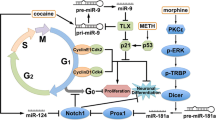
Abstract
Up to present, a large number of reports unveiled exacerbating effects of both long- and short-term administration of morphine, as a potent analgesic agent, on opium-addicted individuals and a plethora of cell kinetics, although contradictory effect of morphine on different cells have been introduced until yet. To address the potent modulatory effect of morphine on neural multipotent precursors with emphasis on endogenous sex-related neurosteroids biosynthesis, we primed the rat neural stem cells isolated from embryonic rat telencephalon to various concentrations of morphine including 10, 20, 50 and 100 µM alone or in combination with naloxone (100 µM) over period of 72 h. Flow cytometric Ki-67 expression and Annexin-V/PI based necrosis and apoptosis of exposed cells were evaluated. The total content of dihydrotestosterone and estradiol in cell supernatant was measured by ELISA. According on obtained data, both concentration- and time-dependent decrement of cell viability were orchestrated thorough down-regulation of ki-67 and simultaneous up-regulation of Annexin-V. On the other hand, the addition of naloxone (100 µM), as Mu opiate receptor antagonist, could blunt the morphine-induced adverse effects. It also well established that time-course exposure of rat neural stem cells with morphine potently could accelerate the endogenous dihydrotestosterone and estradiol biosynthesis. Interestingly, naloxone could consequently attenuate the enhanced neurosteroidogenesis time-dependently. It seems that our results discover a biochemical linkage between an accelerated synthesis of sex-related steroids and rat neural stem cells viability.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhuo M, Wu G, Wu L-J (2011) Neuronal and microglial mechanisms of neuropathic pain. Mol Brain 4:31
Abs R, Verhelst J, Maeyaert J, Van Buyten J-P, Opsomer F, Adriaensen H, Verlooy J, Van Havenbergh T, Smet M, Van Acker K (2000) Endocrine consequences of long-term intrathecal administration of opioids. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85:2215–2222
Hutchinson MR, Bland ST, Johnson KW, Rice KC, Maier SF, Watkins LR (2007) Opioid-induced glial activation: mechanisms of activation and implications for opioid analgesia, dependence, and reward. Sci World J 7:98–111
Mao J, Sung B, Ji R-R, Lim G (2002) Neuronal apoptosis associated with morphine tolerance: evidence for an opioid-induced neurotoxic mechanism. J Neurosci 22:7650–7661
Chau DL, Walker V, Pai L, Cho LM (2008) Opiates and elderly: use and side effects. Clin Interv Aging 3(2):273–278
Gil M, Sala M, Anguera I, Chapinal O, Cervantes M, Guma JR, Segura F (2003) QT prolongation and torsades de pointes in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus and treated with methadone. Am J Cardiol 92(8):995–997
Cherny N, Ripamonti C, Pereira J, Davis C, Fallon M, McQuay H, Mercadante S, Pasternak G, Ventafridda V (2001) Strategies to manage the adverse effects of oral morphine: an evidence-based report. J Clin Oncol 19:2542–2554
Bueno L, Fioramonti J (1988) 7 Action of opiates on gastrointestinal function. Baillieres Clin Gastroenterol 2(1):123–139
Esmaeili-Mahani S, Satarian L (2015) Changes in regulator of G protein signaling-4 gene expression in the spinal cord of adrenalectomized rats in response to intrathecal morphine. Physiol Pharmacol 19(1):38–45
Jin J, Kittanakom S, Wong V, Reyes BA, Van Bockstaele EJ, Stagljar I, Berrettini W, Levenson R (2010) Interaction of the mu-opioid receptor with GPR177 (Wntless) inhibits Wnt secretion: potential implications for opioid dependence. BMC Neurosci 11:33
Borlongan CV, Hayashi T, Oeltgen PR, Su T-P, Wang Y (2009) Hibernation-like state induced by an opioid peptide protects against experimental stroke. BMC Biol 7:31
Al-Hasani R, Bruchas MR (2011) Molecular mechanisms of opioid receptor-dependent signaling and behavior. Anesthesiology 115:1363
Morshead CM, Craig CG, van der Kooy D (1998) In vivo clonal analyses reveal the properties of endogenous neural stem cell proliferation in the adult mammalian forebrain. Development 125:2251–2261
Zhao C, Sun G, Li S, Lang M-F, Yang S, Li W, Shi Y (2010) MicroRNA let-7b regulates neural stem cell proliferation and differentiation by targeting nuclear receptor TLX signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:1876–1881
