Abstract
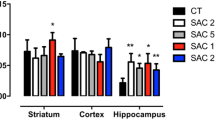
Long-term intake of aspartame at the acceptable daily dose causes oxidative stress in rodent brain mainly due to the dysregulation of glutathione (GSH) homeostasis. N-Acetylcysteine provides the cysteine that is required for the production of GSH, being effective in treating disorders associated with oxidative stress. We investigated the effects of N-acetylcysteine treatment (150 mg kg−1, i.p.) on oxidative stress biomarkers in rat brain after chronic aspartame administration by gavage (40 mg kg−1). N-Acetylcysteine led to a reduction in the thiobarbituric acid reactive substances, lipid hydroperoxides, and carbonyl protein levels, which were increased due to aspartame administration. N-Acetylcysteine also resulted in an elevation of superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase, glutathione reductase activities, as well as non-protein thiols, and total reactive antioxidant potential levels, which were decreased after aspartame exposure. However, N-acetylcysteine was unable to reduce serum glucose levels, which were increased as a result of aspartame administration. Furthermore, catalase and glutathione S-transferase, whose activities were reduced due to aspartame treatment, remained decreased even after N-acetylcysteine exposure. In conclusion, N-acetylcysteine treatment may exert a protective effect against the oxidative damage in the brain, which was caused by the long-term consumption of the acceptable daily dose of aspartame by rats.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Butchko HH, Stargel WW, Comer CP, Mayhew DA, Benninger C, Blackburn GL, Sonneville LM, Geha RS, Hertelendy Z, Koestner A, Leon AS, Liepa GU, McMartin KE, Mendenhall CL, Munro IC, Novotny EJ, Renwick AG, Schiffman SS, Schomer DL, Shaywitz BA, Spiers PA, Tephly TR, Thomas JA, Trefz FK (2002) Aspartame: review of safety. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 35:S1–S93
Oyama Y, Sakai H, Arata T, Okano Y, Akaike N, Sakai K, Noda K (2002) Cytotoxic effects of methanol, formaldehyde, and formate on dissociated rat thymocytes: a possibility of aspartame toxicity. Cell Biol Toxicol 18:43–50
Humphries P, Pretorius E, Naudé H (2008) Direct and indirect cellular effects of aspartame on the brain. Eur J Clin Nutr 62:451–462
Ranney RE, Oppermann JA, Muldoon E, McMahon FG (1976) Comparative metabolism of aspartame in experimental animals and humans. J Toxicol Environ Health 2:441–451
Krebs MO (1992) Excitatory amino acids: a new class of neurotransmitters: pharmacology and functional properties. Encephale 18:271–279
Fernstrom JD, Fernstrom MH, Gillis MA (1983) Acute effects of aspartame on large neutral amino acid and mono-amines in rat brain. Life Sci 32:1651–1658
Massachusetts Medical Society (1984) Evaluation of consumer complaints related to aspartame use. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 33:605–607
Stegink LD, Brummel MC, Filer LJ, Baker GL (1983) Blood methanol concentrations in one year old infants administered graded doses of aspartame. J Nutr 113:1600–1606
Trocho C, Pardo R, Rafecas I, Virgili J, Remesar X, Fernández-López JA, Amemany M (1998) Formaldehyde derived from dietary aspartame binds to tissue components in vivo. Life Sci 63:337–349
European Food Safety Authority (2006) EFSA assesses new aspartame study and reconfirms its safety. European Food Safety Authority, Bologna
Mourad IM, Noor NA (2011) Aspartame (a widely used artificial sweetener) and oxidative stress in the rat cerebral cortex. Int J Pharm Biomed Sci 2:4–10
Abdel-Salam OME, Salem NA, El-Shamarka MES, Hussein JS, Ahmed NAS, El-Nagar MES (2012) Studies on the effects of aspartame on memory and oxidative stress in brain of mice. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 16:2092–2210
