Abstract
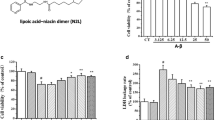
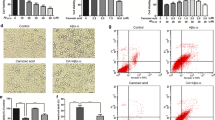
Inflammatory process has a fundamental role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease and insoluble amyloid beta deposits and neurofibrillary tangles provide the obvious stimuli for inflammation. The present study demonstrate the effect of pretreatment of 1,8-cineole (Cin) on inflammation induced by Aβ(25–35) in differentiated PC12 cells. The cells were treated with Cin at different doses for 24 h and then replaced by media containing Aβ(25–35) for another 24 h. The cell viability was decreased in Aβ(25–35) treated cells which was significantly restored by Cin pretreatment. Cin successfully reduced the mitochondrial membrane potential, ROS and NO levels in Aβ(25–35) treated cells. Cin also lowered the levels of proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 in Aβ(25–35) treated cells. Moreover, Cin also succeeded in lowering the expression of NOS-2, COX-2 and NF-κB. This study suggests the protective effects of Cin on inflammation and provides additional evidence for its potential beneficial use in therapy as an anti-inflammatory agent in neurodegenerative disease.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wimo A, Jonsson L, Winblad B (2006) An estimate of the worldwide prevalence and direct costs of dementia in 2003. Dement Geriatr 21(3):175–181
Hebert LE, Scherr PA, Bienias JL, Bennett DA, Evans DA (2003) Alzheimer disease in the US population: prevalence estimates using the 2000 census. Arch Neurol 60(8):1119–1122
Couturier J, Paccalin M, Morel M, Terro F, Milin S, Pontcharraud R, Fauconneau B, Page G (2011) Prevention of the β-amyloid peptide-induced inflammatory process by inhibition of double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase in primary murine mixed co-cultures. J Neuroinflamm 8:72
Bakshi P, Margenthaler E, Laporte V, Crawford F, Mullan M (2008) Novel role of CXCR2 in regulation of gamma-secretase activity. ACS Chem Biol 3(12):777–789
Liao YF, Wang BJ, Cheng HT, Kuo LH, Wolfe MS (2004) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-1beta, and interferon-gamma stimulate gamma secretase-mediated cleavage of amyloid precursor protein through a JNK-dependent MAPK pathway. J Biol Chem 279(47):49523–49532
Juergens UR, Stober M, Vetter H (1998) Inhibition of cytokine production and arachidonic acid metabolism by eucalyptol (1,8-cineole) in human blood monocytes in vitro. Eur J Med Res 3(11):508–510
Juergens UR, Stober M, Schmidt-Schilling L, Kleuver T, Vetter H (1998) Antiinflammatory effects of eucalyptol (1.8-cineole) in bronchial asthma: inhibition of arachidonic acid metabolism in human blood monocytes ex vivo. Eur J Med Res 3(9):407–412
Santos FA, Rao VS (2000) Antiinflammatory and antinociceptive effects of 1,8-cineole a terpenoid oxide present in many plant essential oils. Phytother Res 14(4):240–244
Juergens UR, Engelen T, Racké K, Stöber M, Gillissen A, Vetter H (2004) Inhibitory activity of 1,8 cineol (eucalyptol) on cytokine production in cultured human lymphocytes and monocytes. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 17(5):281–287
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193(1):265–275
Ciftci O, Ozdemir I, Tanyildizi S, Yildiz S, Oguzturk H (2011) Antioxidative effects of curcumin, β-myrcene and 1,8-cineole against 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced oxidative stress in rats liver. Toxicol Ind Health 27(5):447-453
Hochstrasser T, Hohsfield LA, Sperner-Unterweger B, Humpel C (2012) β-Amyloid induced effects on cholinergic, serotonergic, and dopaminergic neurons is differentially counteracted by anti-inflammatory drugs. J Neurosci Res 91(1):83–94
Heneka MT, O’Banion MK (2007) Inflammatory processes in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroimmunol 184(1–2):69–91
Tuppo EE, Arias HR (2005) The role of inflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37(2):289–305