Ma J, Yuan X, Qu H, Zhang J, Wang D, Sun X, Zheng Q (2015) The role of reactive oxygen species in morphine addiction of SH-SY5Y cells. Life Sci 124:128–135
Galea LA, Spritzer MD, Barker JM, Pawluski JL (2006) Gonadal hormone modulation of hippocampal neurogenesis in the adult. Hippocampus 16:225–232
Malinowska-Kolodziej I, Larysz-Brysz M, Jedrzejowska-Szypulka H, Marcol W, Wlaszczuk A, Lewin-Kowalik J (2008) 17beta-estradiol and predegenerated nerve graft effect on hippocampal neurogenesis in adult female rats. Neuro Endocrinol lett 30:195–203
Nguyen T-VV, Yao M, Pike CJ (2009) Dihydrotestosterone activates CREB signaling in cultured hippocampal neurons. Brain Res 1298:1–12
Liu H, Jia D, Li A, Chau J, He D, Ruan X, Liu F, Li J, He L, Li B (2012) p53 regulates neural stem cell proliferation and differentiation via BMP-Smad1 signaling and Id1. Stem cells Dev 22:913–927
Shoae-Hassani A, Sharif S, Verdi J (2011) A 5α-reductase inhibitor, finasteride, increases differentiation and proliferation of embryonal carcinoma cell-derived-neural cells. Med Hypotheses 76(1):11–13
Pradeep P, Li X, Peegel H, Menon K (2002) Dihydrotestosterone inhibits granulosa cell proliferation by decreasing the cyclin D2 mRNA expression and cell cycle arrest at G1 phase. Endocrinology 143:2930–2935
Shoae-Hassani A, Sharif S, Tabatabaei SAM, Verdi J (2011) Could the endogenous opioid, morphine, prevent neural stem cell proliferation? Med Hypotheses 76:225–229
Sharif A, Shoae-Hassani A, Sharif S, Banafshe HR, Mortazavi-Tabatabaei SA, Verdi J (2013) 5α-reductase 1 regulates spinal cord testosterone after morphine administration. Neurol Sci 34:19–23
Goodman Y, Bruce AJ, Cheng B, Mattson MP (1996) Estrogens attenuate and corticosterone exacerbates excitotoxicity, oxidative injury, and amyloid β-peptide toxicity in hippocampal neurons. J Neurochem 66:1836–1844
Maric D, Maric I, Chang YH, Barker JL (2003) Prospective cell sorting of embryonic rat neural stem cells and neuronal and glial progenitors reveals selective effects of basic fibroblast growth factor and epidermal growth factor on self-renewal and differentiation. J Neurosci 23:240–251
Mohammad Hossein Geranmayeh AB, Barin A, Salar-Amoli J, Dehghan MM, Rahbarghazi R, Azari H (2015) Paracrine neuroprotective effects of neural stem cells on glutamate-induced cortical neuronal cell excitotoxicity. Adv Pharm Bull. doi:10.15171/apb.2015.070
Girard SD, Devéze A, Nivet E, Gepner B, Roman FS, Féron F (2011) Isolating nasal olfactory stem cells from rodents or humans. J Vis Exp 54 pii: 2762
Ghods AJ, Irvin D, Liu G, Yuan X, Abdulkadir IR, Tunici P, Konda B, Wachsmann-Hogiu S, Black KL, Yu JS (2007) Spheres isolated from 9L gliosarcoma rat cell line possess chemoresistant and aggressive cancer stem-like cells. Stem Cells 25:1645–1653
Rahbarghazi R, Nassiri SM, Khazraiinia P, Kajbafzadeh A-M, Ahmadi SH, Mohammadi E, Molazem M, Zamani-Ahmadmahmudi M (2012) Juxtacrine and paracrine interactions of rat marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells, muscle-derived satellite cells, and neonatal cardiomyocytes with endothelial cells in angiogenesis dynamics. Stem Cells Dev 22:855–865
Willner D, Cohen-Yeshurun A, Avidan A, Ozersky V, Shohami E, Leker RR (2014) Short term morphine exposure in vitro alters proliferation and differentiation of neural progenitor cells and promotes apoptosis via mu receptors. PLoS One 9(7):e103043
Whittington M, Traub R, Faulkner H, Jefferys J, Chettiar K (1998) Morphine disrupts long-range synchrony of gamma oscillations in hippocampal slices. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:5807–5811
Saboory E, Derchansky M, Ismaili M, Jahromi SS, Brull R, Carlen PL, El Beheiry H (2007) Mechanisms of morphine enhancement of spontaneous seizure activity. Anesth Analg 105:1729–1735
Lewis SS, Loram LC, Hutchinson MR, Li C-M, Zhang Y, Maier SF, Huang Y, Rice KC, Watkins LR (2012) (+)-naloxone, an opioid-inactive toll-like receptor 4 signaling inhibitor, reverses multiple models of chronic neuropathic pain in rats. J Pain 13:498–506
Feng X, Ippolito GC, Tian L, Wiehagen K, Oh S, Sambandam A, Willen J, Bunte RM, Maika SD, Harriss JV (2010) Foxp1 is an essential transcriptional regulator for the generation of quiescent naive T cells during thymocyte development. Blood 115:510–518
Challen GA, Boles N, Lin KYK, Goodell MA (2009) Mouse hematopoietic stem cell identification and analysis. Cytometry A 75:14–24