Abhilash M, Sauganth PMV, Varghese MV, Nair RH (2013) Long-term consumption of aspartame and brain antioxidant defense status. Drug Chem Toxicol 36:135–140
Iyyaswamy A, Rathinasamy S (2012) Effect of chronic exposure to aspartame on oxidative stress in the brain of albino rats. J Biosci 37:679–688
Ruiz NAL, Mejía AV, Hernández-Martínez NL, Gómez-Garduño J, Dorado-González VM, Osnaya-Brizuela N, García-Álvarez R, Barragán-Mejía G, Guzmán DC (2008) Efecto de aspartame, fenilalanina y ácido aspártico sobre los niveles de glutatión y peroxidación de lípidos en cérebro de rata. Arch Neurocien (Mex) 13:79–83
Farbiszewski R, Witek A, Skrzydlewska E (2000) N-Acetylcysteine or trolox derivate mitigate the toxic effects of methanol on the antioxidant system of rat brain. Toxicology 156:47–55
Samuni Y, Goldstein S, Dean OM, Berk M (2013) The chemistry and biological activities of N-acetylcysteine. Biochim Biophys Acta 1830:4117–4129
Sies H (1999) Glutathione and its role in cellular functions. Free Radic Biol Med 27:916–921
Jiang ZY, Woollard ACS, Wolff SP (1991) Lipid hydroperoxide measurement by oxidation of Fe2+ in the presence of xylenol orange. Comparison with the TBA assay and an iodometric method. Lipid 26:853–856
Buege JA, Aust SD (1978) Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 52:302–309
Reznick AZ, Packer L (1994) Carbonyl assay for determination of oxidatively modified proteins. Methods Enzymol 233:357–363
Misra HP, Fridovich I (1972) The role of superoxide anion in the autoxidation of epinephrine and a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem 247:3170–3175
Chance B, Sies H, Boveris A (1979) Hydroperoxide metabolism in mammalian organs. Physiol Rev 59:527–625
Flohé L, Gunzler WA (1984) Assays of glutathione peroxidase. In: Packer L (ed) Methods in enzymology. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 114–121
Carlberg I, Mannervik B (1985) Glutathione reductase. Methods Enzymol 113:484–499
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB (1974) Glutathione S-transferases the first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem 249:7130–7139
Ellman L (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82:70–77
Roe JH, Kuether CA (1942) A color reaction for dehydroascorbic acid useful in the determination of vitamin C. Science 95:77
Evelson P, Travacio M, Repetto M, Escobar J, Llesuy S, Lissi EA (2001) Evaluation of total reactive antioxidant potential (TRAP) of tissue homogenates and their cytosols. Arch Biochem Biophys 388:261–266
Lowry OH, Rosebrough MJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–269
Kim JY, Seo J, Cho KH (2011) Aspartame-fed zebrafish exhibit acute deaths with swimming defects and saccharin-fed zebrafish have elevation of cholesteryl ester transfer protein activity in hypercholesterolemia. Food Chem Toxicol 49:2899–2905
Collison KS, Makhoul NJ, Zaidi MZ, Al-Rabiah R, Inglis A, Andres BL, Ubungen R, Shoukri M, Al-Mohanna FA (2012) Interactive effects of neonatal exposure to monosodium glutamate and aspartame on glucose homeostasis. Nutr Metab (Lond) 9:58
Ferland A, Brassard P, Poirier P (2007) Is aspartame really safer in reducing the risk of hypoglycemia during exercise in patients with type 2 diabetes? Diabetes Care 30:e59
Nuttall FQ, Schweim KJ, Gannon MC (2006) Effect of orally administered phenylalanine with and without glucose on insulin, glucagon and glucose concentrations. Horm Metab Res 38:518–523
Piccardo MG, Rosa M, Russo L (1983) The effects of a load of phenylalanine on glucose metabolism. Boll Soc Ital Bio Sper 59:167–170
