod BK et al (2009) Effect of hypercarbia and isoflurane on brain cell death and neurocognitive dysfunction in 7-day-old rats. Anesthesiology 110(4):849–861
Terry RD, Masliah E, Salmon DP, Butters N, DeTeresa R, Hill R et al (1991) Physical basis of cognitive alterations in Alzheimer’s disease: synapse loss is the major correlate of cognitive impairment. Ann Neurol 30(4):572–580
Scheff SW, Price DA, Schmitt FA, Mufson EJ (2006) Hippocampal synaptic loss in early Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Neurobiol Aging 27(10):1372–1384
Wang WY, Luo Y, Jia LJ, Hu SF, Lou XK, Shen SL et al (2014) Inhibition of aberrant cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activity attenuates isoflurane neurotoxicity in the developing brain. Neuropharmacology 77:90–99
Tanabe K, Yamazaki H, Inaguma Y, Asada A, Kimura T, Takahashi J et al (2014) Phosphorylation of drebrin by cyclin-dependent kinase 5 and its role in neuronal migration. PLoS ONE 9(3):e92291
Worth DC, Daly CN, Geraldo S, Oozeer F, Gordon-Weeks PR (2013) Drebrin contains a cryptic F-actin-bundling activity regulated by Cdk5 phosphorylation. J Cell Biol 202(5):793–806
Bellani S, Sousa VL, Ronzitti G, Valtorta F, Meldolesi J, Chieregatti E (2010) The regulation of synaptic function by alpha-synuclein. Commun Integr Biol 3(2):106–109
Beique JC, Andrade R (2003) PSD-95 regulates synaptic transmission and plasticity in rat cerebral cortex. J Physiol 546(Pt 3):859–867
Wang SQ, Fang F, Xue ZG, Cang J, Zhang XG (2013) Neonatal sevoflurane anesthesia induces long-term memory impairment and decreases hippocampal PSD-95 expression without neuronal loss. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 17(7):941–950
Dent EW, Gupton SL, Gertler FB (2011) The growth cone cytoskeleton in axon outgrowth and guidance. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 3:3
Carcak N, Yavuz M, Eryigit KT, Kurt AH, Urhan KM, Onat FY et al (2018) Suppressive effect of Rho-kinase inhibitors Y-27632 and fasudil on spike-and-wave discharges in genetic absence epilepsy rats from Strasbourg (GAERS). Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 391(11):1275–1283
Tan M, Cha C, Ye Y, Zhang J, Li S, Wu F et al (2015) CRMP4 and CRMP2 interact to coordinate cytoskeleton dynamics, regulating growth cone development and axon elongation. Neural Plast 2015:947423
Arimura N, Inagaki N, Chihara K, Menager C, Nakamura N, Amano M et al (2000) Phosphorylation of collapsin response mediator protein-2 by Rho-kinase. Evidence for two separate signaling pathways for growth cone collapse. J Biol Chem 275(31):23973–23980
Han T, Hu Z, Tang Y, Shrestha A, Ouyang W, Liao Q (2015) Inhibiting Rho kinase 2 reduces memory dysfunction in adult rats exposed to sevoflurane at postnatal days 7–9. Biomed Rep 3(3):361–364
Uchida Y, Ohshima T, Sasaki Y, Suzuki H, Yanai S, Yamashita N et al (2005) Semaphorin3A signalling is mediated via sequential Cdk5 and GSK3beta phosphorylation of CRMP2: implication of common phosphorylating mechanism underlying axon guidance and Alzheimer’s disease. Genes Cells 10(2):165–179
Liu Y, Liu C, Zeng M, Han X, Zhang K, Fu Y et al (2018) Influence of sevoflurane exposure on mitogen-activated protein kinases and Akt/GSK-3beta/CRMP-2 signaling pathways in the developing rat brain. Exp Ther Med 15(2):2066–2073
Zhang X, Shen F, Xu D, Zhao X (2016) A lasting effect of postnatal sevoflurane anesthesia on the composition of NMDA receptor subunits in rat prefrontal cortex. Int J Dev Neurosci 54:62–69
Zhou X, Lu D, Li WD, Chen XH, Yang XY, Chen X et al (2018) Sevoflurane affects oxidative stress and alters apoptosis status in children and cultured neural stem cells. Neurotox Res 33(4):790–800
Ju LS, Jia M, Sun J, Sun XR, Zhang H, Ji MH et al (2016) Hypermethylation of hippocampal synaptic plasticity-related genes is involved in neonatal sevoflurane exposure-induced cognitive impairments in rats. Neurotox Res 29(2):243–255
Xu C, Tan S, Zhang J, Seubert CN, Gravenstein N, Sumners C et al (2015) Anesthesia with sevoflurane in neonatal rats: developmental neuroendocrine abnormalities and alleviating effects of the corticosteroid and Cl(-) importer antagonists. Psychoneuroendocrinology 60:173–181
Orliaguet G, Vivien B, Langeron O, Bouhemad B, Coriat P, Riou B (2001) Minimum alveolar concentration of volatile anesthetics in rats during postnatal maturation. Anesthesiology 95(3):734–739
Li Y, Liu C, Zhao Y, Hu K, Zhang J, Zeng M et al (2013) Sevoflurane induces short-term changes in proteins in the cerebral cortices of developing rats. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 57(3):380–390
Zhao T, Li Y, Wei W, Savage S, Zhou L, Ma D (2014) Ketamine administered to pregnant rats in the second trimester causes long-lasting behavioral disorders in offspring. Neurobiol Dis 68:145–155
Sholl DA (1953) Dendritic organization in the neurons of the visual and motor cortices of the cat. J Anat 87(4):387–406
Han D, Xu L, Xiao H, Prado SG, Shi S (2013) Dizocilpine reduces head diameter of dendritic spines in the hippocampus of adolescent rats. Psychiatry Res 210(1):351–356
Zhao YD, Ou S, Cheng SY, Xiao Z, He WJ, Zhang JH et al (2013) Dendritic development of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells in a neonatal hypoxia-ischemia injury model. J Neurosci Res 91(9):1165–1173
Lau AA, Crawley AC, Hopwood JJ, Hemsley KM (2008) Open field locomotor activity and anxiety-related behaviors in mucopolysaccharidosis type IIIA mice. Behav Brain Res 191(1):130–136
Sanders RD, Xu J, Shu Y, Januszewski A, Halder S, Fidalgo A et al (2009) Dexmedetomidine attenuates isoflurane-induced neurocognitive impairment in neonatal rats. Anesthesiology 110(5):1077–1085
Liu MG, Kang SJ, Shi TY, Koga K, Zhang MM, Collingridge GL et al (2013) Long-term potentiation of synaptic transmission in the adult mouse insular cortex: multielectrode array recordings. J Neurophysiol 110(2):505–521
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81371259); the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China (Nos. 2016A030313251; 2018A0303130272); the Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangzhou, China (No. 201707010207) and the fundamental research funds for the central universities (No. 17ykjc26).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZL and JL: Investigation, Methodology, Writing, Original draft preparation. HL and LM: Conceptualization, Data curation. ZH, WH and YL: Visualization, Software, Supervision. YL: Designing, Writing-Reviewing and Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, Z., Li, J., Miao, L. et al. Inhibition of RhoA Activity Does Not Rescue Synaptic Development Abnormalities and Long-Term Cognitive Impairment After Sevoflurane Exposure. Neurochem Res 46, 468–481 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-020-03180-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-020-03180-2