Arguello AA, Harburg GC, Schonborn JR, Mandyam CD, Yamaguchi M, Eisch AJ (2008) Time course of morphine’s effects on adult hippocampal subgranular zone reveals preferential inhibition of cells in S phase of the cell cycle and a subpopulation of immature neurons. Neuroscience 157:70–79
Ha JS, Lee C-S, Maeng J-S, Kwon K-S, Park SS (2009) Chronic glutamate toxicity in mouse cortical neuron culture. Brain Res 1273:138–143
Sahebgharani M, Nejati M, Sepehrizadeh Z, Khorramizadeh M-R, Bahrololoumi-Shapourabadi M, Hashemi-Bozchlou S, Esmaeili J, Ghazi-Khansari M (2008) Lithium chloride protects PC12 pheochromocytoma cell line from morphine-induced apoptosis. Arch Iran Med 11:639–648
Boronat MA, García-Fuster MJ, García-Sevilla JA (2001) Chronic morphine induces up-regulation of the pro-apoptotic Fas receptor and down-regulation of the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 oncoprotein in rat brain. Br J Pharmacol 134:1263–1270
Tegeder I, Grösch S, Schmidtko A, Häussler A, Schmidt H, Niederberger E, Scholich K, Geisslinger G (2003) G protein-independent G1 cell cycle block and apoptosis with morphine in adenocarcinoma cells: involvement of p53 phosphorylation. Cancer Res 63:1846–1852
Gupta K, Kshirsagar S, Chang L, Schwartz R, Law P-Y, Yee D, Hebbel RP (2002) Morphine stimulates angiogenesis by activating proangiogenic and survival-promoting signaling and promotes breast tumor growth. Cancer Res 62:4491–4498
Gan TJ, Ginsberg B, Glass P, Fortney J, Jhaveri R, Perno R (1997) Opioid-sparing effects of a low-dose infusion of naloxone in patient-administered morphine sulfate. Anesthesiology 87:1075–1081
Wang Q, Zhou H, Gao H, Chen S-H, Chu C-H, Wilson B, Hong J-S (2012) Naloxone inhibits immune cell function by suppressing superoxide production through a direct interaction with gp91phox subunit of NADPH oxidase. J Neuroinflammation 9:32
Wang H-Y, Friedman E, Olmstead M, Burns L (2005) Ultra-low-dose naloxone suppresses opioid tolerance, dependence and associated changes in mu opioid receptor–G protein coupling and Gβγ signaling. Neuroscience 135:247–261
Cui J, Wang Y, Dong Q, Wu S, Xiao X, Hu J, Chai Z, Zhang Y (2011) Morphine protects against intracellular amyloid toxicity by inducing estradiol release and upregulation of Hsp70. J Neurosci 31:16227–16240
Ghiafeh Davoodi F, Javan M, Ahmadiani A (2010) The effect of swim stress on morphine tolerance development and the possible role of nitric oxide in this process. Iran J Pharm Res 4:167–173
Vuong C, Van Uum SH, O’Dell LE, Lutfy K, Friedman TC (2010) The effects of opioids and opioid analogs on animal and human endocrine systems. Endocr Rev 31:98–132
Mensah-Nyagan AG, Do-Rego JL, Feuilloley M, Marcual A, Lange C, Pelletier G, Vaudry H (1996) In vivo and in vitro evidence for the biosynthesis of testosterone in the telencephalon of the female frog. J Neurochem 67:413–422
Spritzer MD, Galea LA (2007) Testosterone and dihydrotestosterone, but not estradiol, enhance survival of new hippocampal neurons in adult male rats. Dev Neurobiol 67:1321–1333
Estrada M, Varshney A, Ehrlich BE (2006) Elevated testosterone induces apoptosis in neuronal cells. J Biol Chem 281:25492–25501
Singer CA, Rogers KL, Strickland TM, Dorsa DM (1996) Estrogen protects primary cortical neurons from glutamate toxicity. Neurosci Lett 212:13–16
Chabab A, Sultan C, Fenart O, Descomps B (1986) Stimulation of aromatase activity by dihydrotestosterone in human skin fibroblasts. J Steroid Biochem 25:165–169
Bethea CL, Reddy AP, Robertson N, Coleman K (2013) Effects of aromatase inhibition and androgen activity on serotonin and behavior in male macaques. Behav Neurosci 127:400–414
Marić D, Stojilković S, Krsmanović L, Simonović I, Kovačević R, Andjus R (1987) Rapid naloxone-induced alterations of androgen variables in the growing male rat. Neuroendocrinology 46:167–175
Matthes HW, Maldonado R, Simonin F, Valverde O, Slowe S, Kitchen I, Befort K, Dierich A, Le Meur M, Dollé P (1996) Loss of morphine-induced analgesia, reward effect and withdrawal symptoms in mice lacking the µ-opioid-receptor gene. Nature 383(6603):819–823
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feizy, N., Nourazarian, A., Rahbarghazi, R. et al. Morphine Inhibited the Rat Neural Stem Cell Proliferation Rate by Increasing Neuro Steroid Genesis. Neurochem Res 41, 1410–1419 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-1847-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-1847-7