Christian B, McConnaughey K, Bethea E, Brantley S, Coffey A, Hammond L, Harrell S, Metcalf K, Muehlenbein D, Spruil W, Brinson L, McConnaughey M (2004) Chronic aspartame affects T-maze performance, brain cholinergic receptors and Na+K+-ATPase in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 78:121–127
Takahashi A, Kishi E, Ishimaru H, Ikarashi Y, Maruyama Y (1998) Stimulation of rat hypothalamus by microdialysis with K + : increase of ACh release elevates plasma glucose. Am J Physiol 275:R1647–R1653
Shigeta H, Yoshida T, Nakai M, Mori H, Nishioka H, Kajiyama S, Kitagawa Y, Kanatsuna T, Kondo M (1985) Effects of aspartame on diabetic rats and diabetic patients. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo) 31:533–540
Halliwell B (2001) Role of free radicals in the neurodegenerative diseases: therapeutic implications for antioxidant treatment. Drugs Aging 18:685–716
Simintzi I, Schulpis KH, Angelogianni P, Liapi C, Tsakiris S (2008) l-cysteine and glutathione restore the modulation of rat frontal cortex Na+, K+-ATPase activity induced by aspartame metabolites. Food Chem Toxicol 46:2074–2079
Finamor IA, Saccol EM, Gabriel D, Ourique GM, Riffel AP, Konrad SP, Belló-Klein A, Partata W, Baldisserotto B, Llesuy SF, Pavanato MA (2012) Effects of parboiled rice diet on oxidative stress parameters in kidney of rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. J Med Food 15:598–604
Rice ME, Russo-Menna I (1998) Differential compartmentalization of brain ascorbate and glutathione between neuron and glia. Neuroscience 82:1213–1223
Skrzydlewska E, Witek A, Farbiszewski R (1998) The comparison of the antioxidant defense potential of brain to liver of rats after methanol ingestion. Comp Biochem Physiol C 120:289–294
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC (1999) Free radicals in biology and medicine. Oxford University Press, New York
Pigeolet E, Corbisier P, Houbion A, Lambert D, Michiels C, Raes M, Zachary MD, Remacle J (1990) Glutathione peroxidase, superoxide dismutase, and catalase inactivation by peroxides and oxygen derived free radicals. Mech Ageing Dev 15:283–297
Jain A, Mårtensson J, Stole E, Auld PA, Meister A (1991) Glutathione deficiency leads to mitochondrial damage in brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:1913–1917
De Flora S, Bennicelli C, Camoirano A, Serra D, Romano M, Rossi GA, Morelli A, De Flora A (1985) In vivo effects of N-acetylcysteine on glutathione metabolism and on the biotransformation of carcinogenic and or mutagenic compounds. Carcinogenesis 6:1735–1745
Yang Y, Cheng JZ, Singhal SS, Saini M, Pandya U, Awasthi S (2001) Role of glutathione S-transferase in protection against lipid peroxidation. Overexpression of hGSTA2-2 in K562 cells protects against hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis and inhibits JNK and caspase 3 activation. J Biol Chem 276:19220–19230
Simintzi I, Schulpis KH, Angelogianni P, Liapi C, Tsakiris S (2007) l-cysteine and glutathione restore the reduction of rat hippocampal Na+, K+-ATPase activity induced by aspartame metabolites. Toxicology 237:177–183
Meister A (1983) Selective modification of glutathione metabolism. Science 220:472–477
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Tecnológico (CNPq), to the Comissão de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) and to the Fundo de Incentivo a Pesquisa da Universidade Federal de Santa Maria (FIPE-UFSM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Finamor, I.A., Ourique, G.M., Pês, T.S. et al. The Protective Effect of N-Acetylcysteine on Oxidative Stress in the Brain Caused by the Long-Term Intake of Aspartame by Rats. Neurochem Res 39, 1681–1690 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-014-1360-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-014-1360-9