Akiyama H, Arai T, Kondo H, Tanno E, Haga C, Ikeda K (2000) Cell mediators of inflammation in the Alzheimer disease brain. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 14(1):S47–S53
Griffin WST, Sheng JG, Royston MC, Gentleman SM, McKenzie JE, Graham DI et al (1998) Glial-neuronal interactions in Alzheimer’s disease: the potential role of a ‘cytokine cycle’ in disease progression. Brain Pathol 8(1):65–72
Mrak RE, Sheng JG, Griffin WS (1995) Glial cytokines in Alzheimer’s disease: review and pathogenic implications. Hum Pathol 26(8):816–823
Griffin WST, Stanley LC, Ling C, White L, MacLeod V, Perrot LJ et al (1989) Brain interleukin 1 and S-100 immunoreactivity are elevated in Down syndrome and Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86(19):7611–7615
Griffin ST, Sheng JG, Roberts GW, Mrak RE (1995) Interleukin-1 (IL-1) expression in different plaque types in Alzheimer’s disease: significance in plaque evolution. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 54(2):276–281
Stoll G, Jander S, Schroeter M (2000) Cytokines in CNS disorders: neurotoxicity versus neuroprotection. J Neural Transm 59:81–89
Dickson DW, Lee SC, Mattiace LA, Yen SH, Brosnan C (1993) Microglia and cytokines in neurological disease, with special reference to AIDS and Alzheimer’s disease. Glia 7(1):75–83
Hull M, Fiebich BL, Lieb K, Strauss S, Berger SS, Volk B, Bauer J (1996) Interleukin-6-associated inflammatory processes in Alzheimer’s disease: new therapeutic options. Neurobiol Aging 17(5):795–800
Serafino A, Vallebona PS, Andreola F, Zonfrillo M, Mercuri L, Federici M, Rasi G, Garaci E, Pierimarchi P (2008) Stimulatory effect of Eucalyptus essential oil on innate cell-mediated immune response. BMC Immunol 9:17
Bales KR, Du Y, Holtzman D, Cordell B, Paul SM (2000) Neuroinflammation and Alzheimer’s disease: critical roles for cytokine/Ab-induced glial activation, NF-kB, and apolipoprotein E. Neurobiol Aging 21(3):427–432
Akama KT, Albanese C, Pestell RG, Van Eldik LJ (1998) Amyloid b-peptide stimulates nitric oxide production in astrocytes through an NFkB-dependent mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95(10):5795–5800
Giuffre A, Sarti P, D’Itri E, Buse G, Soulimane T, Brunori M (1996) On the mechanism of inhibition of cytochrome c oxidase by nitric oxide. J Biol Chem 271(52):33404–33408
Halliwell B (2006) Oxidative stress and neurodegeneration: where are we now? J Neurochem 97(6):1634–1658
Behrens MM, Ali SS, Dugan LL (2008) Interleukin-6 mediates the increase in NADPH-oxidase in the ketamine model of schizophrenia. J Neurosci 28(51):13957–13966
Khan A, Vaibhav K, Javed H, Khan MM, Tabassum R, Ahmed ME, Khuwaja G, Islam F, Siddiqui MS, Shafi MM, Islam F (2012) Attenuation of Aβ-induced neurotoxicity by thymoquinone via inhibition of mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress. Mol Cell Biochem 369(1–2):55–65
Khan MB, Khan MM, Khan A, Ahmed ME, Ishrat T, Tabassum R, Vaibhav K, Ahmad A, Islam F (2012) Naringenin ameliorates Alzheimer’s disease (AD)-type neurodegeneration with cognitive impairment (AD-TNDCI) caused by the intracerebroventricular-streptozotocin in rat model. Neurochem Int 61(7):1081–1093
Acknowledgments
The author (A.K.) thanks Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), Government of India, New Delhi for the financial assistance. We highly appreciate Dharamvir Singh and Mohd Idris for technical assistance. We also acknowledge SABiosciences as the source of the original pathway map.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, A., Vaibhav, K., Javed, H. et al. 1,8-Cineole (Eucalyptol) Mitigates Inflammation in Amyloid Beta Toxicated PC12 Cells: Relevance to Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurochem Res 39, 344–352 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-1231-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-1231-9